Abstract
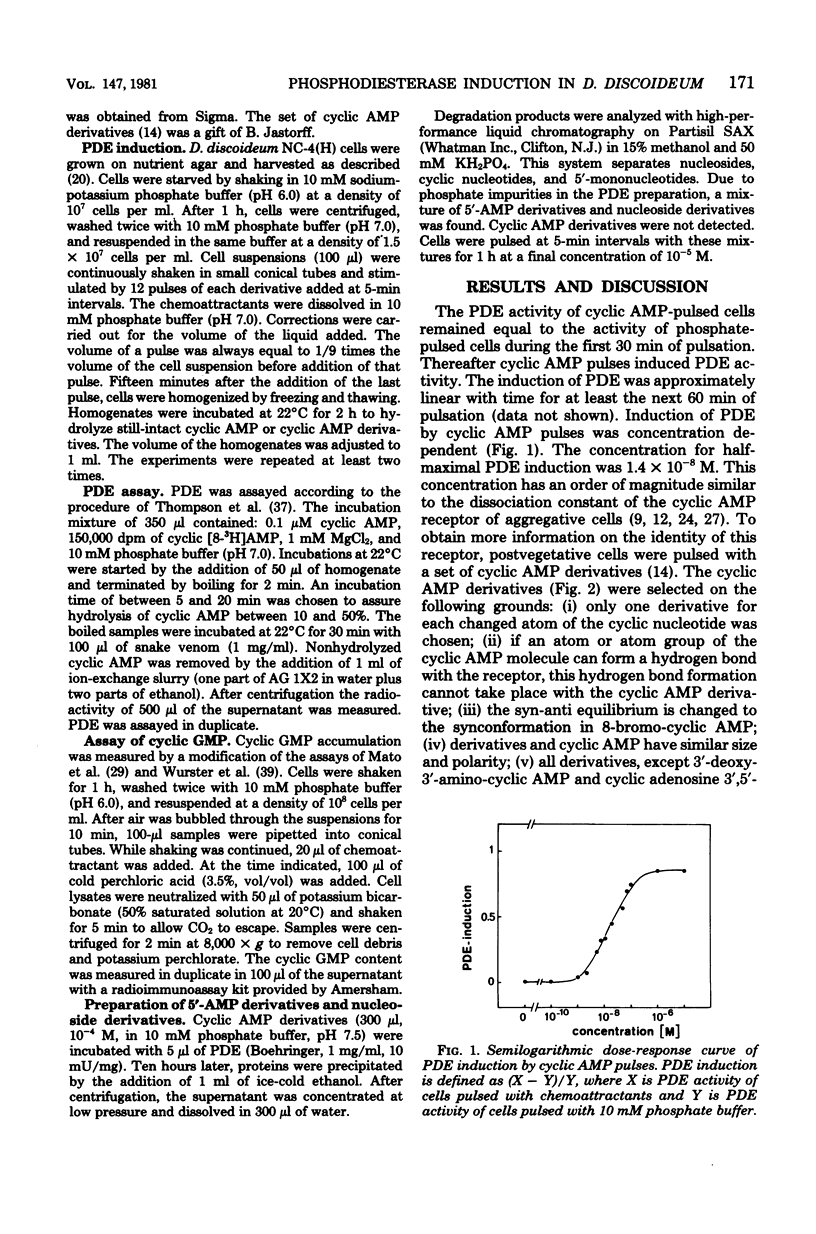
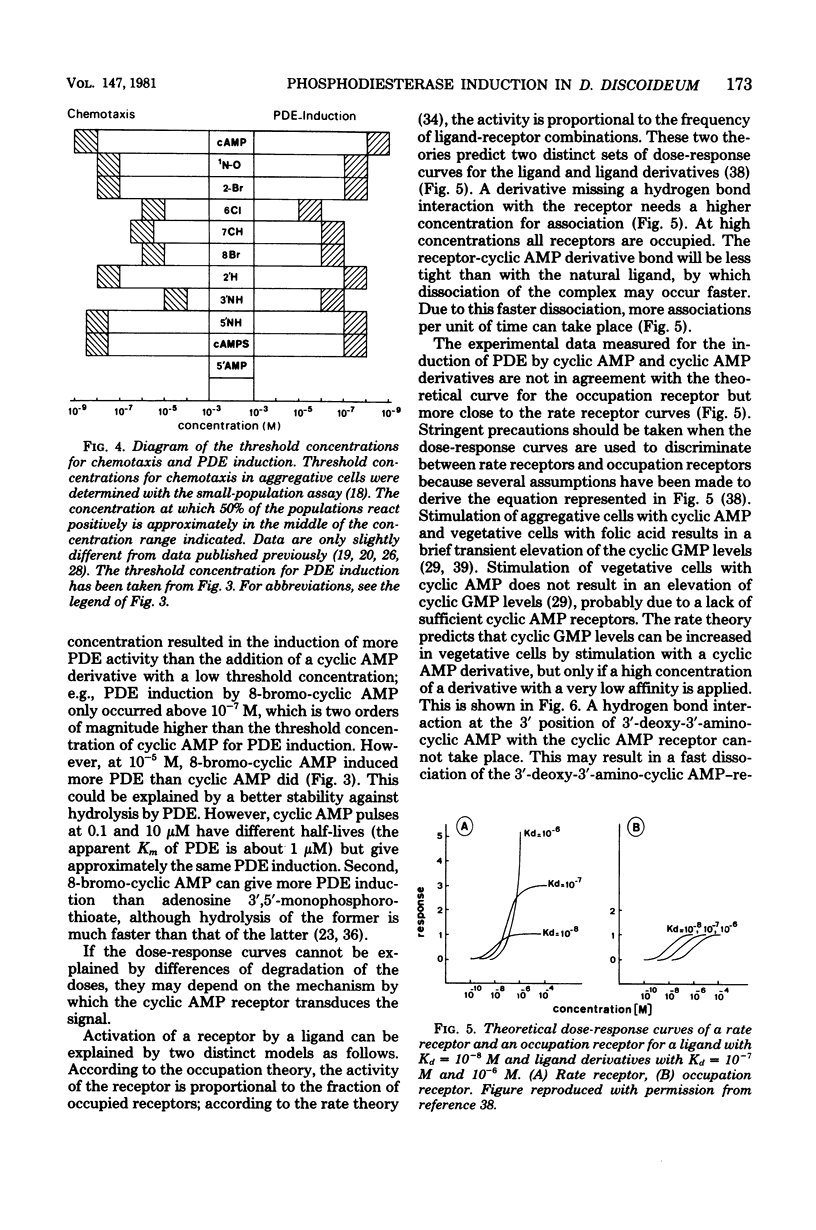
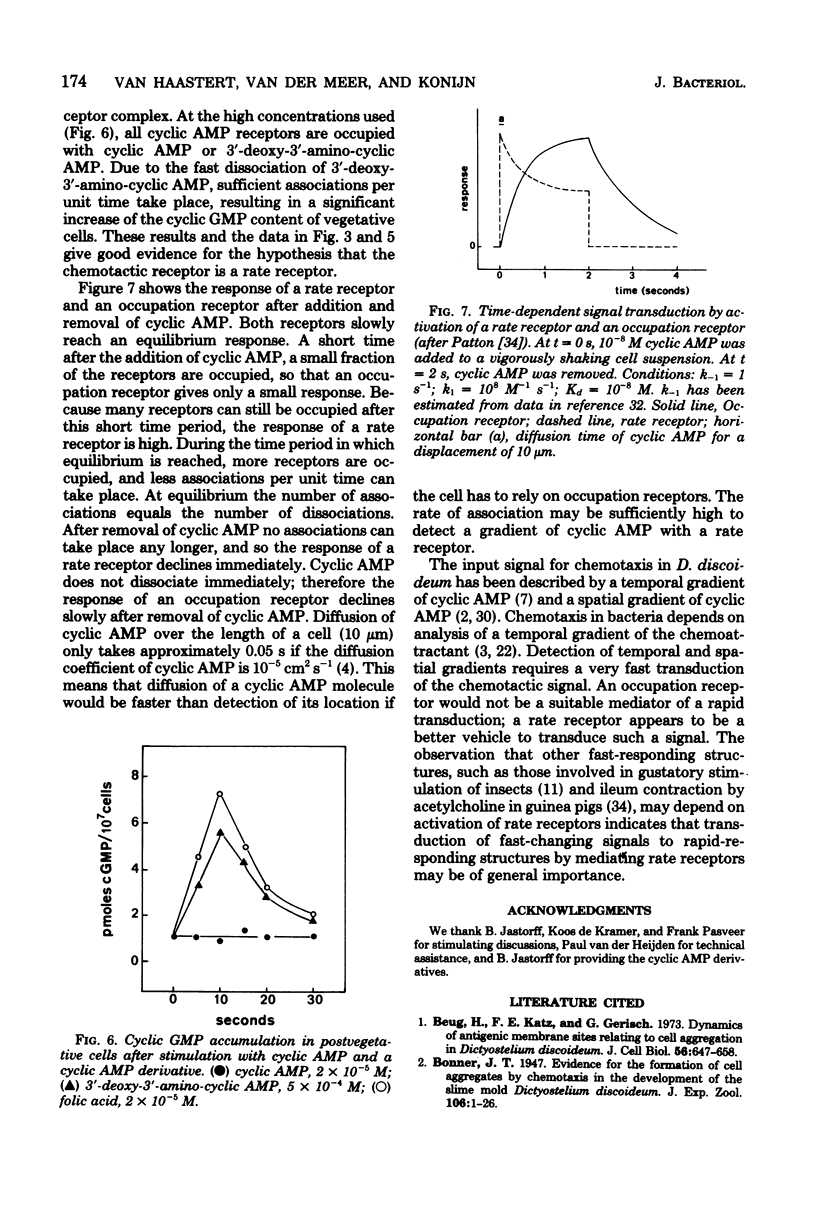
Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) mediates cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell aggregation is enhanced by pulses of cyclic AMP. Application of pulses of cyclic AMP to cells that were starved only for 1 h (postvegetative cells) induces enzyme activity. One of the enzymes induced by cyclic AMP pulses is phosphodiesterase. We pulsed postvegetative cells with a set of cyclic AMP derivatives that were selected according to certain conformational and physical-chemical properties, and we measured their effect on the induction of phosphodiesterase activity. The cyclic nucleotide specificity for chemotaxis in the aggregative phase was similar to the specificity for phosphodiesterase induction in the postvegetative phase. The shape of the dose-response curves shows a paradox: the activity of a derivative, when applied at receptor-saturating concentrations, is inversely related to its affinity. These results can be explained by the assumption that the response of the chemoreceptor to different cyclic AMP derivatives is proportional to the frequency of associations (rate receptor) and not to the proportion of occupied receptors (occupation receptor). The characteristics of rate receptors and occupation receptors during chemosensory transduction will be discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beug H., Katz F. E., Gerisch G. Dynamics of antigenic membrane sites relating to cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):647–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Berg H. C. Temporal stimulation of chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. H., Drage D. J., Robertson A. Iontophoresis of cyclic AMP. Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):753–763. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85852-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M., Brachet P., Da Silva L. H. Chemotactic signals induce cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3163–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Fromm H., Huesgen A., Wick U. Control of cell-contact sites by cyclic AMP pulses in differentiating Dictyostelium cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):547–549. doi: 10.1038/255547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Wick U. Intracellular oscillations and release of cyclic AMP from Dictyostelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):364–370. