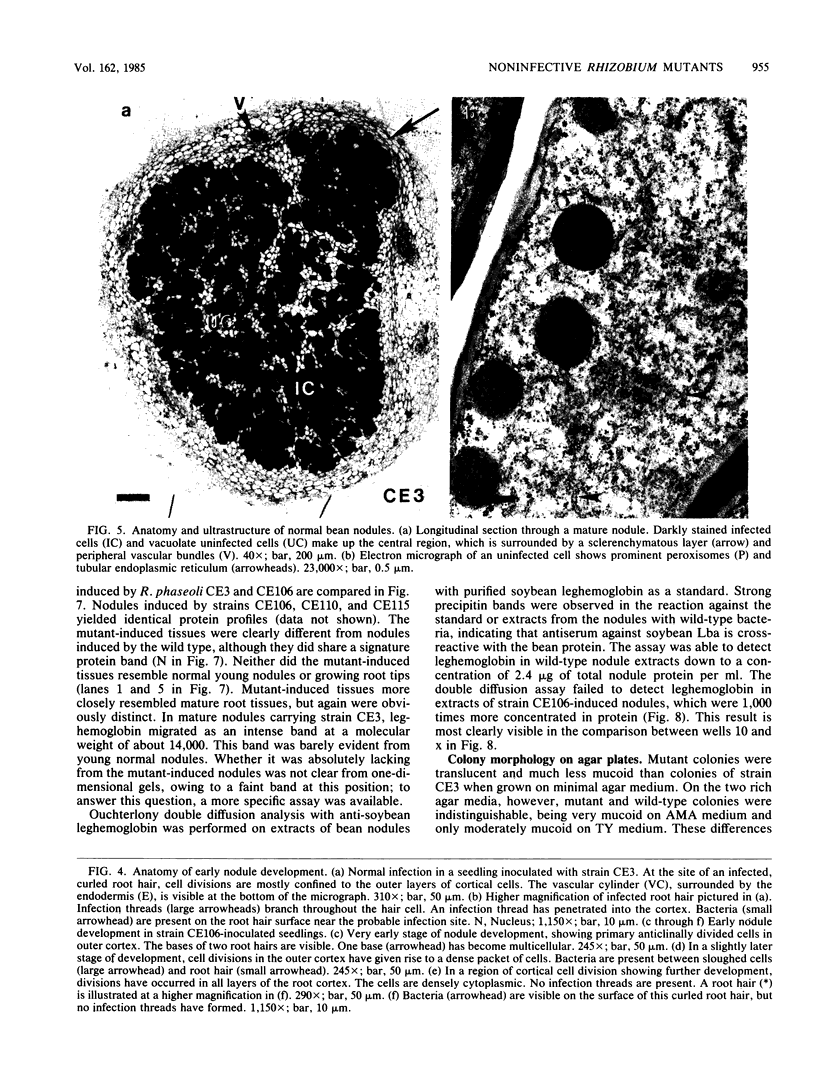
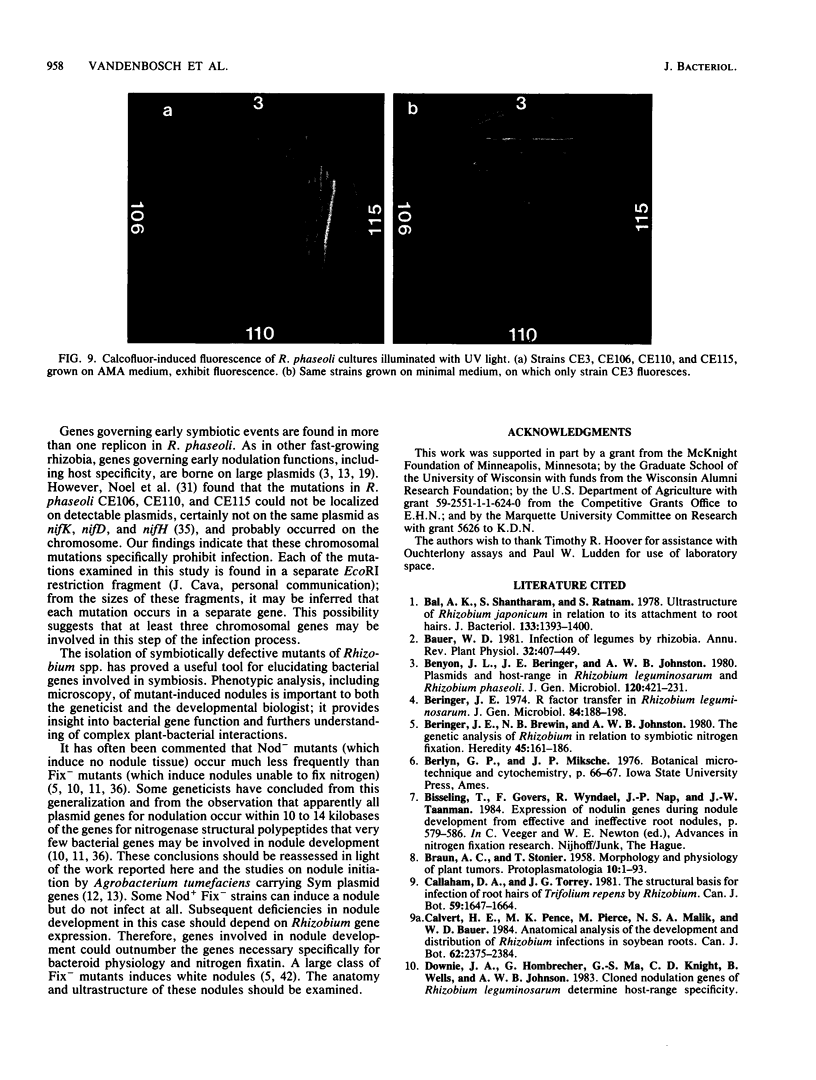
Abstract
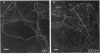
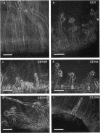
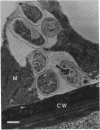
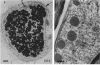
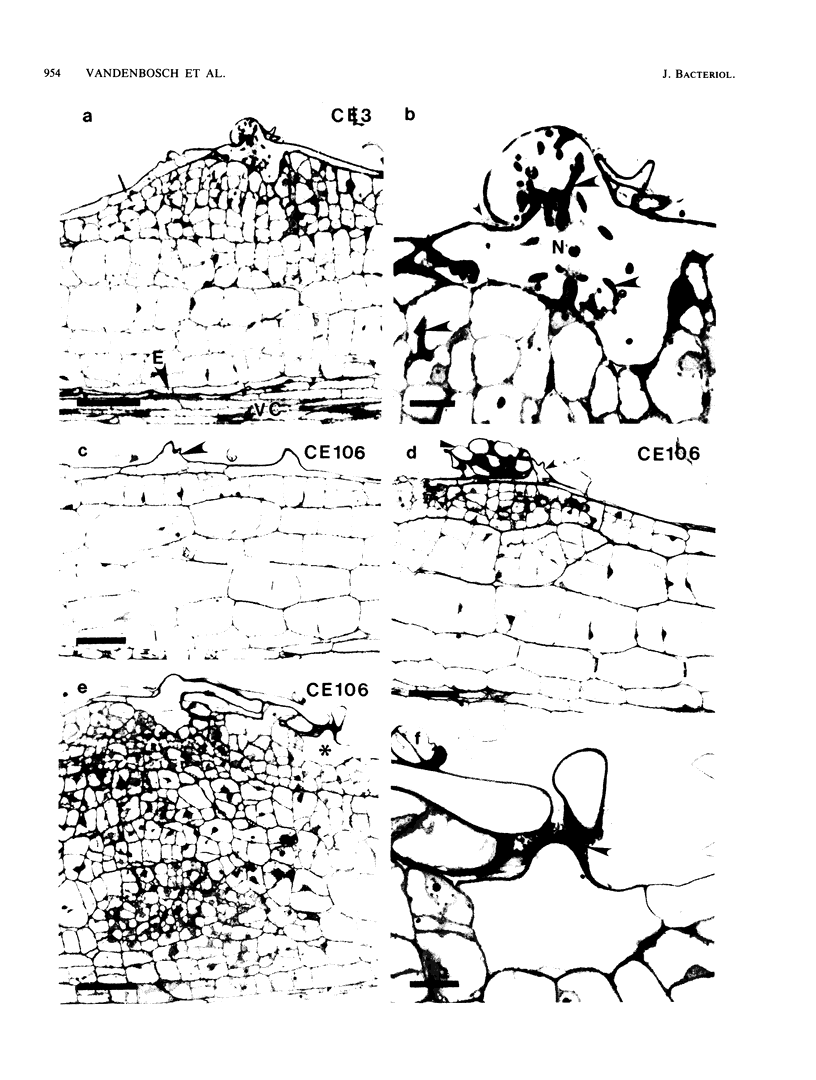
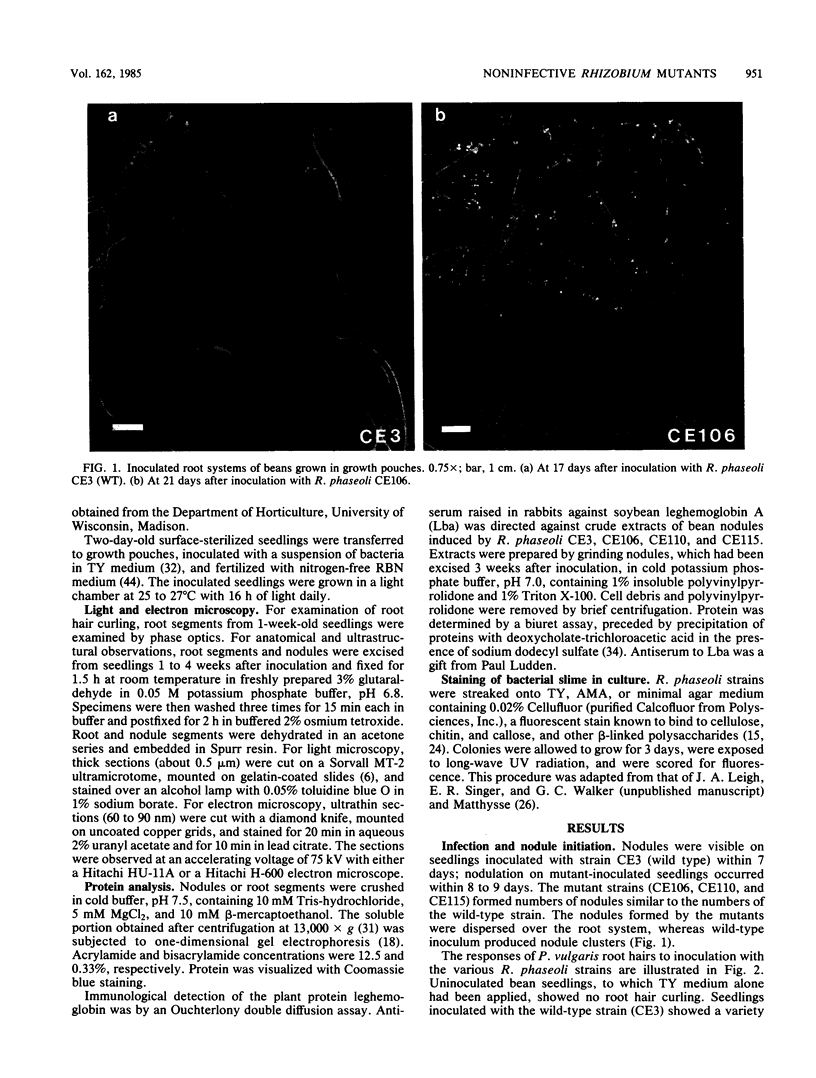
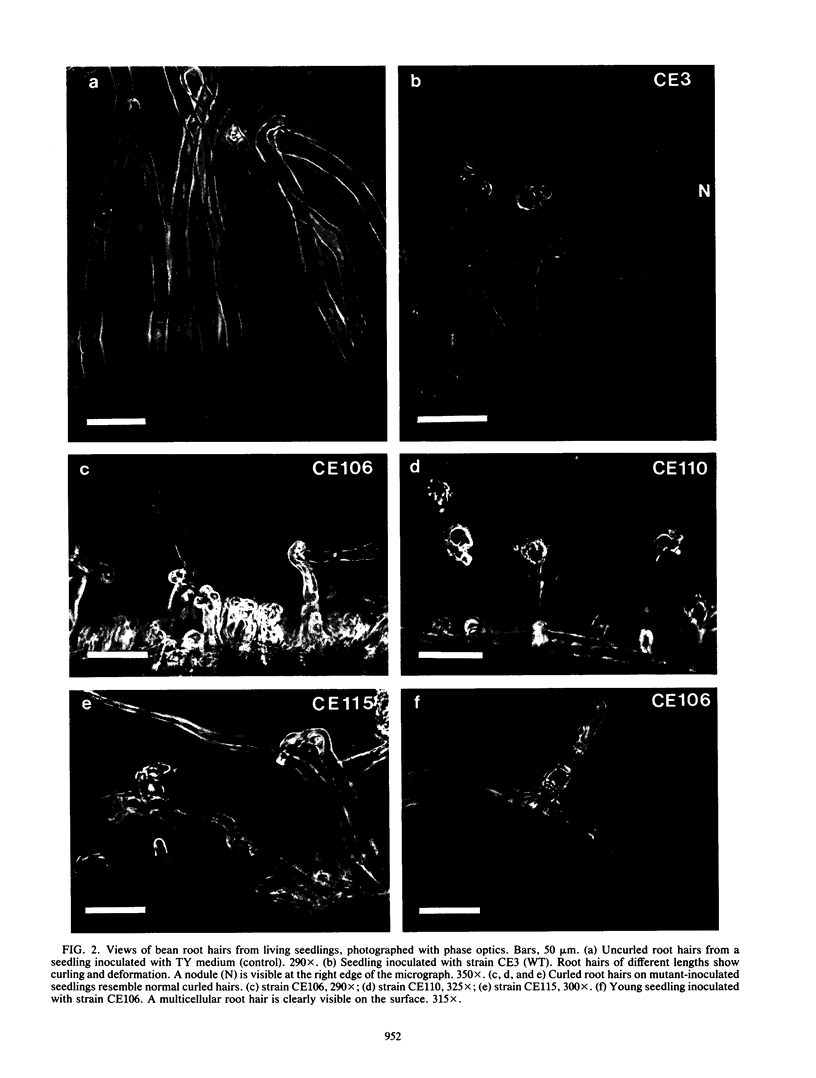
Rhizobium phaseoli CE106, CE110, and CE115, originally derived by transposon mutagenesis (Noel et al., J. Bacteriol. 158:149-155, 1984), induced the formation of uninfected root nodule-like swellings on bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Bacteria densely colonized the root surface, and root hair curling and initiation of root cortical-cell divisions occurred normally in mutant-inoculated seedlings, although no infection threads formed. The nodules were ineffective, lacked leghemoglobin, and were anatomically distinct from normal nodules. Ultrastructural specialization for ureide synthesis, characteristic of legumes that form determinate nodules, was absent. Colony morphology of the mutant strains on agar plates was less mucoid than that of the wild type, and under some cultural conditions, the mutants did not react with Cellufluor, a fluorescent stain for beta-linked