Abstract
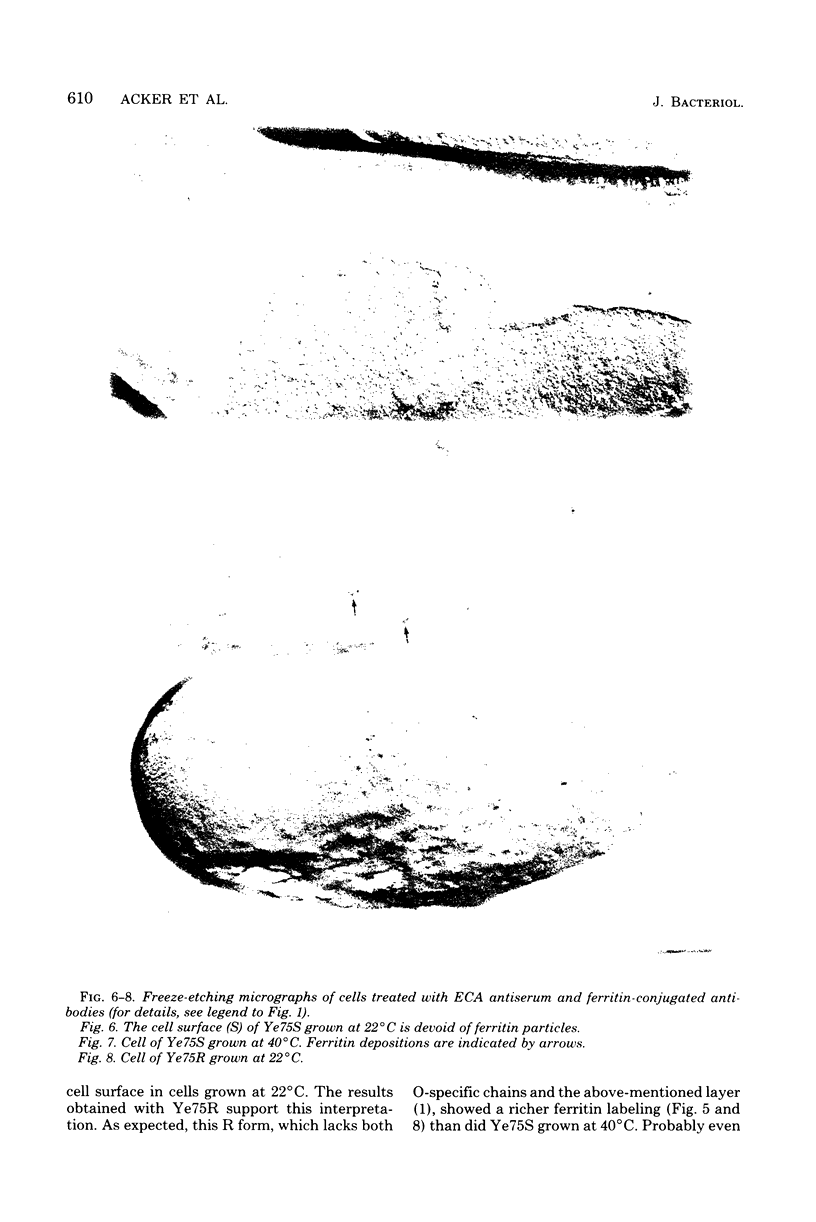
Rabbits were immunized with the enterobacterial common antigen (ECA)-immunogenic strain Escherichia coli F470. ECA-specific antiserum was obtained by absorbing the resulting antisera with the genetically closely related ECA-negative strain E. coli F1283. These two strains also served as positive and negative controls in the localization study of ECA in Yersinia enterocolitica strain 75, smooth and rough forms (Ye75S and Ye75R), by the indirect immunoferritin technique. Cells of Ye75S grown at 22 degrees C showed no labeling with ferritin after treatment with the ECA-specific antiserum and subsequent ferritin-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibodies. If the cells were grown at 40 degrees C, however, most of the cells showed weak ferritin labeling. At this higher growth temperature, the lipopolysaccharide of this strain contains less O-specific chains (6-deoxy-L-altrose), as was shown in a previous study. The rough mutant Ye75R, which lacks O-specific chains completely, showed denser labeling with ferritin. These results indicate that ECA on the cell surface of Ye75S is covered by O-specific chains of the lipopolysaccharide if grown at 22 degrees C and is therefore not accessible to ECA antibodies. It becomes accessible, however, when O-chains are lacking (R mutants) or when they are reduced in size or amount (growth at 40 degrees C).
