Abstract
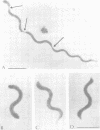
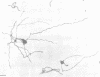
The helical mycoplasma Spiroplasma citri was examined by electron microscopy with a newly developed transfer technique which preserves the helical morphology of the organism. The smallest viable cell was found to be a two-turn (elementary) helix. During the logarithmic phase of growth, organisms increased in length and divided by constriction, liberating two-turn elementary helices. The most frequently dividing parental helix was one with approximately four turns, yielding two elementary helices. Influence of pH and temperature on the morphology of the organism was also investigated. In unbuffered medium, growth of the organism produced a significant decrease in pH and a consequent formation of abnormal morphological forms and cell lysis. At 37 degrees C, cell division was inhibited, leading to a progressive disappearance of two-turn helices and an increase in the average length of other helices. Finally, helices were never seen to arise from round bodies at any stage of the growth cycle.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole R. M., Tully J. G., Popkin T. J., Bové J. M. Morphology, ultrastructure, and bacteriophage infection of the helical mycoplasma-like organism (Spiroplasma citri gen. nov., sp. nov.) cultured from "stubborn" disease of citrus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):367–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.367-386.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Sissenstein R., McManus T. T., Woodward J. E., Lee I. M., Mudd J. B. Lipid composition and lipid metabolism of Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):946–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.946-954.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULSON D. F., SAKAGUCHI B. Nature of "sex-ratio" agent in Drosophila. Science. 1961 May 12;133(3463):1489–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3463.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. R., Mayberry-Carson K. J., Smith P. F. Effect of external environmental factors on the morphology of Spiroplasma citri. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):925–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.925-931.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Binding of proteins to mycoplasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 16;298(4):876–886. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]