polysaccharide. These observations suggest that the genetic lesions in these mutants may be related to extracellular polysaccharide synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bal A. K., Shantharam S., Ratnam S. Ultrastructure of Rhizobium japonicum in relation to its attachment to root hairs. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1393-1400.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrai T., Vincze E., Bánfalvi Z., Kiss G. B., Randhawa G. S., Kondorosi A. Localization of symbiotic mutations in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):635–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.635-643.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Wilson K. J., Jones J. D., Bang M., Walker V. V., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes allow Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Escherichia coli to form pseudonodules on alfalfa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1133–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1133-1143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell D. H., Morales V. M., Umali-Garcia M. Pectolytic enzymes in Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):210–213. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.210-213.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., McCully M. E. The use of an optical brightener in the study of plant structure. Stain Technol. 1975 Sep;50(5):319–329. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGGREN H., FAHRAEUS G. Effect of Rhizobium polysaccharide on the formation of polygalacturonase in lucerne and clover. Nature. 1959 Nov 14;184(Suppl 20):1578–1580. doi: 10.1038/1841578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGGREN H., FAHRAEUS G. The role of polygalacturonase in root-hair invasion by nodule bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Nov;26:521–528. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-3-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Ishida N. Specificity of binding of hexopyranosyl polysaccharides with fluorescent brightener. J Biochem. 1967 Aug;62(2):276–278. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Molina E., Morales V. M., Hubbell D. H. Hydrolytic enzyme production by Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1186–1188. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1186-1188.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G. Role of bacterial cellulose fibrils in Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):906–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.906-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Sanchez A., Fernandez L., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A. Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.148-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Stacey G., Tandon S. R., Silver L. E., Brill W. J. Rhizobium japonicum mutants defective in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):485–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.485-494.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Julliot J. S., Camut S., Denarie J. Transfer of Rhizobium meliloti pSym genes into Agrobacterium tumefaciens: host-specific nodulation by atypical infection. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.134-142.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H., Pankhurst C. E., Kondorosi A., Broughton W. J. Morphology of root nodules and nodule-like structures formed by Rhizobium and Agrobacterium strains containing a Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):787–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurkowski W. Specific adsorption of bacteria to clover root hairs, related to the presence of the plasmid pWZ2 in cells of Rhizobium trifolii. Microbios. 1980;27(107):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]