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. A., Newell P. C. Evidence for the existence of two types of cAMP binding sites in aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Yamasaki F. Characteristics of the induction of phosphodiesterases by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1978 Oct;26(10):2977–2982. doi: 10.1248/cpb.26.2977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck G. L., Erickson R. P. A rate theory of gustatory stimulation. Behav Biol. 1973 Jun;8(6):687–712. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(73)80112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. J. The cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Binding characteristics of aggregation-competent cells and variation of binding levels during the life cycle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4730–4736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIJN T. M., RAPER K. B. Cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1961 Dec;3:725–756. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(61)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. Adenylate cyclase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae and its changes during differentiation. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Darmon M. Effects of cyclic AMP pulses on adenylate cyclase and the phosphodiesterase inhibitor of D. discoideum. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):76–78. doi: 10.1038/268076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Darmon M. The relationship of phosphodiesterase to the developmental cycle of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):440–447. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90335-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP as a first messenger. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Fuchila J., Jastorff B. Correlation of substrate specificity of cAMP-phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium discoideum with chemotactic activity of cAMP-analogues. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80690-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Gerisch G. Short-term binding and hydrolysis of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate by aggregating Dictyostelium cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Nägele B., Schwarz H., Gerisch G. Membrane-bound cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in chemotactically responding cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Jastorff B., Morr M., Konijn T. M. A model for cyclic AMP-chemoreceptor interaction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 