Abstract
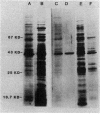
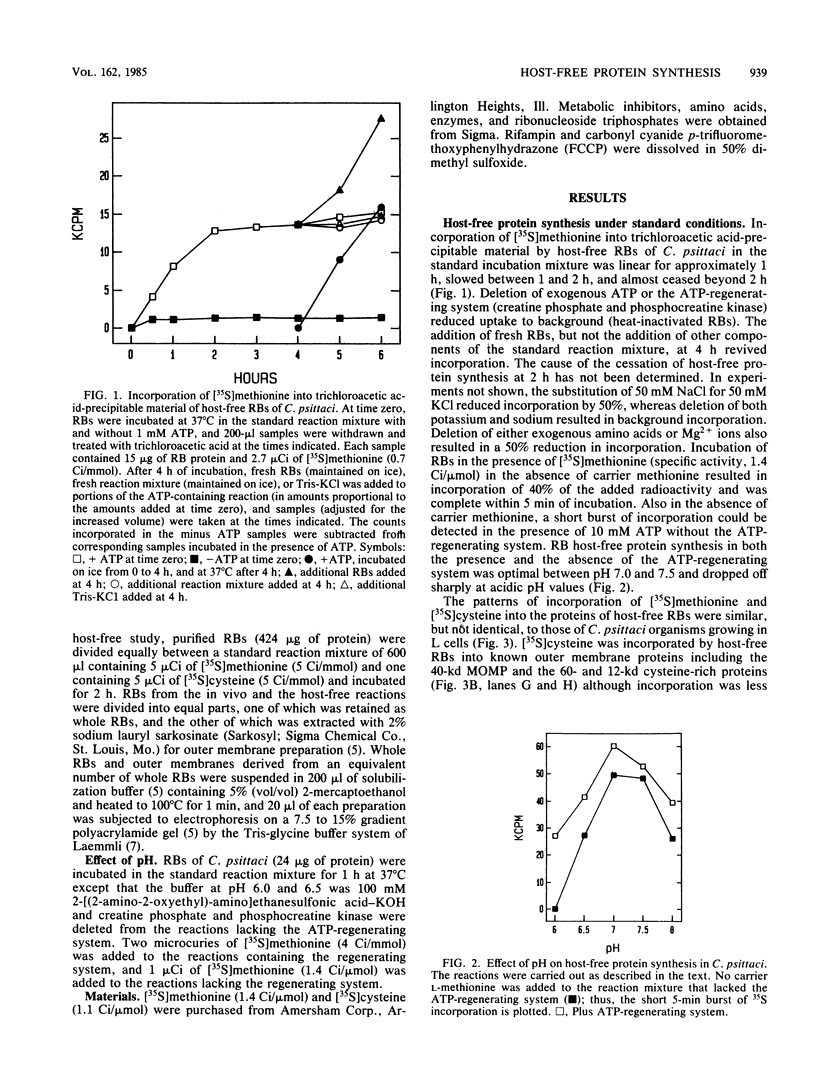
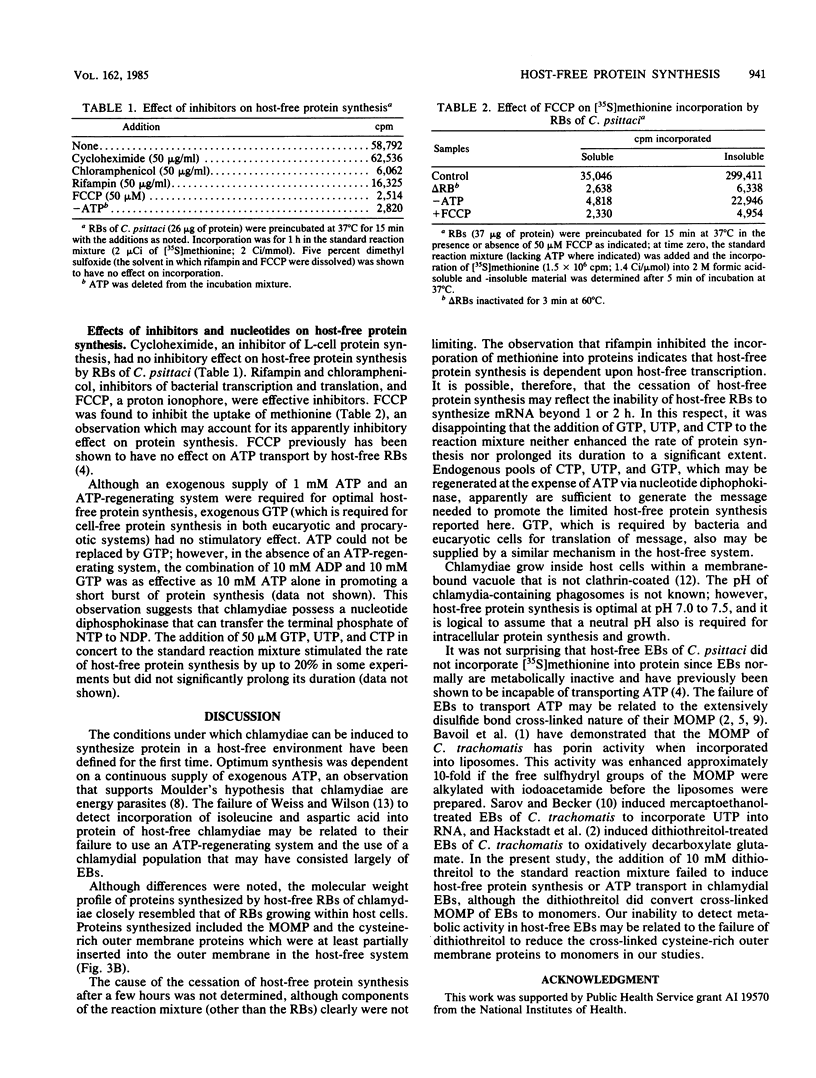
Synthesis of protein by the obligate intracellular parasitic bacteria Chlamydia psittaci (6BC) and Chlamydia trachomatis (serovar L2) isolated from host cells (host-free chlamydiae) was demonstrated for the first time. Incorporation of [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine into trichloroacetic acid-precipitable material by reticulate bodies of chlamydiae persisted for 2 h and was dependent upon a exogenous source of ATP, an ATP-regenerating system, and potassium or sodium ions. Magnesium ions and amino acids stimulated synthesis; chloramphenicol, rifampin, oligomycin, and carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone (a proton ionophore) inhibited incorporation. Ribonucleoside triphosphates (other than ATP) had little stimulatory effect. The optimum pH for host-free synthesis was between 7.0 and 7.5. The molecular weights of proteins synthesized by host-free reticulate bodies closely resembled the molecular weights of proteins synthesized by reticulate bodies in an intracellular environment, and included outer membrane proteins. Elementary bodies of chlamydiae were unable to synthesize protein even when incubated in the presence of 10 mM dithiothreitol, a reducing agent which converted the highly disulfide bond cross-linked major outer membrane protein to monomeric form.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. Disulfide-mediated interactions of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein: role in the differentiation of chlamydiae? J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Vance D. W., Jr, Al-Hossainy E. Identification of a major envelope protein in Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.426-429.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Becker Y. Deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in purified trachoma elementary bodies: effect of sodium chloride on ribonucleic acid transcription. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):593–598. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.593-598.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Murray A. Control mechanisms governing the infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis for HeLa cells: mechanisms of endocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1765–1780. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Wilson N. N. Role of exogenous adenosine triphosphate in catabolic and synthetic activities of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):719–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.719-724.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]