Abstract
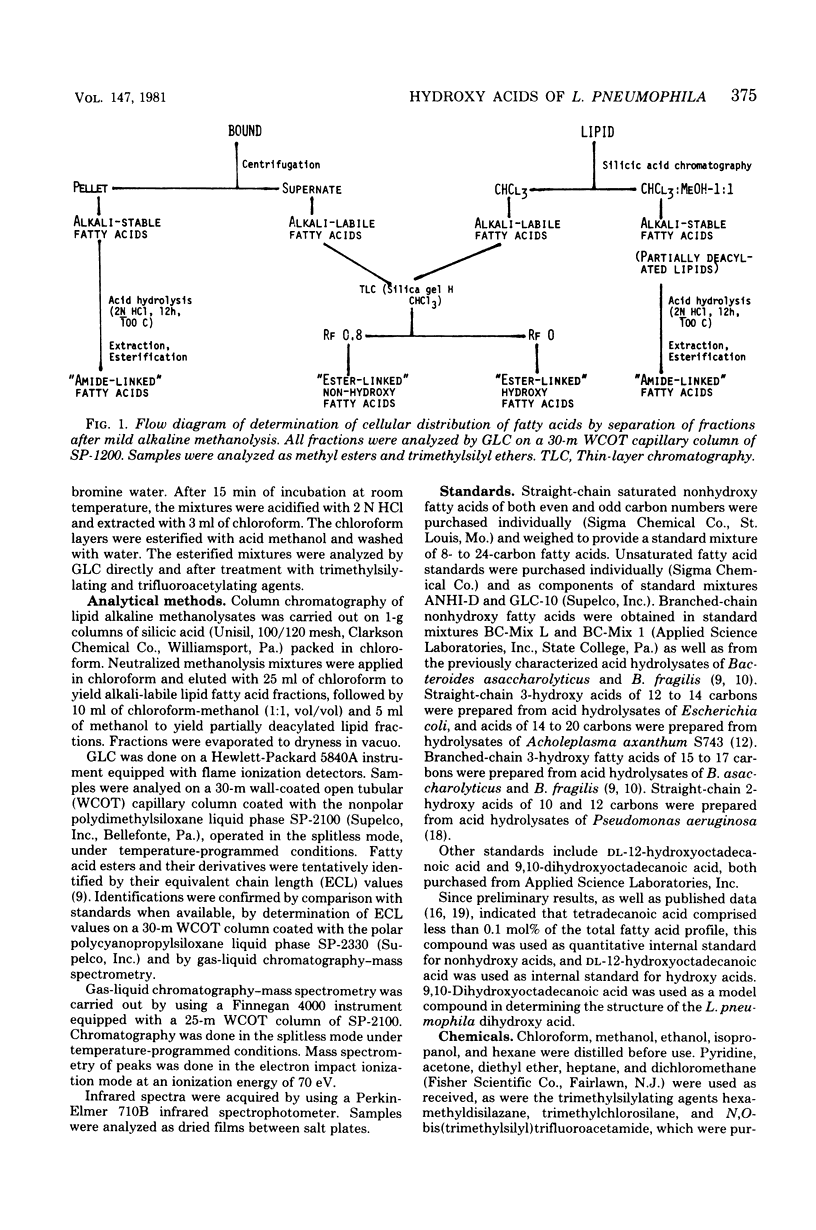
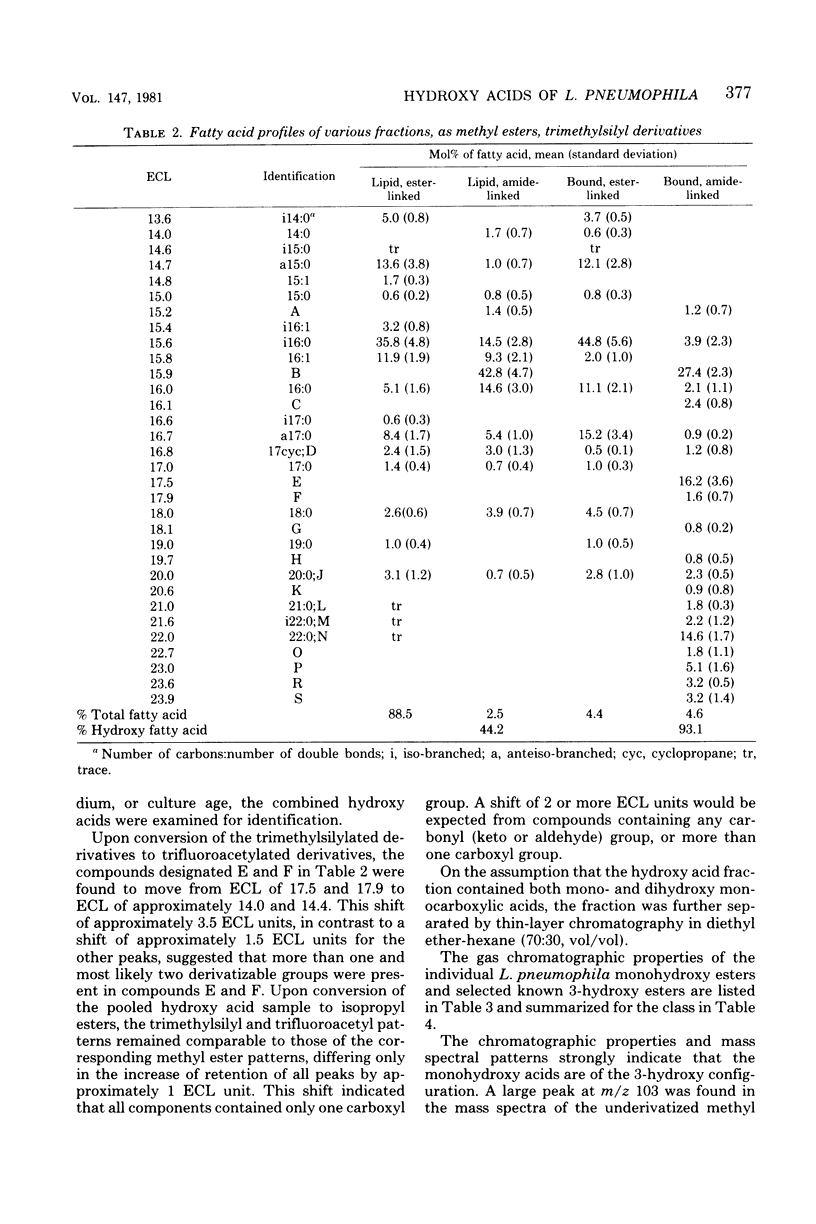
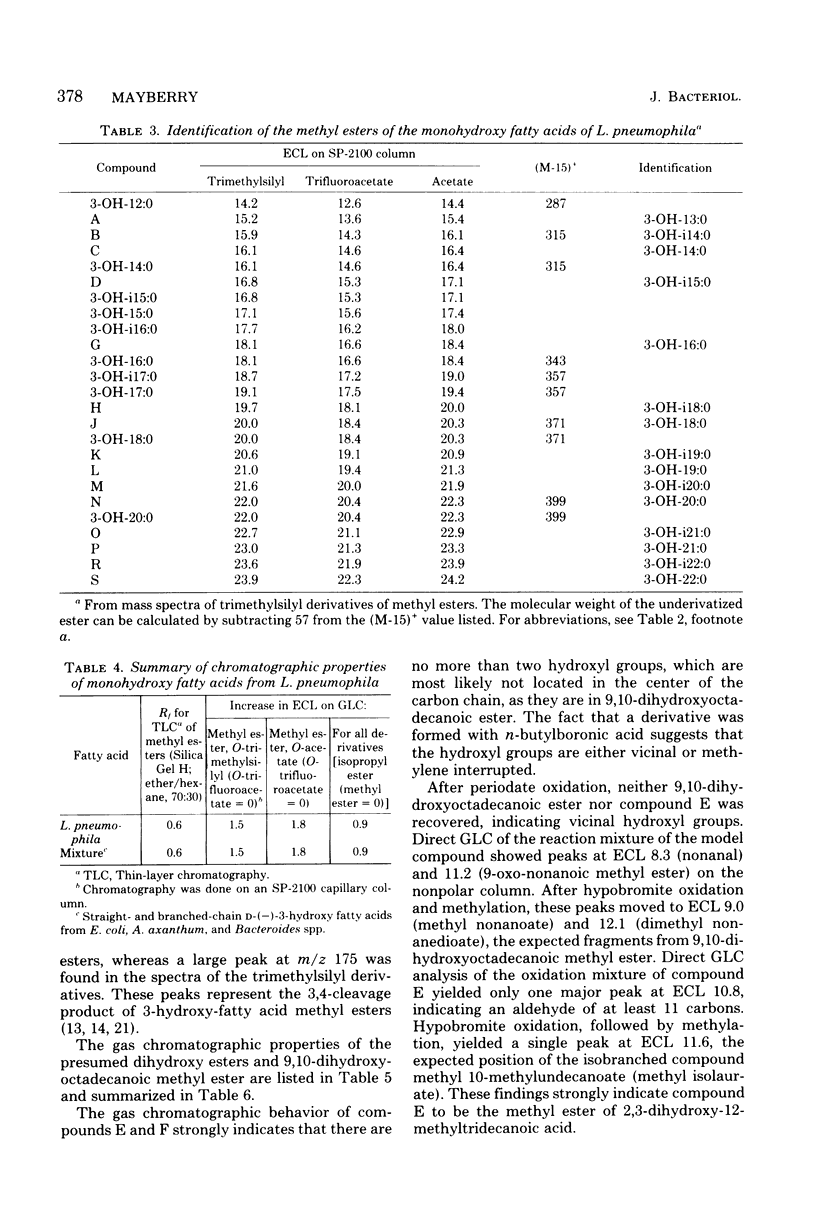
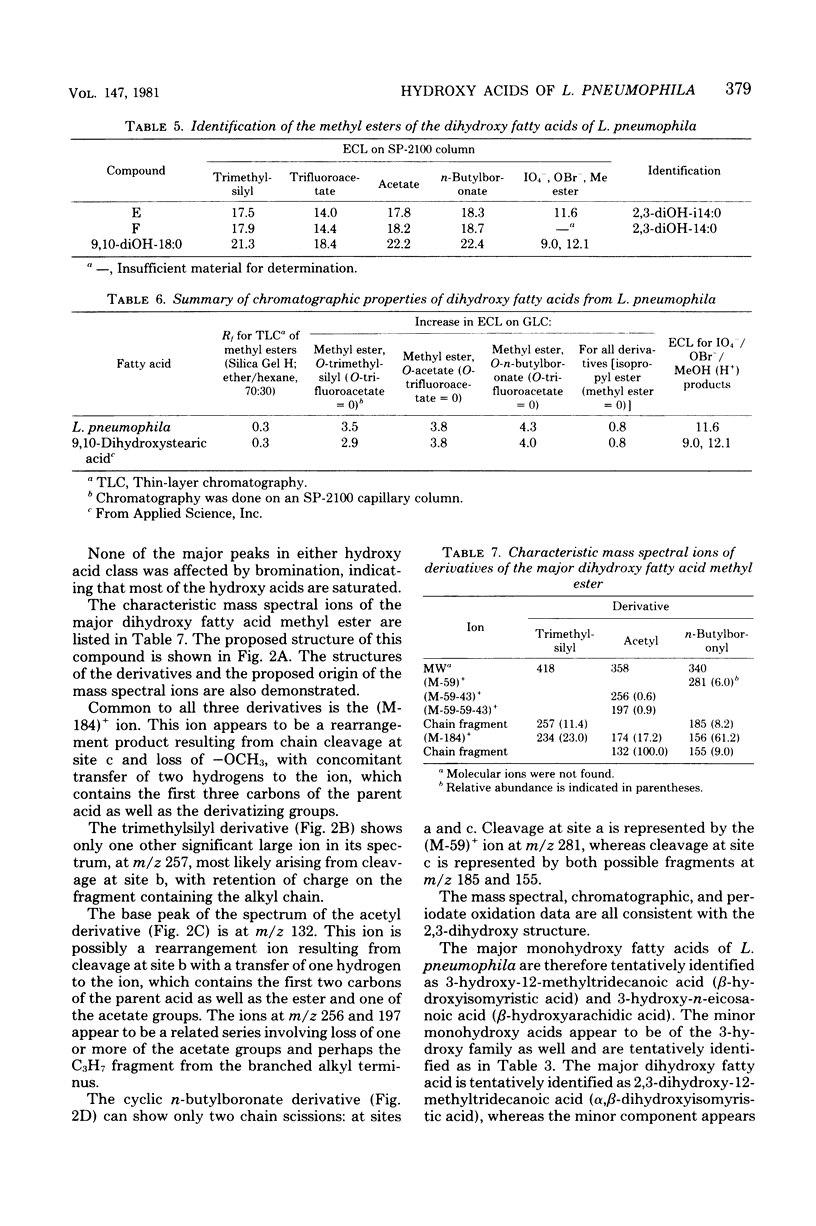
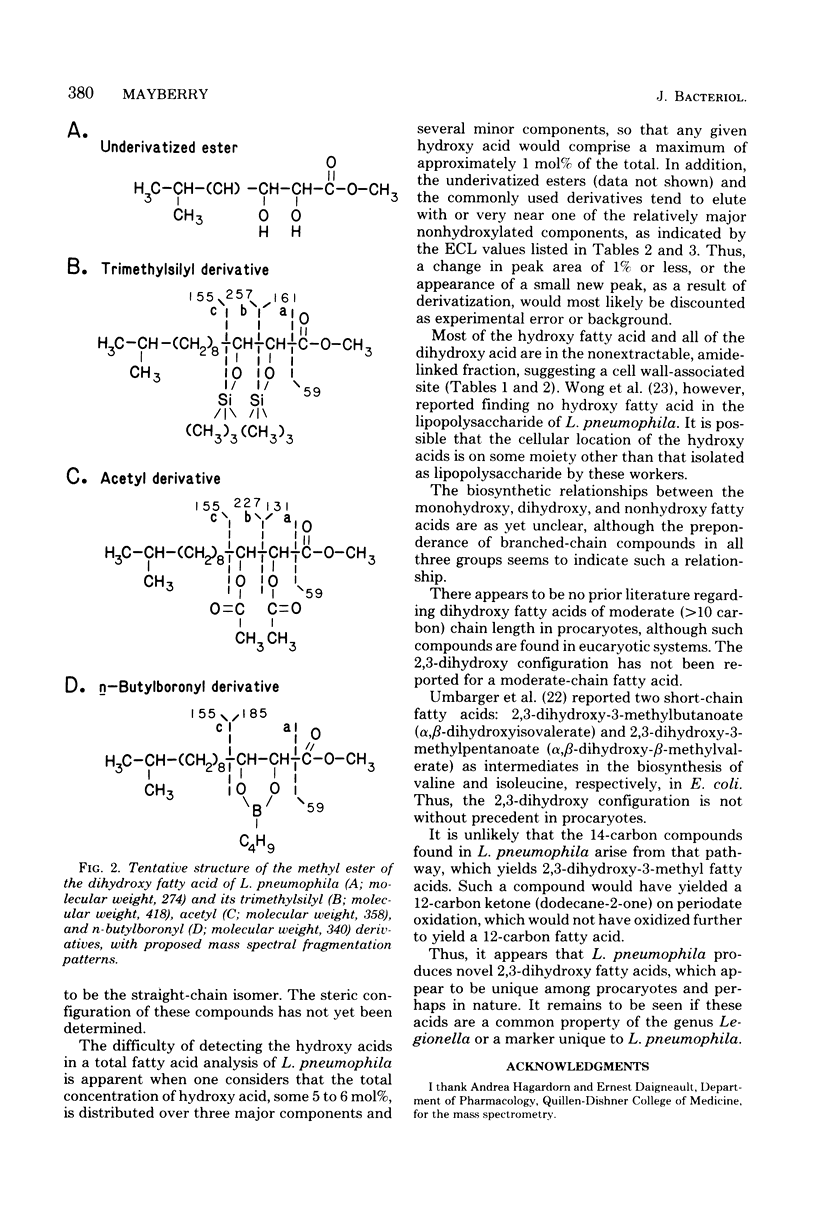
Five strains of Legionella pneumophila were examined for the presence of hydroxy fatty acid. The cellular distribution of the fatty acids was also determined, as was the variation of hydroxy acid production on five growth media. The strains tested all produced approximately 5 mol% of hydroxy fatty acid, most of which was found in the nonextractable, alkali-stable, acid-labile (wall-associated, amide-linked) fraction. Three major hydroxy acids were found, along with several minor components. The major hydroxy acids were analyzed by thin-layer chromatography, gas-liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, and infrared spectrophotometry. These compounds were tentatively identified as 3-hydroxy-12-methyltridecanoate, 3-hydroxy-n-eicosanoate, and a novel dihydroxy