Abstract
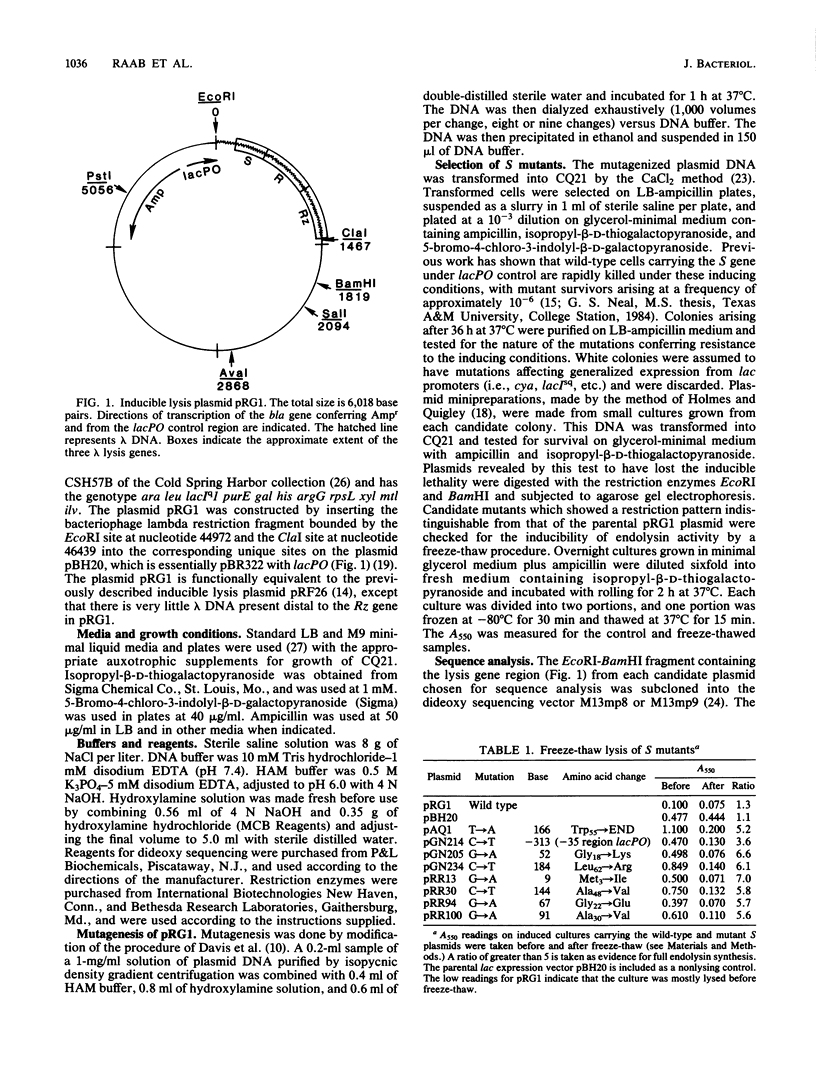
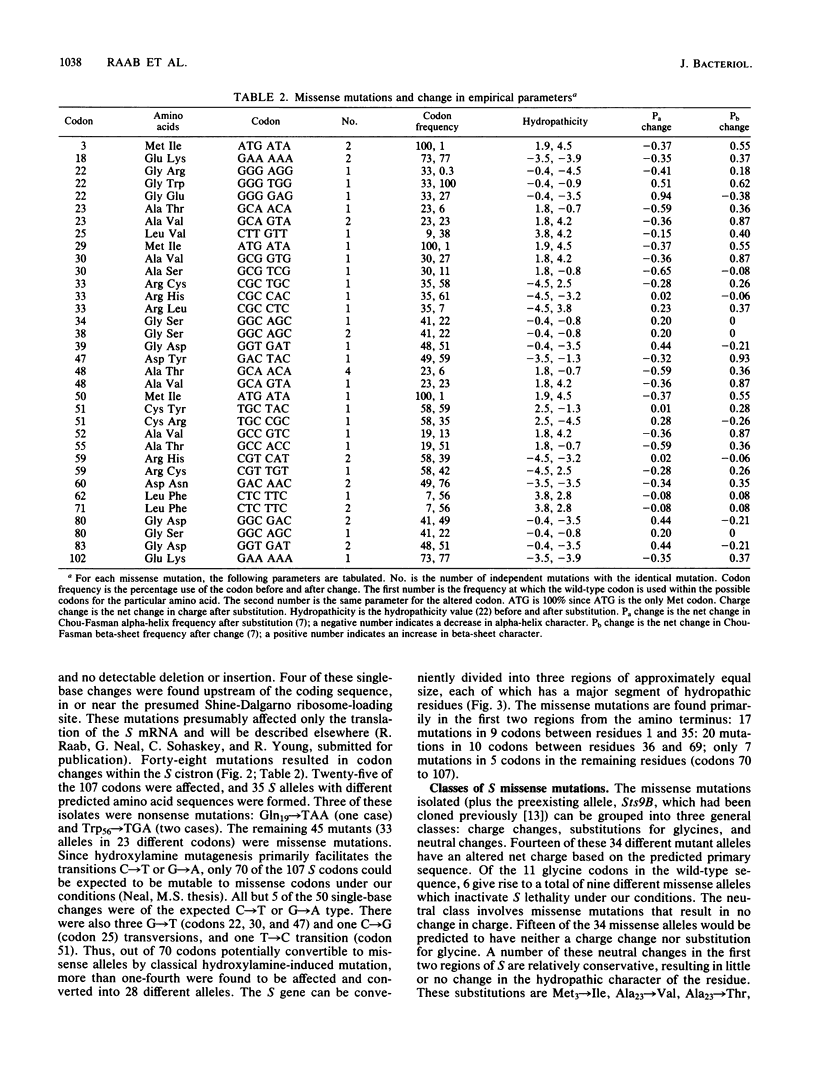
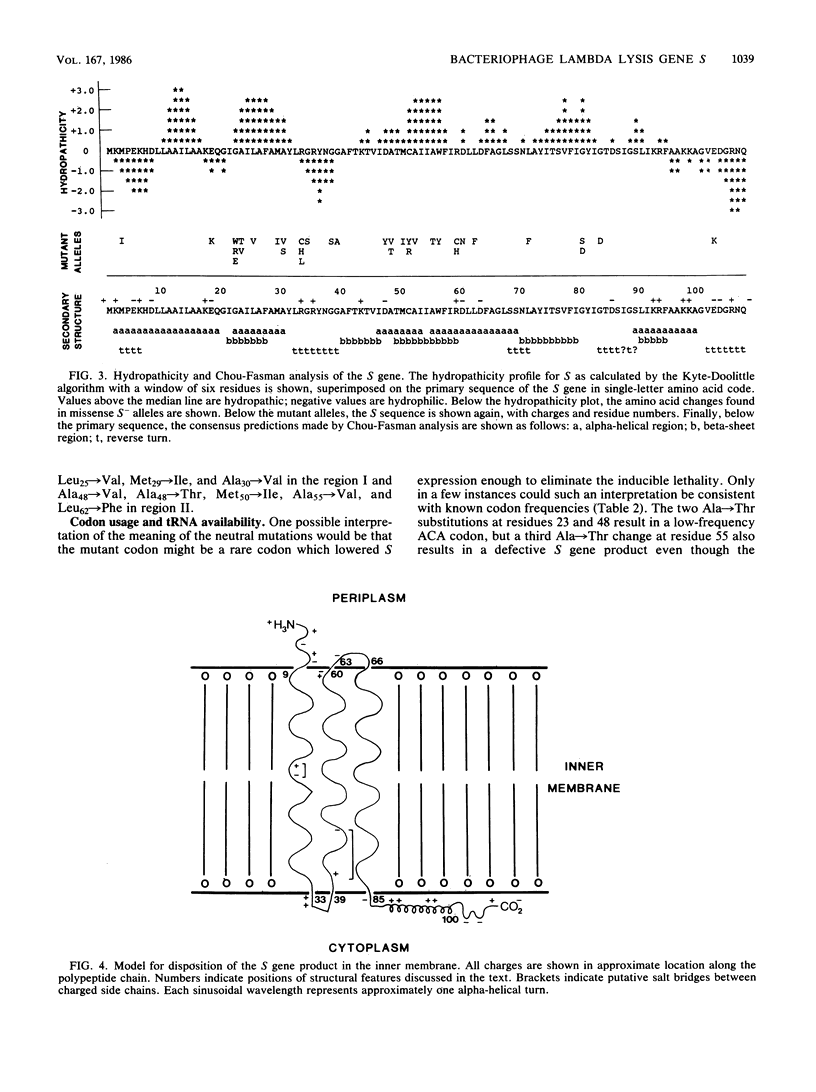
A plasmid carrying the bacteriophage lambda lysis genes under lac control was subjected to hydroxylamine mutagenesis, and mutations eliminating the host lethality of the S gene were selected. DNA sequence analysis revealed 48 single-base mutations which resulted in alterations within the coding sequence of the S gene. Thirty-three different missense alleles were generated. Most of the missense changes clustered in the first two-thirds of the molecule from the N terminus. A simple model for the disposition of the S protein within the inner membrane can be derived from inspection of the primary sequence. In the first 60 residues, there are two distinct stretches of predominantly hydrophobic amino acids, each region having a net neutral charge and extending for at least 20 residues. These regions resemble canonical membrane-spanning domains. In the model, the two domains span the bilayer as a pair of net neutral charge helices, and the N-terminal 10 to 12 residues extend into the periplasm. The mutational pattern is largely consistent with the model. Charge changes within the putative imbedded regions render the protein nonfunctional. Loss of glycine residues at crucial reverse-turn domains which would be required to reorient the molecule to reenter the membrane also inactivate the molecule. Finally, a number of neutral and rather subtle mutations such as Ala to Val and Met to Ile are found, mostly within the putative spanning regions. Although no obvious explanation exists for this subtle and heterogeneous class of mutations, it is noted that all of the changes result in a loss of alpha-helical character as predicted by Chou-Fasman theoretical analysis. Alternative explanations for some of these changes are also possible, including a reduction in net translation rate due to substitution of a rare codon for a common one. The model and the pattern of mutations have implications for the probable oligomerization of the S protein at the time of endolysin release at the end of the vegetative growth period.