Abstract
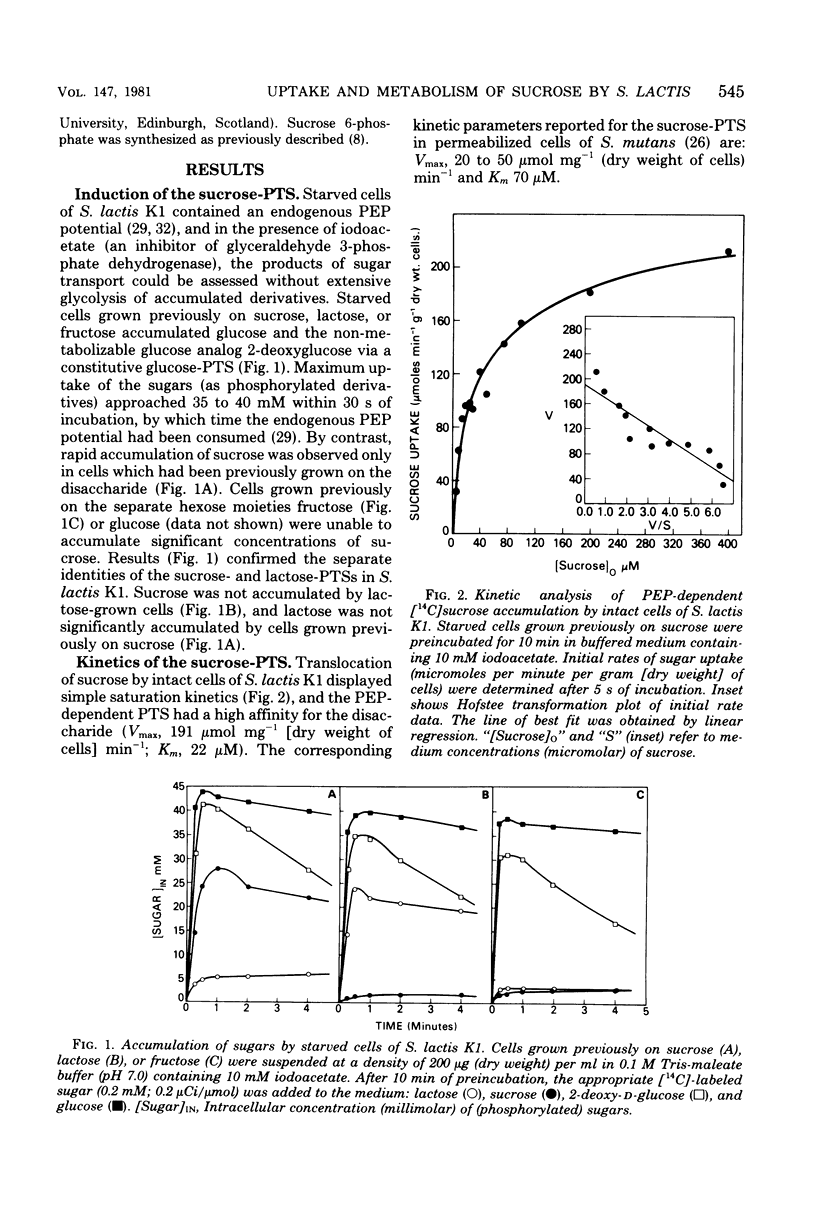
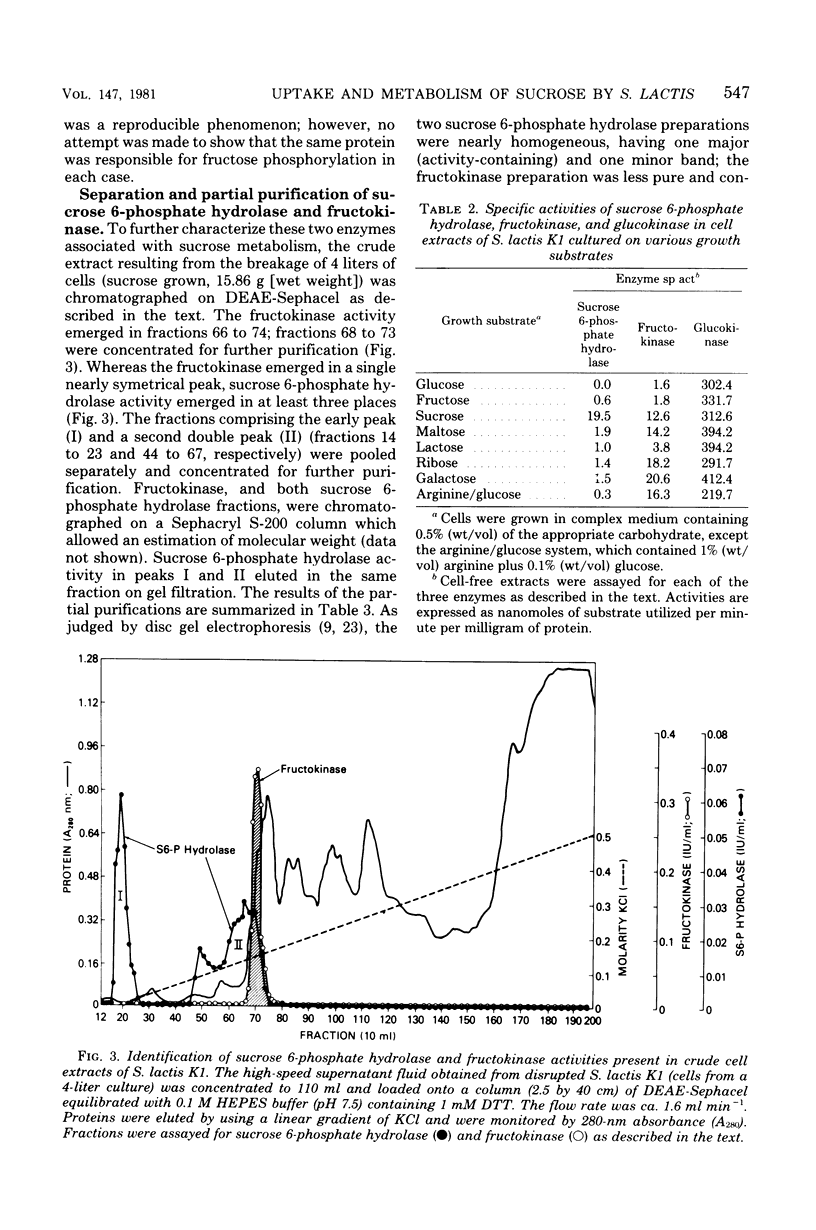
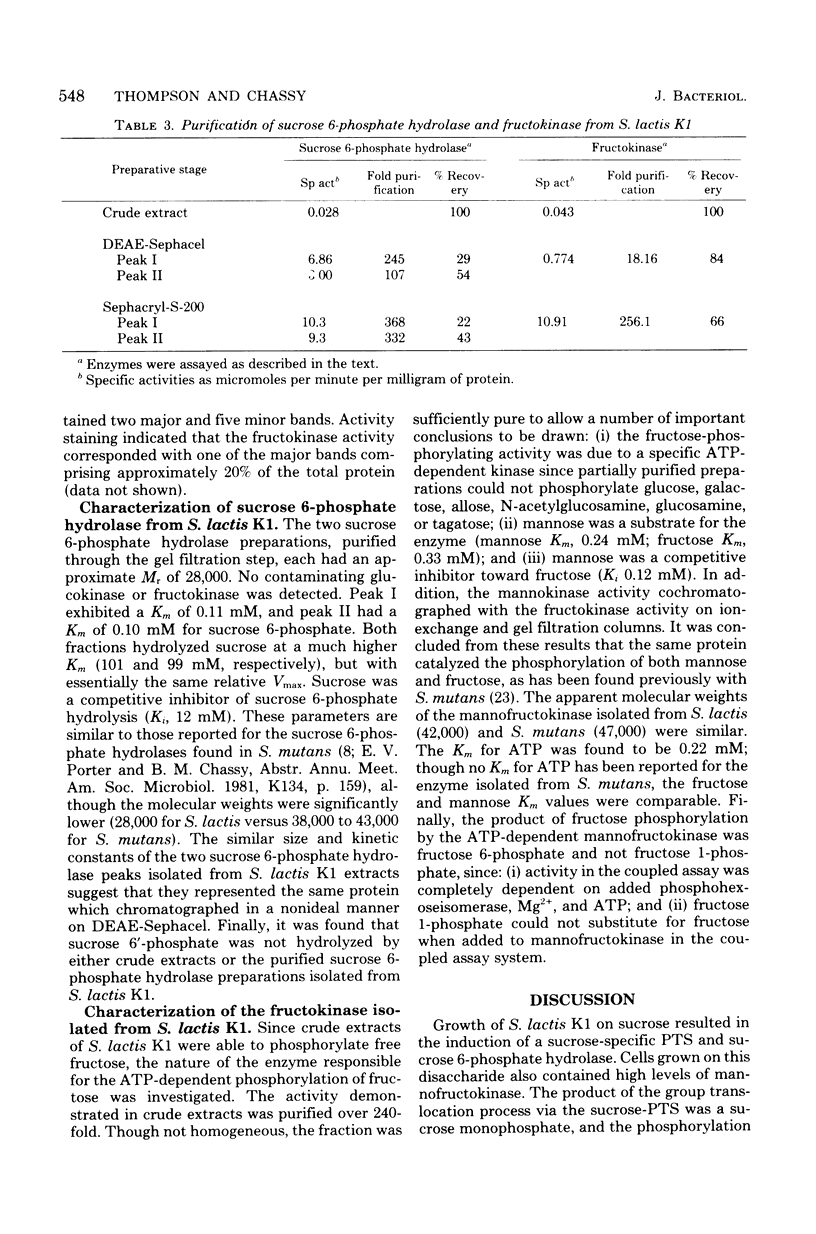
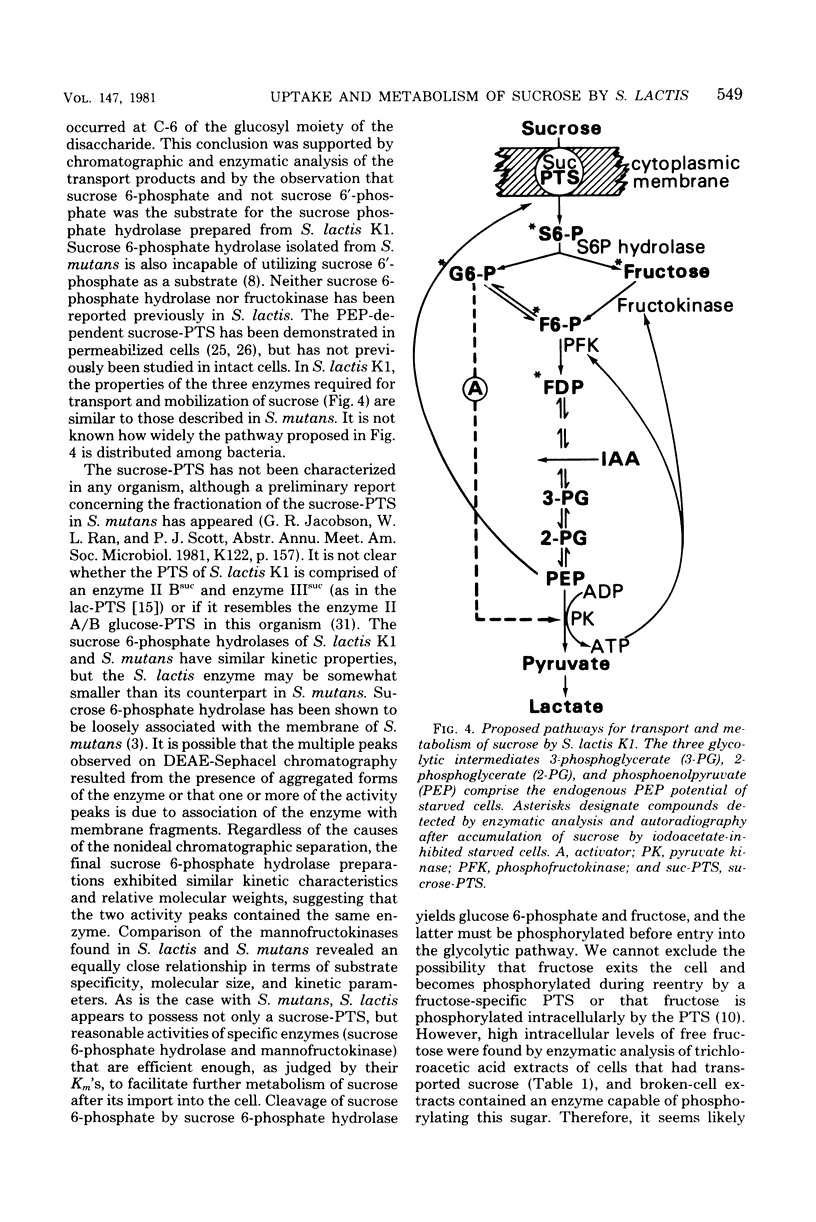
Transport and metabolism of sucrose in Streptococcus lactis K1 have been examined. Starved cells of S. lactis K1 grown previously on sucrose accumulated [14C]sucrose by a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system (PTS) (sucrose-PTS; Km, 22 microM; Vmax, 191 mumol transported min-1 g of dry weight of cells-1). The product of group translocation was sucrose 6-phosphate (6-O-phosphoryl-D-glucopyranosyl-1-alpha-beta-2-D-fructofuranoside). A specific sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase was identified which cleaved the disaccharide phosphate (Km, 0.10 mM) to glucose 6-phosphate and fructose. The enzyme did not cleave sucrose 6'-phosphate(D-glucopyranosyl-1-alpha-beta-2-D-fructofuranoside-6'-phosphate). Extracts prepared from sucrose-grown cells also contained an ATP-dependent mannofructokinase which catalyzed the conversion of fructose to fructose 6-phosphate (Km, 0.33 mM). The sucrose-PTS and sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase activities were coordinately induced during growth on sucrose. Mannofructokinase appeared to be regulated independently of the sucrose-PTS and sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase, since expression also occurred when S. lactis K1 was grown on non-PTS sugars. Expression of the mannofructokinase may be negatively regulated by a component (or a derivative) of the PTS.