Abstract
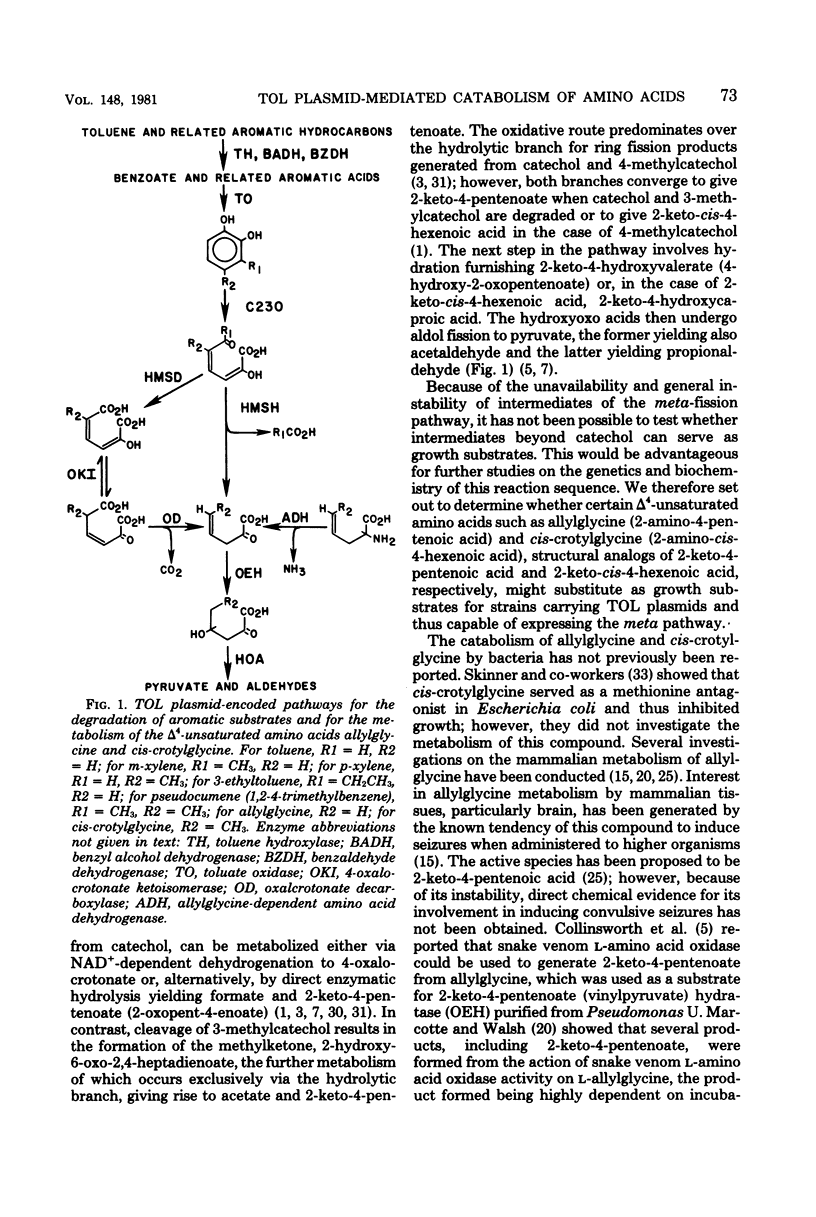
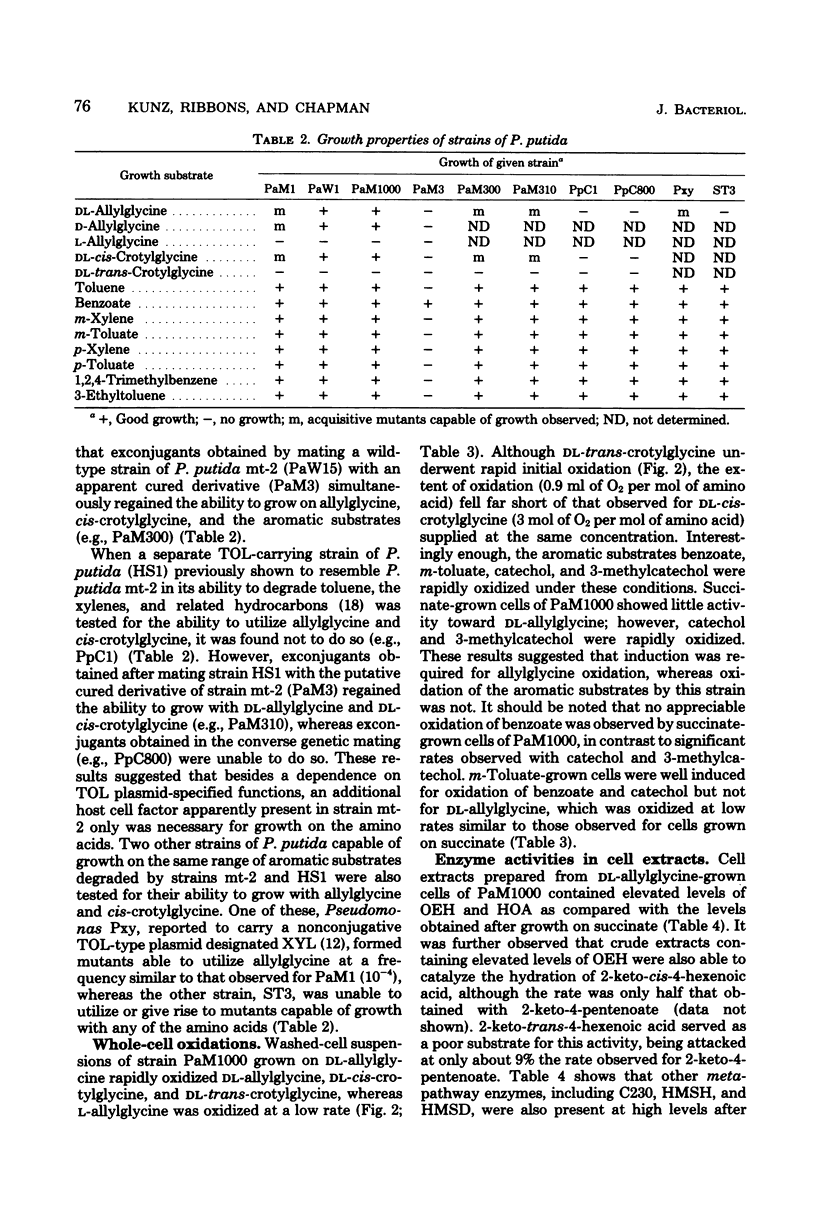
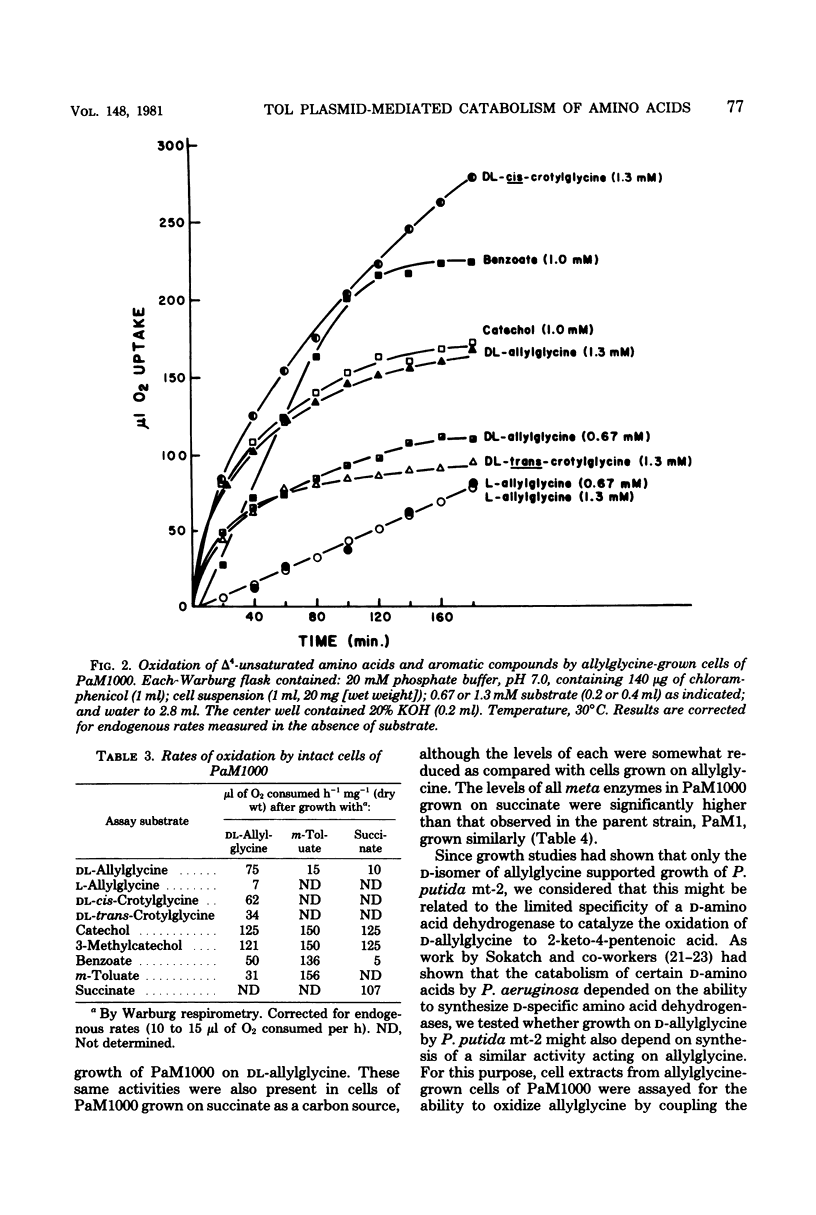
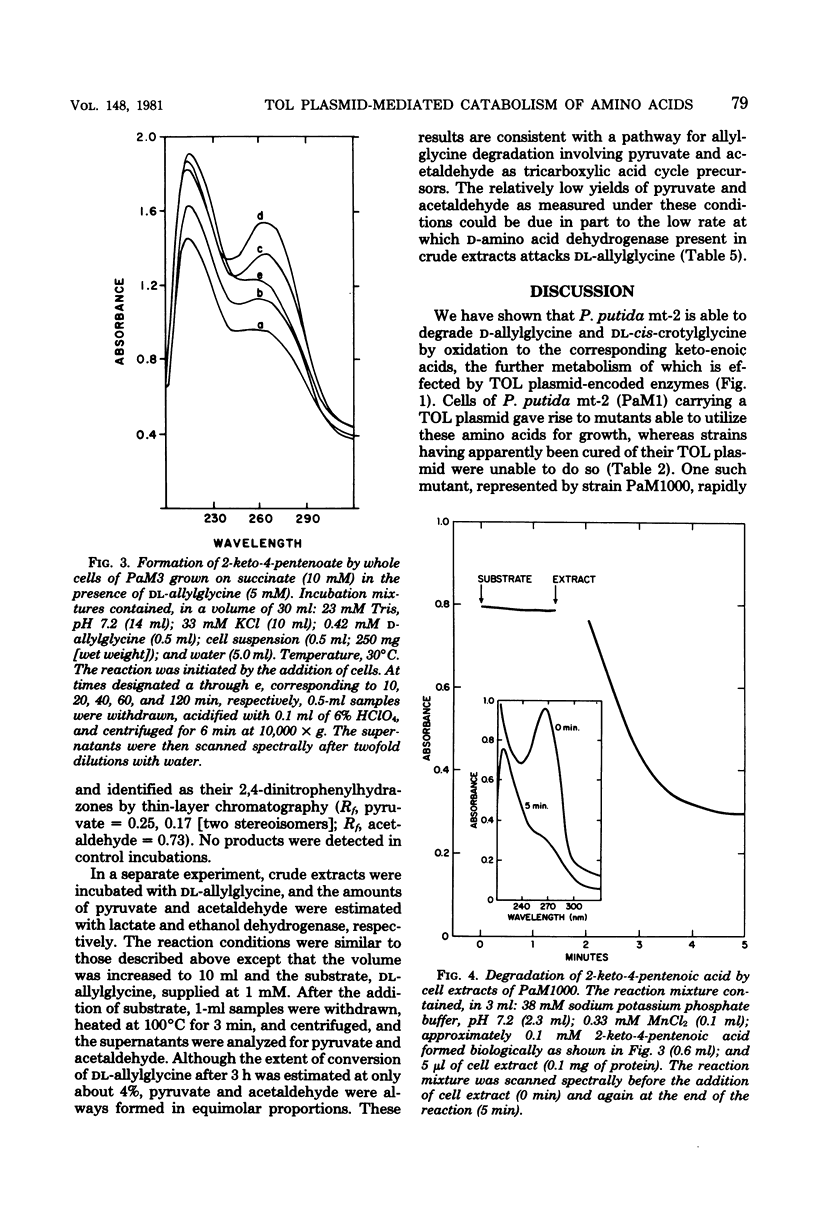
Spontaneous mutants which acquired the ability to utilize d-allylglycine (d-2-amino-4-pentenoic acid) and dl-cis-crotylglycine (dl-2-amino-cis-4-hexenoic acid) but not l-allylglycine or dl-trans-crotylglycine could be readily isolated from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 (PaM1). Derivative strains of PaM1 putatively cured of the TOL (pWWO) plasmid were incapable of forming mutants able to utilize the amino acids for growth; however, this ability could be regained by conjugative transfer of the TOL (pWWO) plasmid from a wild-type strain of mt-2 or of the TOL (pDK1) plasmid from a related strain of P. putida (HS1), into cured recipients. dl-Allylglycine-grown cells of one spontaneous mutant (PaM1000) extensively oxidized dl-allylglycine and dl-cis-crotylglycine, whereas only a limited oxidation was observed toward l-allylglycine and dl-trans-crotylglycine. Cell extracts prepared from PaM1000 cells contained high levels of 2-keto-4-hydroxyvalerate aldolase and 2-keto-4-pentenoic acid hydratase, the latter enzyme showing higher activity toward 2-keto-cis-4-hexenoic acid than toward the trans isomer. Levels of other enzymes of the TOL degradative pathway, including toluate oxidase, catechol-2,3-oxygenase, 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolase, and 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, were also found to be elevated after growth on allylglycine. Whole cells of a putative cured strain, PaM3, accumulated 2-keto-4-pentenoic acid from d-allylglycine, which was shown to be rapidly degraded by cell extracts of PaM1000 grown on dl-allylglycine. These same cell extracts were also capable of catalyzing the dehydrogenation of d- but not l-allylglycine and were further found to metabolize the amino acid completely to pyruvate and acetaldehyde. Differential centrifugation of crude cell extracts localized d-allylglycine dehydrogenase activity to membrane fractions. The results are consistent with a catabolic pathway for d-allylglycine and dl-cis-crotylglycine involving the corresponding keto-enoic acids as intermediates, the further metabolism of which is effected by the action of TOL plasmid-encoded enzymes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S. Oxoenoic acids as metabolites in the bacterial degradation of catechols. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(3):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall F. A., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The coexistence of two pathways for the metabolism of 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde in a naphthalene-grown pseudomonad. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinsworth W. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Stereospecific enzymes in the degradation of aromatic compounds by pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.922-931.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter A. W., Talalay P. Studies on the microbiological degradation of steroid ring A. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3238–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Bacterial metabolism of para- and meta-xylene: oxidation of a methyl substituent. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):923–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.923-929.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrank J. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: ring cleavage of 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate and subsequent reactions. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1365–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1365-1374.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friello D. A., Mylroie J. R., Gibson D. T., Rogers J. E., Chakrabarty A. M. XYL, a nonconjugative xylene-degradative plasmid in Pseudomonas Pxy. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1217–1224. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1217-1224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T. Initial reactions in the bacterial degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig B. 1976 Jul;162(1-2):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymatic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2653–2662. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. W., Meldrum B. S. Seizures induced by allylglycine, 3-mercaptopropionic acid and 4-deoxypyridoxine in mice and photosensitive baboons, and different modes of inhibition of cerebral glutamic acid decarboxylase. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):52–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D. A., Chapman P. J. Catabolism of pseudocumene and 3-ethyltoluene by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for new functions of the TOL (pWWO) plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):179–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.179-191.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D. A., Chapman P. J. Isolation and characterization of spontaneously occurring TOL plasmid mutants of Pseudomonas putida HS1. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):952–964. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.952-964.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcotte P., Walsh C. Sequence of reactions which follows enzymatic oxidation of allylglycine. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5620–5626. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall V. P., Sokatch J. R. Oxidation of D-amino acids by a particulate enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1419–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1419-1424.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON J. E., BULMER G. S., SOKATCH J. R. THE OXIDATION OF D-ALANINE BY CELL MEMBRANES OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 8;78:136–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91619-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J. E., Sokath J. R. Oxidation of D- and L-valine by enzymes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):116–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.116-120.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsiewski P. J., Kaczorowski G. J., Walsh C. Purification and properties of D-amino acid dehydrogenase, an inducible membrane-bound iron-sulfur flavoenzyme from Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4487–4494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Reingold D. F., Stanley M. E. D-and L-stereoisomers of allylglycine: convulsive action and inhibition of brain L-glutamate decarboxylase. J Neurochem. 1977 Feb;28(2):349–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raunio R. P., Jenkins W. T. D-alanine oxidase form Escherichia coli: localization and induction by L-alanine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):560–566. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.560-566.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of omicron-cresol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain T1. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):221–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W., Senior P. J. 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate 3,4-oxygenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens--oxidation of a substrate analog. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. A., Borkenhagen L. F., Talalay P. Enzymatic oxidation of steroids by cell-free extracts of Pseudomonas testosteroni: isolation of cleavage products of ring A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):837–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Bacterial degradation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and homoprotocatechuic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.159-167.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada K. D-amino acid dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4522–4528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Worsey M. J. Ubiquity of plasmids in coding for toluene and xylene metabolism in soil bacteria: evidence for the existence of new TOL plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):818–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.818-828.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Williams P. A. Metabolism of toluene and xylenes by Pseudomonas (putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for a new function of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.7-13.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