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Altman R. K., Garrett J. M., Grimaila R. J., Young R. S gene product: identification and membrane localization of a lysis control protein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1130-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Young K., Garrett J., Altman R., Young R. Subcellular localization of lethal lysis proteins of bacteriophages lambda and phiX174. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1008-1011.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Lipinska B., Taylor A. The R gene product of bacteriophage lambda is the murein transglycosylase. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):111–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00271205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. H., Rolfe B. G. Evidence for a dual control of the initiation of host-cell lysis caused by phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00267990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Boeke J. D., Model P. Fine structure of a membrane anchor domain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):371–374. doi: 10.1038/299371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. M., Young R. Lethal action of bacteriophage lambda S gene. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.886-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J., Fusselman R., Hise J., Chiou L., Smith-Grillo D., Schulz J., Young R. Cell lysis by induction of cloned lambda lysis genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):326–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00269678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Hagen D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:399–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josslin R. The lysis mechanism of phage T4: mutants affecting lysis. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W., Godson G. N. Evidence for use of rare codons in the dnaG gene and other regulatory genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):687–691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieschendahl M., Büchel D., Bocklage H., Müller-Hill B. Mutations in the lacY gene of Escherichia coli define functional organization of lactose permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai F., Streisinger G., Miller B. The mechanism of lysis in phage T4-infected cells. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Siminovitch L. Lysis defective mutants of bacteriophage lambda: genetics and physiology of S cistron mutants. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):607–622. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Siminovitch L. Lysis defective mutants of bacteriophage lambda: on the role of the S function in lysis. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):623–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B. G., Campbell J. H. Genetic and physiological control of host cell lysis by bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):626–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.626-636.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar Raj C. V., Wu H. C. Escherichia coli mutants permissive for T4 bacteriophage with deletion in e gene (phage lysozyme). J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):656–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.656-665.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Effect of the lambda S gene product on properties of the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1403–1410. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1403-1410.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R., Way J., Way S., Yin J., Syvanen M. Transposition mutagenesis of bacteriophage lambda: a new gene affecting cell lysis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):307–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane proteins: the amino acid composition of membrane-penetrating segments. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