1;544(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Konijn T. M. Chemotaxis and binding of cyclic AMP in cellular slime molds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Konijn T. M. The chemotactic of cyclic AMP and AMP derivatives with substitutions in the phosphate moiety in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Krens F. A., van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. 3':5'-cyclic AMP-dependent 3':5'-cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2348–2351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Losada A., Nanjundiah V., Konijn T. M. Signal input for a chemotactic response in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4991–4993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Rhijnsburger E. H., Dobbe F. C., Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP and folic acid mediated cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80814-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullens I. A., Newell P. C. cAMP binding to cell surface receptors of Dictyostelium. Differentiation. 1978 May 26;10(3):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1978.tb00960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannbacker R. G., Bravard L. J. Phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium discoideum and the chemotactic response to cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):1014–1015. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel V., Malchow D., Gerisch G., Nägele B. Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase interaction with its inhibitor of the slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90660-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier C., Gerisch G., Malchow D. Action of a slowly hydrolysable cyclic AMP analogue on developing cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:321–338. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Brooker G., Appleman M. M. Assay of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases with radioactive substrates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:205–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Schubiger K., Wick U., Gerisch G. Cyclic GMP in Dictyostelium discoideum, Oscillations and pulses in response to folic acid and cyclic AMP signals. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh R. P., Chan F. K., Coukell M. B. Independent regulation of the extracellular cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-inhibitor system and membrane differentiation by exogenous cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


