Abstract
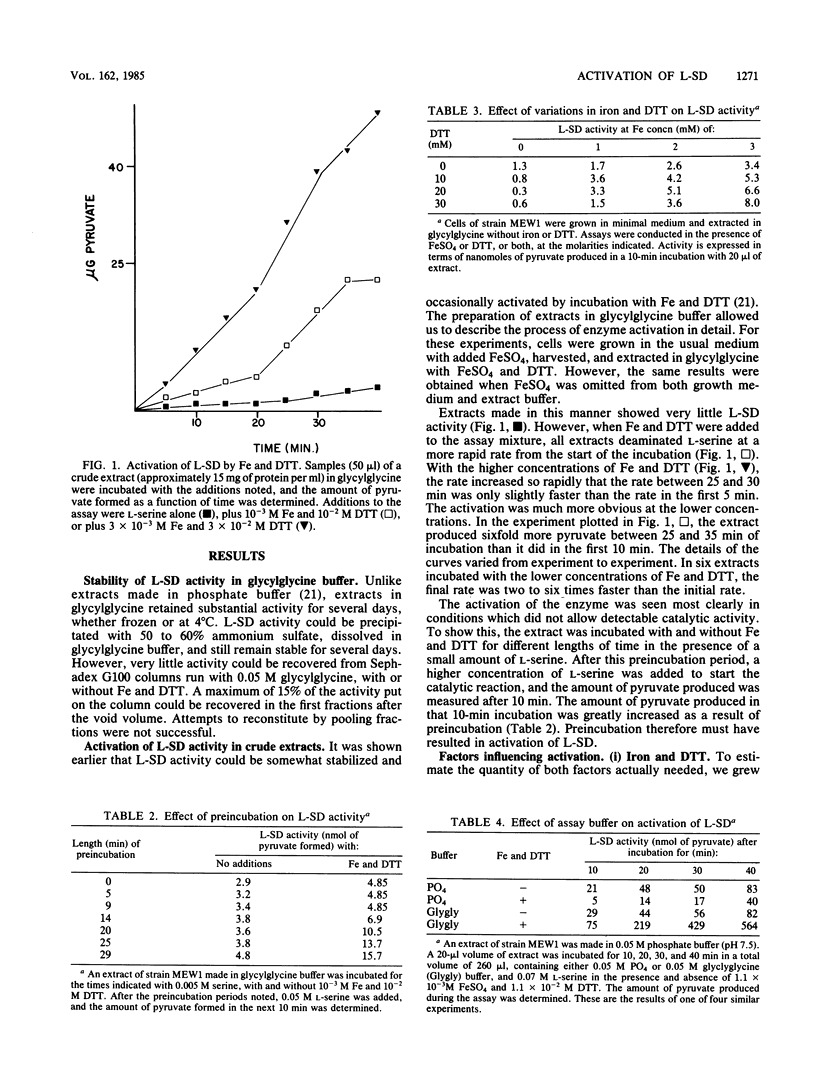
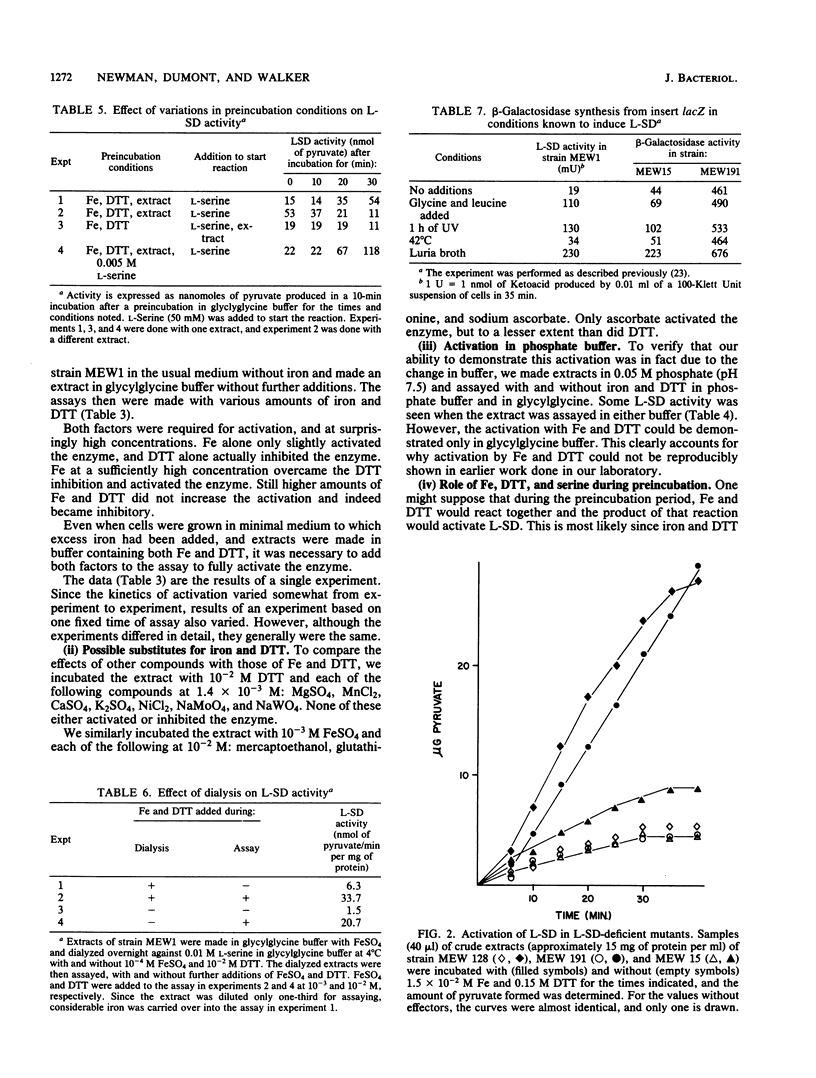
Escherichia coli L-serine deaminase (L-SD) in crude extracts made in glycylglycine could be activated by incubation with iron sulfate and dithiothreitol. This activation could also be demonstrated in vitro in two mutants which were physiologically deficient in L-SD activity in vivo. This suggests that these mutants were deficient not in L-SD but in an enzyme(s) activating L-SD. The suggestion is made that production of a functional L-SD in vivo requires activation of the structural gene product by an enzyme or enzymes that reduce the protein to an active form.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alföldi L., Raskó I., Kerekes E. L-serine deaminase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1512-1518.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apontoweil P., Berends W. Glutathione biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K 12. Properties of the enzymes and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 14;399(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Howe M. M., Gross C. A. Mu dX, a derivative of Mu d1 (lac Apr) which makes stable lacZ fusions at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):970–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.970-974.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. E., Sagers R. D. Ferrous ion-dependent L-serine dehydratase from Clostridium acidiurici. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.757-763.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Kinetic aspects of regulation of metabolic processes. The hysteretic enzyme concept. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5788–5799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman R. B., Tomaro M. L., Awruch J., Frydman B. Interconversion of the molecular forms of biliverdin reductase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 13;759(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs J. Isolation of an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in thioredoxin reductase. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):967–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.967-972.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon F., Bridgeland E. S., Jones K. M. L-serine dehydratase from Arthrobacter globiformis. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):345–355. doi: 10.1042/bj1610345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertig C. M., Wolosiuk R. A. Studies on the hysteretic properties of chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Hydrogen donor system for Escherichia coli ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase dependent upon glutathione. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2275–2279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Kallis G. B., Nordström B. A mutant thioredoxin from Escherichia coli tsnC 7007 that is nonfunctional as subunit of phage T7 DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3118–3124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. C., Emptage M. H., Dreyer J. L., Beinert H. The role of iron in the activation-inactivation of aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11098–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Chase J. W., Richardson C. C. Genetic mapping of trxA, a gene affecting thioredoxin in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 20;155(2):145–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00393153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Ahmad D., Walker C. L-Serine deaminase activity is induced by exposure of Escherichia coli K-12 to DNA-damaging agents. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.702-705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Kapoor V. In vitro studies on L-serine deaminase activity of Escherichia coli K12. Can J Biochem. 1980 Nov;58(11):1292–1297. doi: 10.1139/o80-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Malik N., Walker C. L-serine degradation in Escherichia coli K-12: directly isolated ssd mutants and their intragenic revertants. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.710-715.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Miller B., Colebrook L. D., Walker C. A mutation in Escherichia coli K-12 results in a requirement for thiamine and a decrease in L-serine deaminase activity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):272–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.272-276.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. Induced formation of serine and threonine deaminases by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):667–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.667-674.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Replacement of the fip gene of Escherichia coli by an inactive gene cloned on a plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1034-1039.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. K., Farthing J. E., Brewer S. J. The oxygenation of [3-methyl-3H]desacetoxycephalosporin C [7beta-(5-D-aminadipamido)-3-methylceph-3-em-4-carboxylic acid] to [3-hydroxymethyl-3H]desacetylcephalosporin C by 2-oxoglutarate-linked dioxygenases from Acremonium chrysogenum and Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):839–850. doi: 10.1042/bj1730839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