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G. The arrangement of lipopolysaccharides on the outer membrane of Yersinia enterocolitica: an electron microscopic study. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Apr;237(4):504–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acker G., Wartenberg K., Knapp W. Zuckerzusammensetzung des Lipopolysaccharids und Feinstruktur der äusseren Membran (Zellwand) bei Yersinia enterocolitica. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980;247(2):229–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acker G., Wartenberg K. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharides of Yersinia enterocolitica, Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(4):439–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki S., Merkel M., McCabe W. R. Immunofluorescent demonstration of the common enterobacterial antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):230–234. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J., Lindberg B., Brubaker R. R. Structural studies of the O-specific side-chains of the lipopolysaccharide from Yersinia enterocolitica Ye 128. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Jan 1;78(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83675-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Chatterjee A. K., Sanderson K. E., Costerton J. W. Comparison of the cell envelope structure of a lipopolysaccharide-defective (heptose-deficient) strain and a smooth strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):930–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.930-941.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. SEPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF A COMMON ANTIGEN IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:565–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Lysy J., Knapp C., Stille W., Goll U. Enterale Infektionen beim Menschen durch Yersinia enterocolitica und ihre Diagnose. Infection. 1973;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01638486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Thal E. Die biochemische Charakterisierung von Yersinia enterocolitica (syn. "Pasteurella X") als Grundlage eines vereinfachten O-Antigenschemas. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Jan;223(1):88–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Chalon A. M., Véron M. Recherches sur la présence de l'antigène commun des "Enterobacteriaceae" (antigène Kunin) chez les "Yersinia", "Levinea", "Aeromonas" et "Vibrio". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):761–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A., Digranes A. Common enterobacterial antigen in Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):382–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Petcovici M., Nacescu N., Mayer H., Schmidt G. Demonstration of enterobacterial common antigen by bacterial agglutination. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):563–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.563-567.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer H., Schmidt G. Chemistry and biology of the enterobacterial common antigen (ECA). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;85:99–153. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67322-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D., Mayer H. Serological and immunological properties of isolated enterobacterial common antigen. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):371–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E. Bacterial hemagglutination and hemolysis. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Sep;20(3):166–188. doi: 10.1128/br.20.3.166-188.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinno J., Gmeiner J., Golecki J. R., Mayer H. Localization of enterobacterial common antigen: Proteus mirabilis and its various L-forms. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):822–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.822-827.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinno J., Golecki J. R., Mayer H. Localization of enterobacterial common antigen:immunogenic and nonimmunogenic enterobacterial common antigen-containing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):814–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.814-821.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI T., GORZYNSKI E. A., NETER E. SEPARATION BY ETHANOL OF COMMON AND SOMATIC ANTIGENS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1240–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1240-1243.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Westphal O. Wachstum und Lipopolysaccharid (O-Antigen)-Gehalt von Salmonellen bei Züchtung auf Agarnährböden. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Jun;200(2):241–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. Die Gefrierätzung korrespondierender Bruchhälften: ein neuer Weg zur Aufklärung von Membranstrukturen. Protoplasma. 1970;70(1):101–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01276845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Acker G., Kleber I. Ultrastructural surface alterations of serratia marcescens after exposure to polymyxin B and/or fresh human serum. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(2):104–113. doi: 10.1159/000221919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg K., Lysy J., Knapp W. On the sugar content of the lipopolysaccharides of the various strains known as Yersinia enterocolitica. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;230(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]