acid, 2,3-dihydroxy-12-methyltridecanoate. The total amount of hydroxy acid produced, as well as the profile of the hydroxy acids, remained relatively unchanged with respect to strain and growth medium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Wilkinson H. W., Gorman G. W., Fikes B. J., Fraser D. W. Atypical Legionella-like organisms: fastidious water-associated bacteria pathogenic for man. Lancet. 1979 Nov 3;2(8149):927–930. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92623-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnerty W. R., Makula R. A., Feeley J. C. Cellular lipids of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):631–634. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Moss C. W., McDougal L. K., Bozeman F. M., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. The rickettsia-like organisms TATLOCK (1943) and HEBA (1959): bacteria phenotypically similar to but genetically distinct from Legionella pneumophila and the WIGA bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewallen K. R., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Dail D. H., Thomason B. M., Bright R. A. A newly identified bacterium phenotypically resembling, but genetically distinct from, Legionella pneumophila: an isolate in a case of pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Dec;91(6):831–834. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R. Cellular distribution and linkage of D-(-)-3-hydroxy fatty acids in Bacteroides species. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):200–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.200-204.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R. Hydroxy fatty acids in Bacteroides species: D-(--)-3-hydroxy-15-methylhexadecanoate and its homologs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):582–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.582-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A. Heptose-containing pentaglycosyl diglyceride among the lipids of Acholeplasma modicum. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):898–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.898-904.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Plackett P. Identification of the amide-linked fatty acids of Acholeplasma axanthum S743 as D(-)3-hydroxyhexadecanoate and its homologues. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1091-1095.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A., Feeley J. C., Wong E. S., Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella gormanii sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.718-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of WIGA, a rickettsia-like agent similar to the Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):390–391. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.390-391.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Further studies of the cellular fatty acid composition of Legionnaires disease bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):648–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.648-649.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of selected Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):596–598. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.596-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Weaver R. E., Dees S. B., Cherry W. B. Cellular fatty acid composition of isolates from Legionnaires disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.140-143.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E., BROWN B., EYRING E. J. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. IX. Utilization of acetolactate and acetohydroxybutyrate. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1425–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Moss C. W., Hochstein D. H., Arko R. J., Schalla W. O. "Endotoxicity" of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):624–627. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



