Abstract
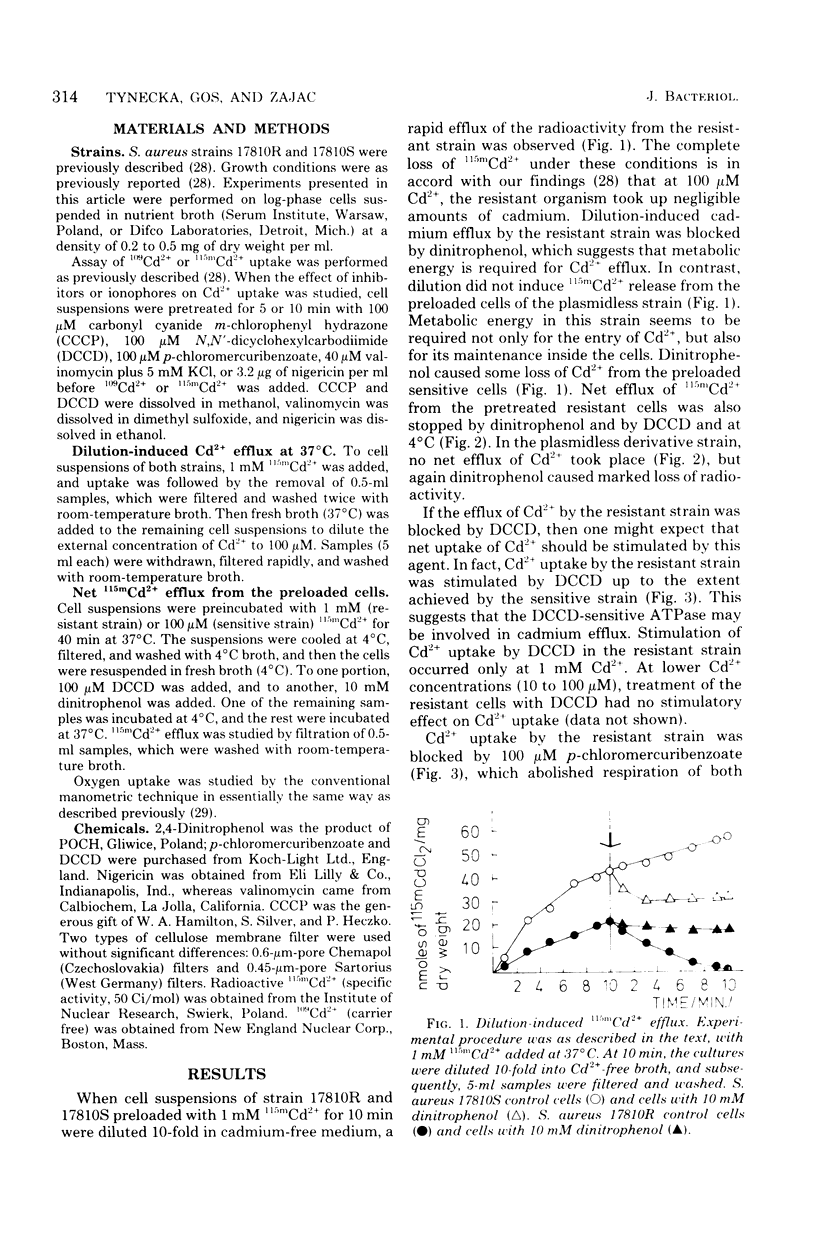
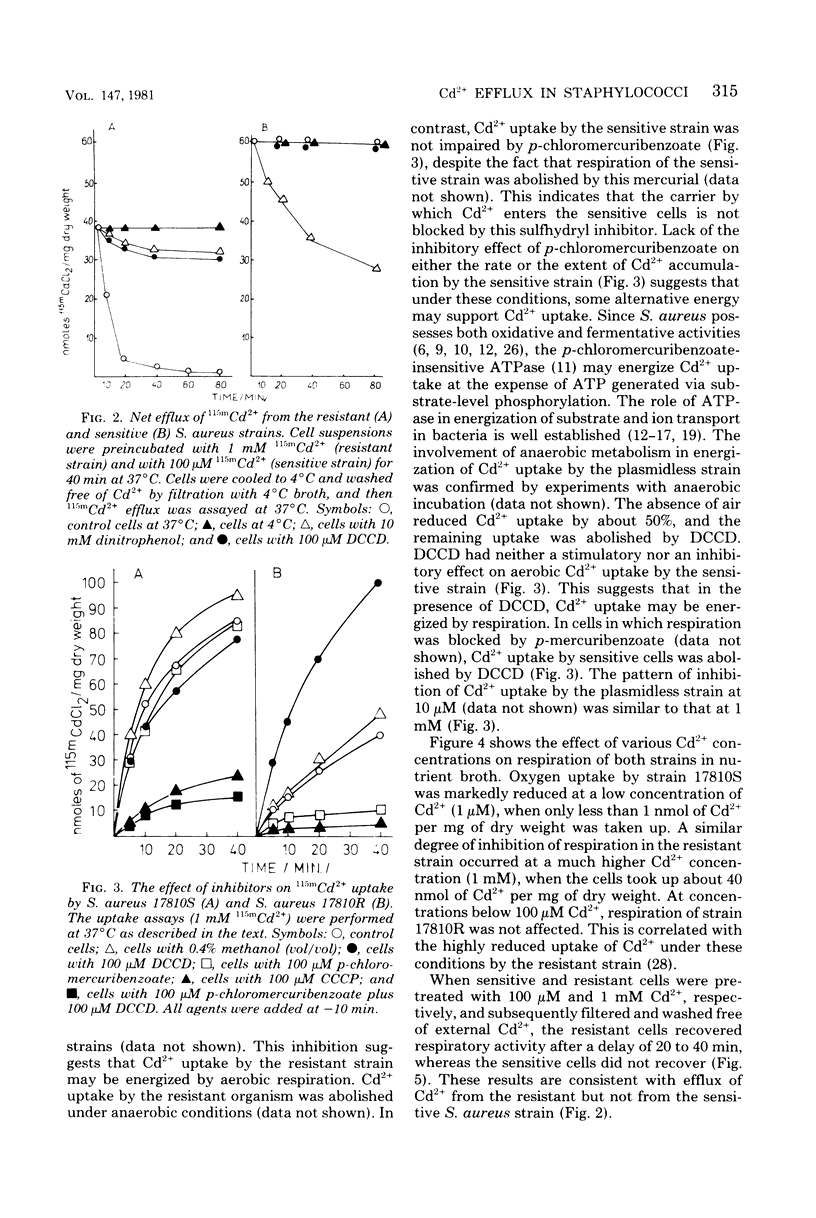
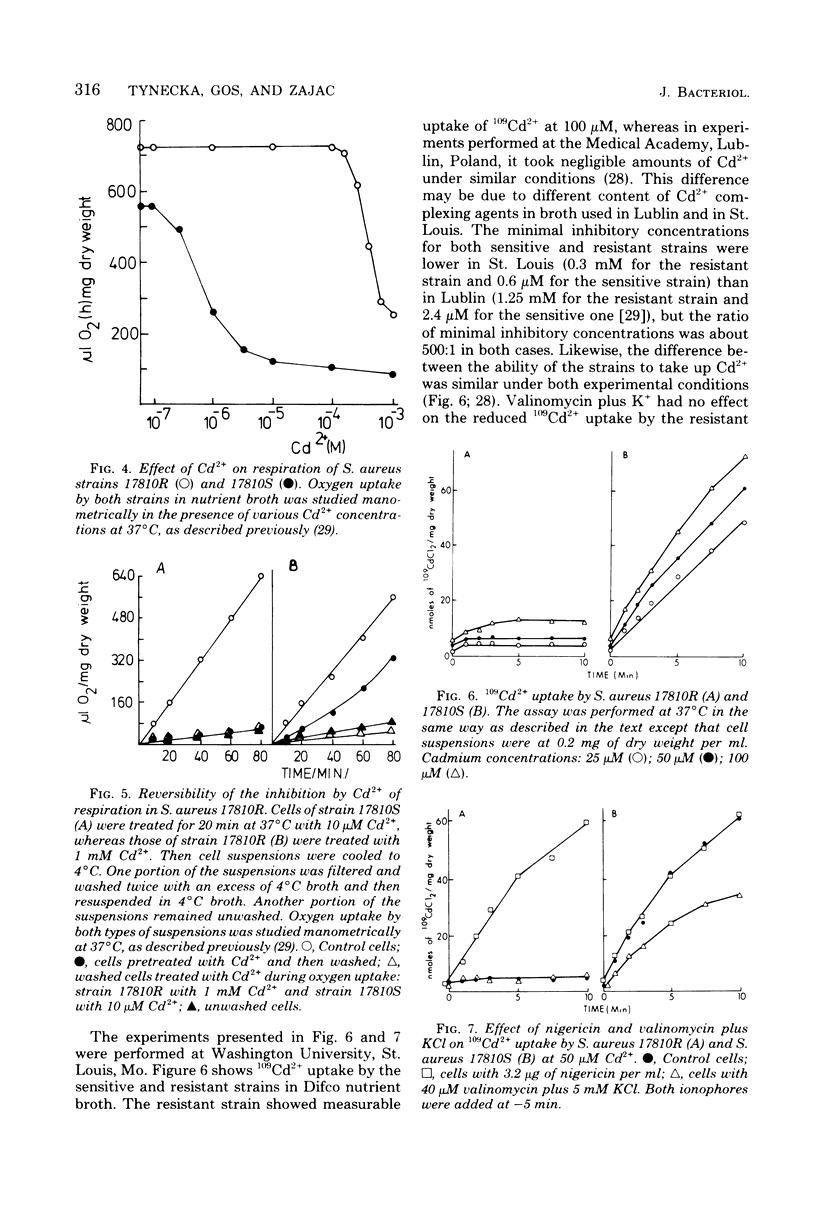
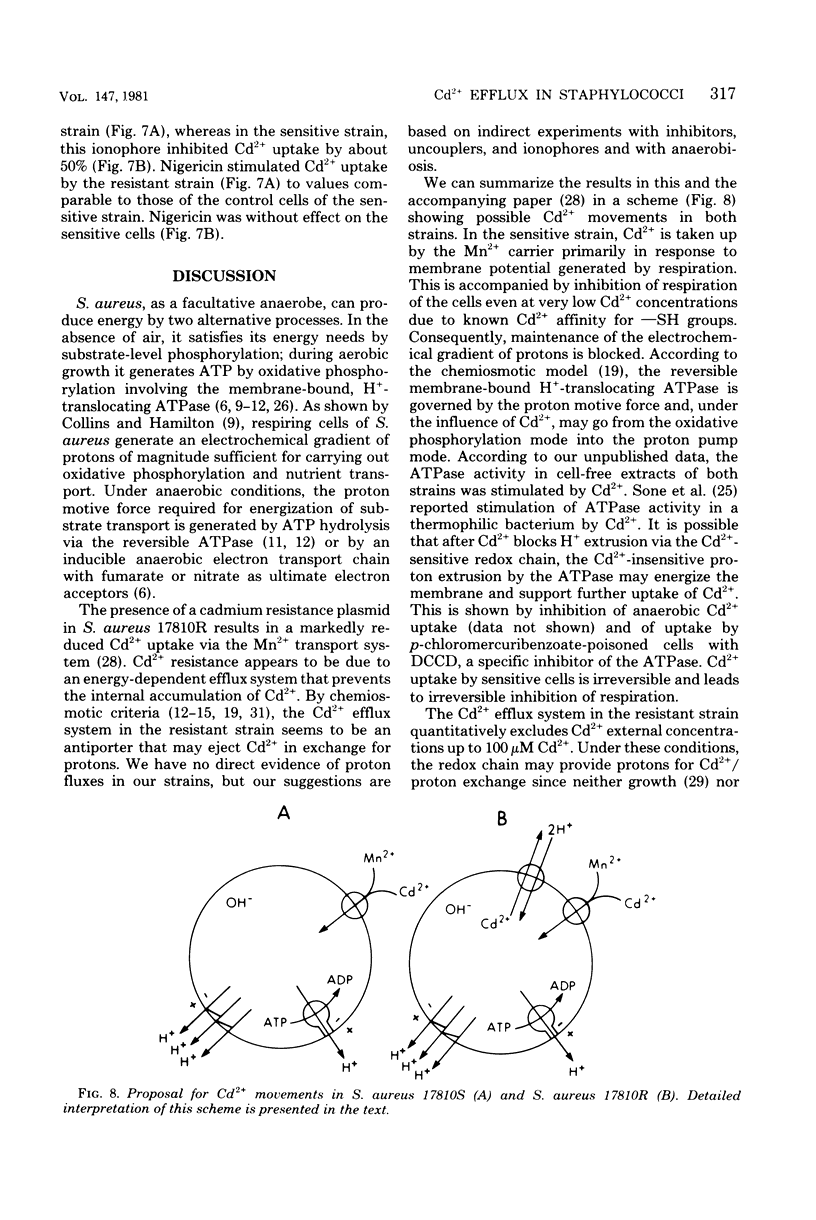
Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus strain 17810R to Cd2+ appears to be due to a plasmid-coded Cd2+ efflux system. Complete efflux of Cd2+ after transfer of preloaded cells into Cd2+-free medium occurred in the resistant strain 17810R, but not in the plasmidless derivative strain 17810S. Net efflux was blocked by 2,4-dinitrophenol, N,N,-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD), and incubation at 4 degrees C. The inhibition of Cd2+ efflux by DCCD paralleled a stimulation of net uptake in the resistant cells by this agent. Cd2+ efflux by the resistant strain was accompanied by a reversal of inhibition of respiration, whereas in the sensitive strain, inhibition of respiration was not reversed after transfer to Cd2+-free medium. Net Cd2+ uptake by strain 17810R was inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzoate. In Cd2+ contrast, Cd2+ uptake by the plasmidless strain 17810S was affected neither by p-chloromercuribenzoate nor by DCCD when added alone, but was blocked by a combination of these two agents. Valinomycin had no effect on the reduced Cd2+ uptake by the resistant strain, whereas nigericin stimulated uptake