Abstract
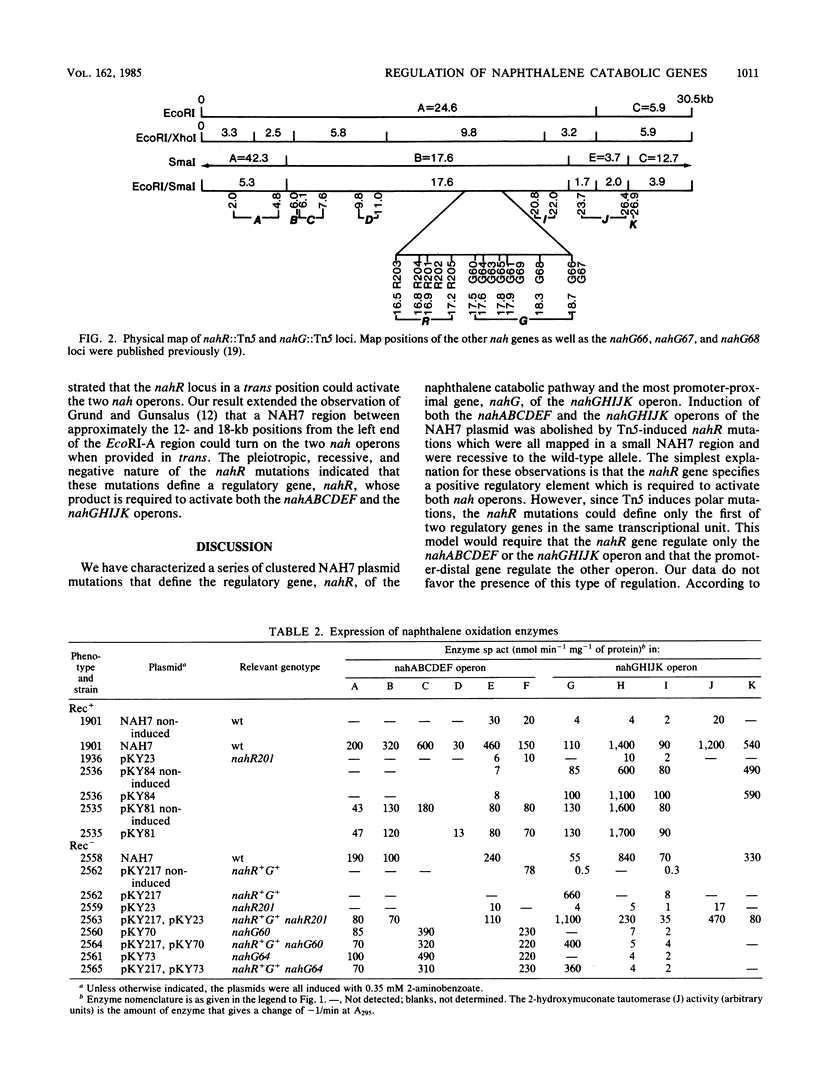
Tn5 insertion mutations defining a regulatory gene, nahR, of the naphthalene catabolic pathway encoded by the NAH7 plasmid were mapped within a small NAH7 region only a few hundred bases upstream of the nahG gene, the most promoter-proximal gene of the nahGHIJK operon. The nahR mutations blocked the induction of both the nahABCDEF and nahGHIJK operons, and the defect was completely corrected in the presence of the wild-type allele in a trans position. The pleiotropic, recessive, and negative nature of these mutations indicates that the nahR gene specifies a regulatory element which is required to activate both nah operons.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Egner C., Hirschel B. J., Howard J., Johnsrud L., Jorgensen R. A., Tlsty T. D. Insertion, excision, and inversion of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):115–123. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Weiss A., Crossland L. Polarity of Tn5 insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.439-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors M. A., Barnsley E. A. Naphthalene plasmids in pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn N. W., Gunsalus I. C. Transmissible plasmid coding early enzymes of naphthalene oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):974–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.974-979.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald M., Shapiro J. Regulatory mutations of the Pseudomonas plasmid alk regulon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):622–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.622-627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Lehrbach P. R., Lurz R., Rueckert B., Bagdasarian M., Timmis K. N. Localization and functional analysis of transposon mutations in regulatory genes of the TOL catabolic pathway. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.676-685.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Williams P. A. Construction of a partial diploid for the degradative pathway encoded by the TOL plasmid (pWWO) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2: evidence for the positive nature of the regulation by the xyIR gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):321–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00267445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grund A. D., Gunsalus I. C. Cloning of genes for naphthalene metabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):89–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.89-94.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinaru A. L., Duggleby C. J., Broda P. Molecular relationships of degradative plasmids determined by in situ hybridisation of their endonuclease-generated fragments. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):347–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00332979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann M., Garg G. K., Gunsalus I. C. Fertility factors in Pseudomonas putida: selection and properties of high-frequency transfer and chromosome donors. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):28–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.28-34.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Gunsalus I. C. Isolation of metabolic plasmid DNA from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrbach P. R., Zeyer J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Enzyme recruitment in vitro: use of cloned genes to extend the range of haloaromatics degraded by Pseudomonas sp. strain B13. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1025–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1025-1032.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Inouye S., Nakazawa A. Physical and functional mapping of RP4-TOL plasmid recombinants: analysis of insertion and deletion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):222–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.222-231.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Sullivan M., Gunsalus I. C. Electron microscope heteroduplex mapping of naphthalene oxidation genes on the NAH7 and SAL1 plasmids. Plasmid. 1983 Mar;9(2):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga M. C., Durham D. R., Welch R. A. Plasmid- and chromosome-mediated dissimilation of naphthalene and salicylate in Pseudomonas putida PMD-1. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.836-843.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



