Abstract
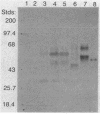
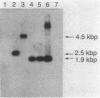
The gene (spg) for an immunoglobulin G (IgG)-binding protein from a Streptococcus clinical isolate of Lancefield group G was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The complete nucleotide sequence of the gene and 5'-flanking sequences was determined. The DNA sequence includes an open reading frame which encodes a hypothetical protein of 448 amino acid residues (Mr = 47,595). The 5' end of this open reading frame encodes a sequence resembling a typical secretion signal sequence, and the remainder of the encoded protein has features reminiscent of staphylococcal protein A and of streptococcal M6 protein, including repeated sequences and a similar C-terminal structure. Aside from this C-terminal structure, the encoded protein has little direct amino acid sequence homology to either protein A or M6 protein. In E. coli, the cloned gene directs the synthesis of a protein which binds to immunoglobulins, including rabbit immunoglobulin, goat IgG, and human IgG3(lambda). Its binding properties are similar to those of the protein G described by Björck and Kronvall (L. Björck and G. Kronvall, J. Immunol. 133:969-974, 1984), a type III Fc receptor from a group G streptococcus.
Full text
PDF

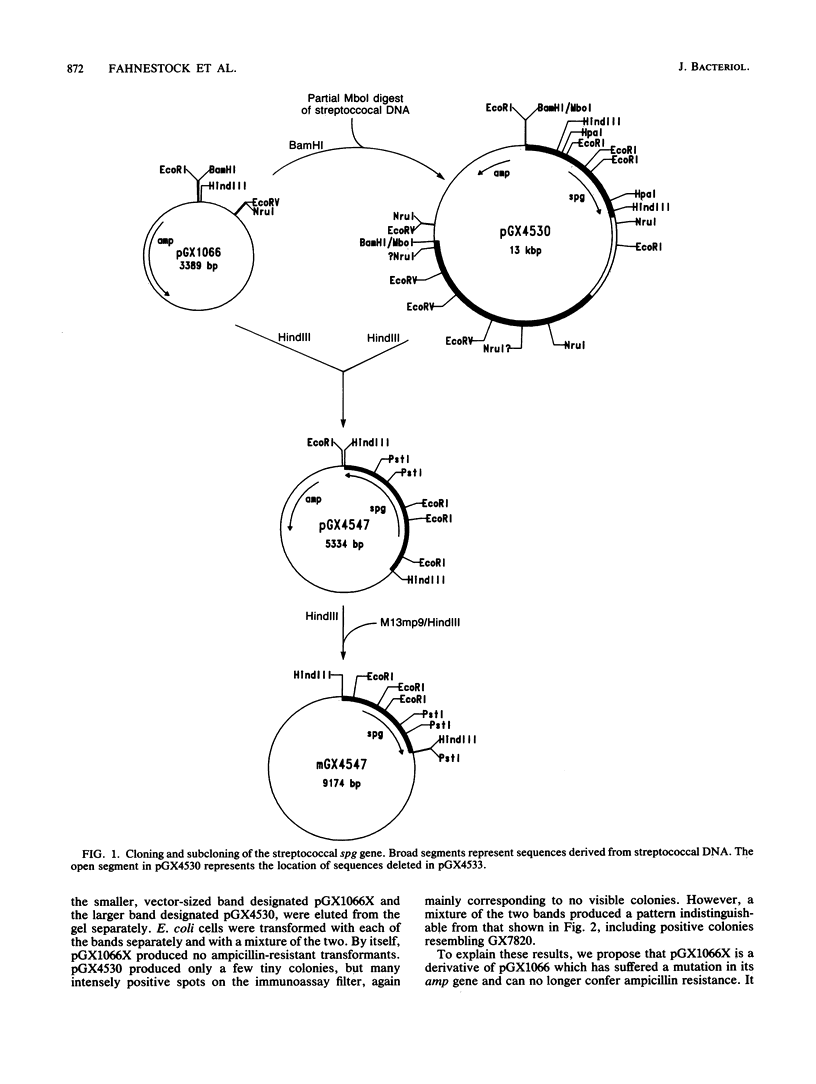

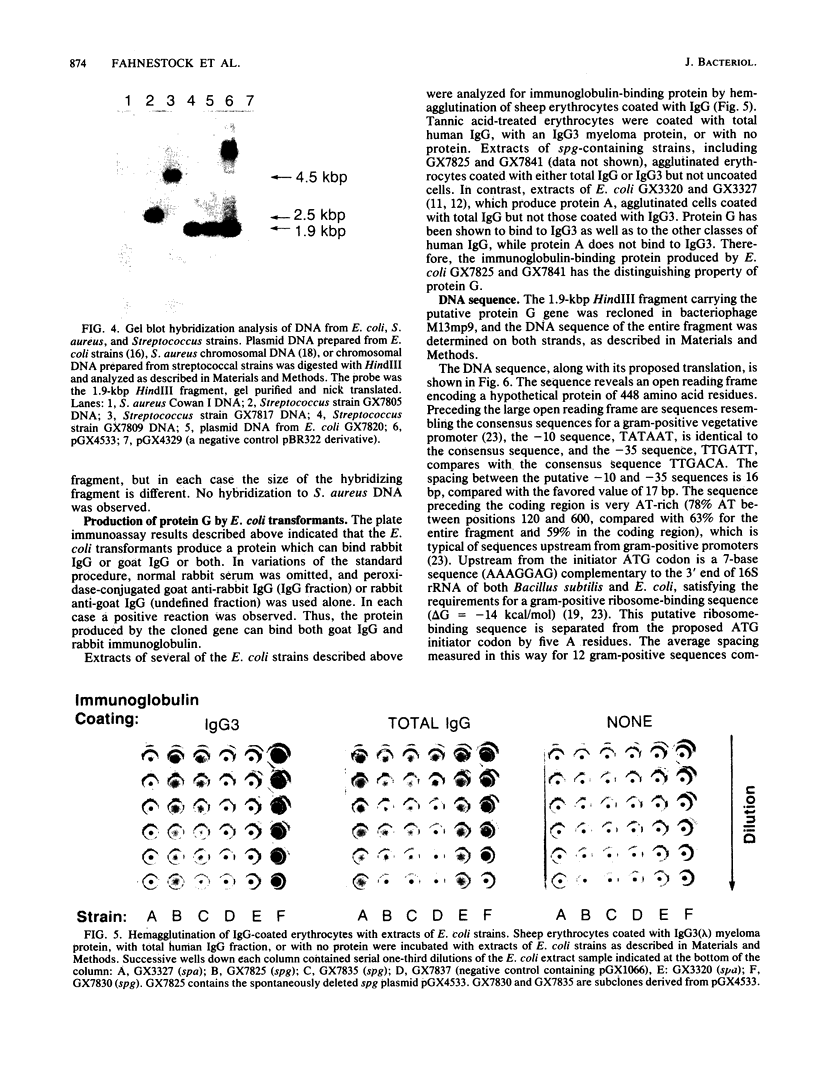

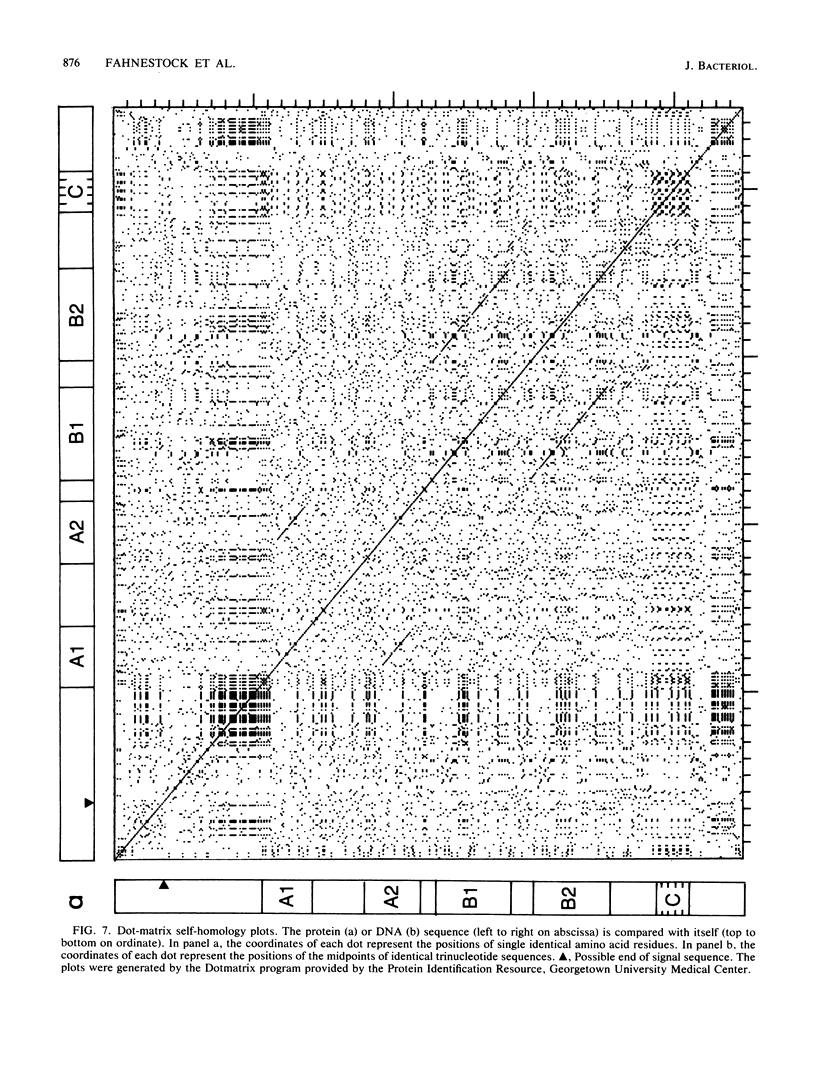
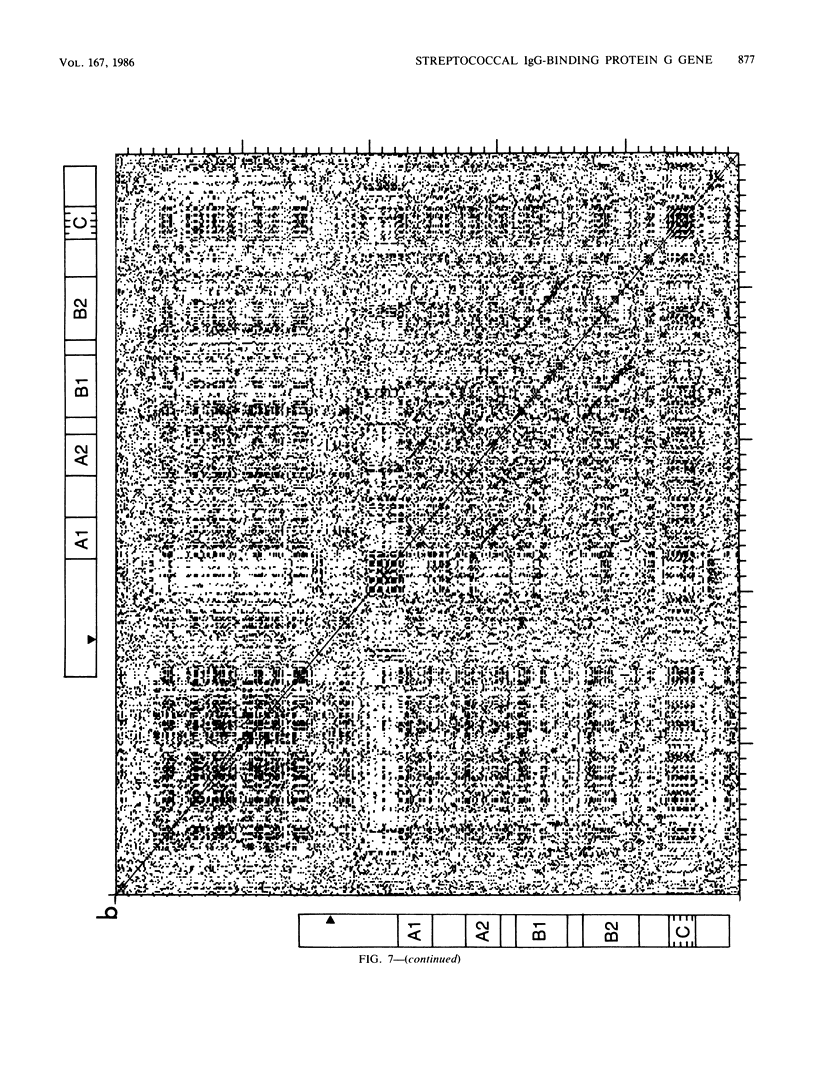