to values comparable to those of the untreated sensitive cells. With sensitive cells, valinomycin reduced Cd2+ uptake by about 50%, whereas nigericin was without effect. A possible mechanism of Cd2+ movements in both strains is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball P. R., Shales S. W., Chopra I. Plasmid-mediated tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli involves increased efflux of the antibiotic. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in escherichia coli: properties of the sodium/proton antiporter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the calcium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1957–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG J. P., LASCELLES J. NITRATE REDUCTASE IN CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF A HAEMIN-REQUIRING STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:503–510. doi: 10.1042/bj0890503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. Decreased uptake of cadmium by a resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):265–267. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. Mechanism of plasmic-mediated resistance to cadmium in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. H., Hamilton W. A. Magnitude of the protonmotive force in respiring Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1224–1231. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1224-1231.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Coles N. W. Adenosine triphosphatase in isolated membranes of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1322–1326. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1322-1326.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R., Baron C., Abrams A. Inhibition of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase and of cation transport in Streptococcus faecalis by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:297–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Ion currents and physiological functions in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:181–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. II. Proton and sodium extrusion. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):45–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01868094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. ATP-linked calcium transport in cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L., Petrucci R. E., Jr, Levy S. B. Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3974–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., McClees J. S. Active transport of calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Yoshida M., Hirata H., Kagawa Y. Purification and properties of a dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase from a thermophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7917–7923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABER H. W., MORRISON M. ELECTRON TRANSPORT IN STAPHYLOCOCCI. PROPERTIES OF A PARTICLE PREPARATION FROM EXPONENTIAL PHASE STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 May;105:367–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Characterization of an active transport system for calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7687–7692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynecka Z., Gos Z., Zajac J. Reduced cadmium transport determined by a resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):305–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.305-312.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynecka Z., Zajac J., Goś Z. Plasmid dependent impermeability barrier to cadmium ions in Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Microbiol Pol A. 1975;7(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Silver S., Kinscherf T. G. Cation transport alteration associated with plasmid-determined resistance to cadmium in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):856–865. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



