Abstract
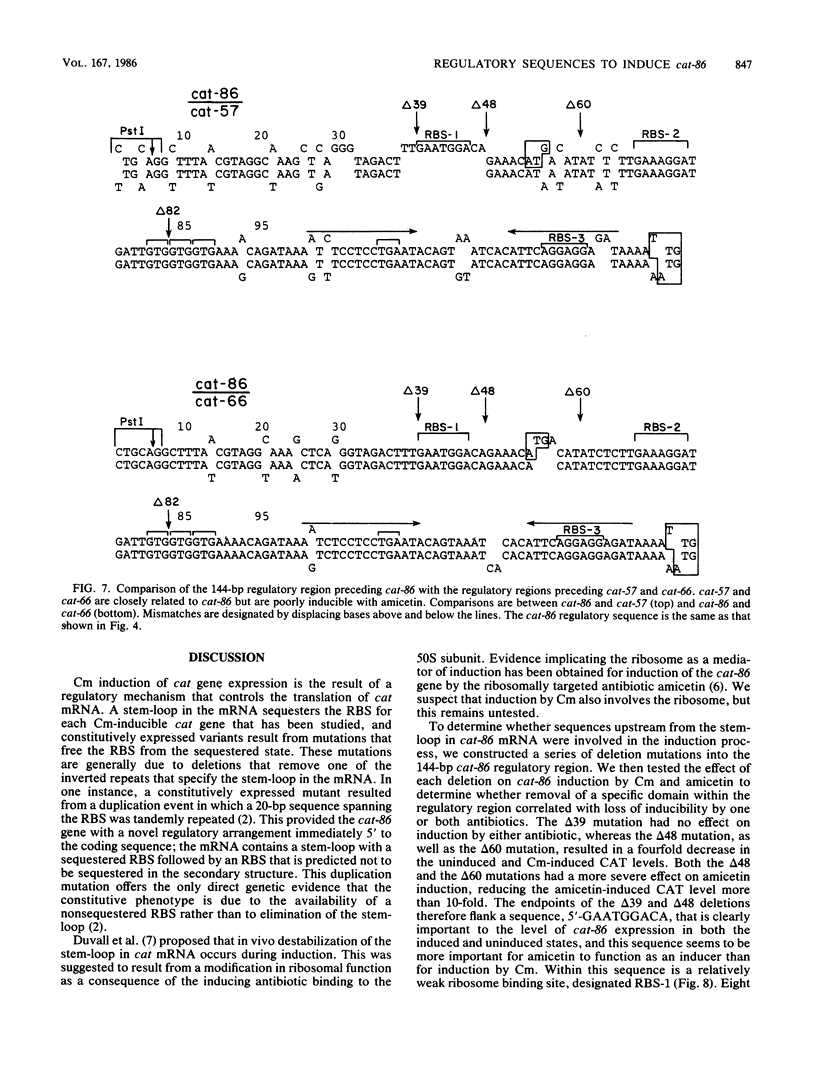
Induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 in Bacillus subtilis results from the activation of translation of cat-86 mRNA. The inducers, chloramphenicol and amicetin, are thought to enable ribosomes to destabilize a stem-loop structure in cat-86 mRNA that sequesters the ribosome binding site for the cat-86 coding sequence, designated RBS-3. The region of cat-86 mRNA which is 5' to the stem-loop contained two additional ribosome binding sites, RBS-1 and RBS-2, located 84 and 56 nucleotides, respectively, upstream from RBS-3. RBS-1 and RBS-2 were each followed by a potential translation initiation codon and a short open reading frame. Bal 31-generated deletions into the 5' end of the regulatory region that removed RBS-1 but did not enter RBS-2 caused a fourfold decrease in the uninduced and chloramphenicol-induced level of cat-86 expression and a more than 10-fold reduction in the amicetin-induced level of expression. Deletions that removed both RBS-1 and RBS-2 but did not enter the stem-loop abolished both chloramphenicol- and amicetin-inducible expression. These data indicate that RBS-2 and sequences 3' to RBS-2 are minimally essential to chloramphenicol induction. However, the presence of RBS-1 in the mRNA elevated the maximum level of expression obtained during chloramphenicol induction. These studies also demonstrate that induction of cat-86 by amicetin is highly dependent on RBS-1. To determine whether a correlation existed between RBS-1 and amicetin inducibility, we examined the sequence of the regulatory regions for two natural variants of cat-86, cat-66 and cat-57, which are chloramphenicol inducible but are very poorly induced by amicetin. Both contained nucleotide sequence differences from cat-86 in the vicinity of RBS-1 that would prevent translation of the leader peptide associated with RBS-1 in cat-86. In contrast, the regulatory regions got the three genes were virtually identical in the vicinity of RBS-2. These data indicate that efficient induction by amicetin requires sequences that are not essential for induction by chloramphenicol.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Chow J. H., Mongkolsuk S., Preis L. H., Vollmar W. R., 2nd, Lovett P. S. Constitutive variants of the pC194 cat gene exhibit DNA alterations in the vicinity of the ribosome binding site sequence. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Mongkolsuk S., Kaufman J. D., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol-induced translation of cat-86 mRNA requires two cis-acting regulatory regions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester S., Lopez P., Alonso J. C., Espinosa M., Lacks S. A. Selective advantage of deletions enhancing chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression in Streptococcus pneumoniae plasmids. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Matzura H. Regulation of the inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of the Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pUB112. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2295–2300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol induces translation of the mRNA for a chloramphenicol-resistance gene in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Mongkolsuk S., Kim U. J., Lovett P. S., Henkin T. M., Chambliss G. H. Induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 through the action of the ribosomal antibiotic amicetin: involvement of a Bacillus subtilis ribosomal component in cat induction. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.665-672.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Williams D. M., Lovett P. S., Rudolph C., Vasantha N., Guyer M. Chloramphenicol-inducible gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Williams D. M., Mongkolsuk S., Lovett P. S. Regulatory regions that control expression of two chloramphenicol-inducible cat genes cloned in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.784-790.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S., Keggins K. M. Bacillus subtilis as a host for molecular cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:342–357. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Katakura Y., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Enzymatic and nucleotide sequence studies of a kanamycin-inactivating enzyme encoded by a plasmid from thermophilic bacilli in comparison with that encoded by plasmid pUB110. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.413-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongkolsuk S., Chiang Y. W., Reynolds R. B., Lovett P. S. Restriction fragments that exert promoter activity during postexponential growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1399–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1399-1406.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Chambliss G. H., Buckbinder L., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Lovett P. S. Isolation and expression of a constitutive variant of the chloramphenicol-inducible plasmid gene cat-86 under control of the Bacillus subtilis 168 amylase promoter. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Brenner D. G., LeGrice S. F., Skinner S. E., Hawkins A. R. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of staphylococcal plasmid pC221. Nucleotide sequence analysis and expression studies. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: enzymology and molecular biology. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Cloning restriction fragments that promote expression of a gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1162–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1162-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yansura D. G., Henner D. J. Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



