Abstract
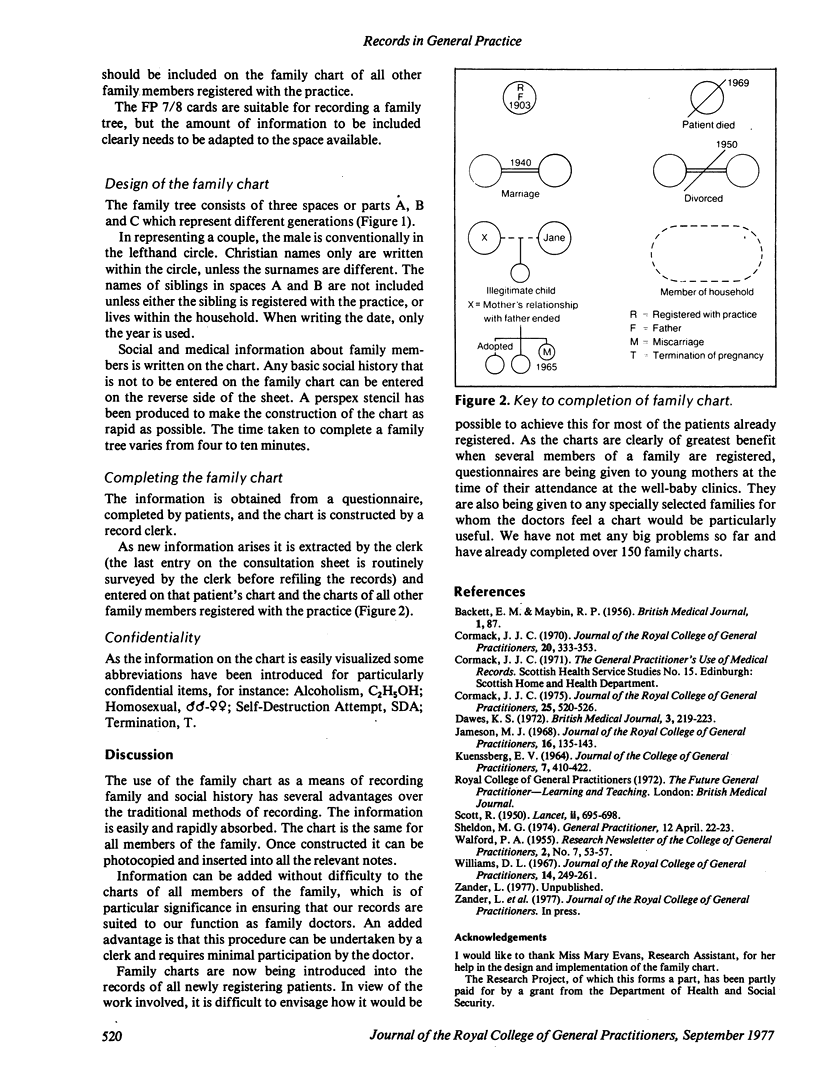
A diagrammatic method of recording family and social history using a family tree is described. Its advantages are identified and details of the way it has been introduced into the records in one general practice are given.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACKETT E. M., MAYBIN R. P. The general practitioner and his records; experience with a family record folder. Br Med J. 1956 Mar 17;1(Suppl 2669):87–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack J. J. Family portraits--a method of recording family history. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1975 Jul;25(156):520–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack J. J. The medical record envelope--a case for reform. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1970 Dec;20(101):333–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes K. S. Survey of general practice records. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 22;3(5820):219–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5820.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson M. J. A system of recording the family history in general practice. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1968 Aug;16(2):135–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUENSSBERG E. V. RECORDING OF MORBIDITY OF FAMILIES: F. BOOK. J Coll Gen Pract. 1964 May;7:410–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT R. A teaching general practice. Lancet. 1950 Dec 2;2(6640):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(50)91640-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