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahmsén L., Moks T., Nilsson B., Hellman U., Uhlén M. Analysis of signals for secretion in the staphylococcal protein A gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3901–3906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler F. L., Adler L. T. Passive hemagglutination and hemolysis for estimation of antigens and antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):455–466. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerström B., Brodin T., Reis K., Björck L. Protein G: a powerful tool for binding and detection of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2589–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kronvall G. Purification and some properties of streptococcal protein G, a novel IgG-binding reagent. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby C. J., Jones S. A. Cloning and expression of the Staphylococcus aureus protein A gene in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3065–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Fisher K. E. Expression of the staphylococcal protein A gene in Bacillus subtilis by gene fusions utilizing the promoter from a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.796-804.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Saunders C. W., Guyer M. S., Löfdahl S., Guss B., Uhlén M., Lindberg M. Expression of the staphylococcal protein A gene in Bacillus subtilis by integration of the intact gene into the B. subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):1011–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.1011-1014.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss B., Uhlén M., Nilsson B., Lindberg M., Sjöquist J., Sjödahl J. Region X, the cell-wall-attachment part of staphylococcal protein A. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl S., Guss B., Uhlén M., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Gene for staphylococcal protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):697–701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Streptococcal Fc receptors. II. Comparison of the reactivity of a receptor from a group C streptococcus with staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3098–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Nakazawa K., Tashiro N., Yamane K., Yanagi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Saito H., Kawade Y., Taniguchi T. Synthesis and secretion of biologically active mouse interferon-beta using a Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase secretion vector. Gene. 1985;34(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Complete sequence of the staphylococcal gene encoding protein A. A gene evolved through multiple duplications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1695–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Götz F., Lindberg M. Expression of the gene encoding protein A in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):713–719. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.713-719.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Freese E. Enzyme changes during Bacillus subtilis sporulation caused by deprivation of guanine nucleotides. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1119-1125.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]