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in group N streptococci: presence of enzymes for both the D-galactose 1-phosphate and D-tagatose 6-phosphate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):318–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.318-320.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzola J. J., Kuramitsu H. K., Maynard M. T. Localization of Streptococcus mutans GS-5 glucosyltransferases and intracellular invertase. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):830–839. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.830-839.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calmes R., Brown A. T. Regulation of lactose catabolism in Streptococcus mutans: purification and regulatory properties of phospho-beta-galactosidase. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):68–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.68-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calmes R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in the catabolism of caries-conducive disaccharides by Streptococcus mutans: lactose transport. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):934–942. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.934-942.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Initial characterization of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans and its apparent identity with intracellular invertase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delobbe A., Chalumeau H., Claverie J. M., Gay P. Phosphorylation of intracellular fructose in Bacillus subtilis mediated by phosphoenolpyruvate-1-fructose phosphotransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezel W., Kopperschläger G., Hofmann E. An improved procedure for protein staining in polyacrylamide gels with a new type of Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):617–620. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., Lebtag H. Lactose metabolism by Streptococcus mutans: evidence for induction of the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1102–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1102-1104.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. V. The accumulation of phosphorylated carbohydrate derivatives, and evidence for a new enzyme-splitting lactose phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):274–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Morse M. L. Purification of the staphylococcal 6-phospho-beta-D-- galactosidase. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M., Holmlund C. E. Partial purification and properties of a mannofructokinase from Streptococcus mutans SL-1. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.43-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):821–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.821-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Activator specificity of pyruvate kinase from lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1240–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1240-1242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Characteristics and energy requirements of an alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport system in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):719–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.719-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis: phosphorylation of galactose and glucose moieties in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):774–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.774-785.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of methyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside-6-phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus lactis by exclusion and expulsion mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.885-894.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Glucose-6-phosphate-dependent pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):562–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.562-563.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



