Abstract
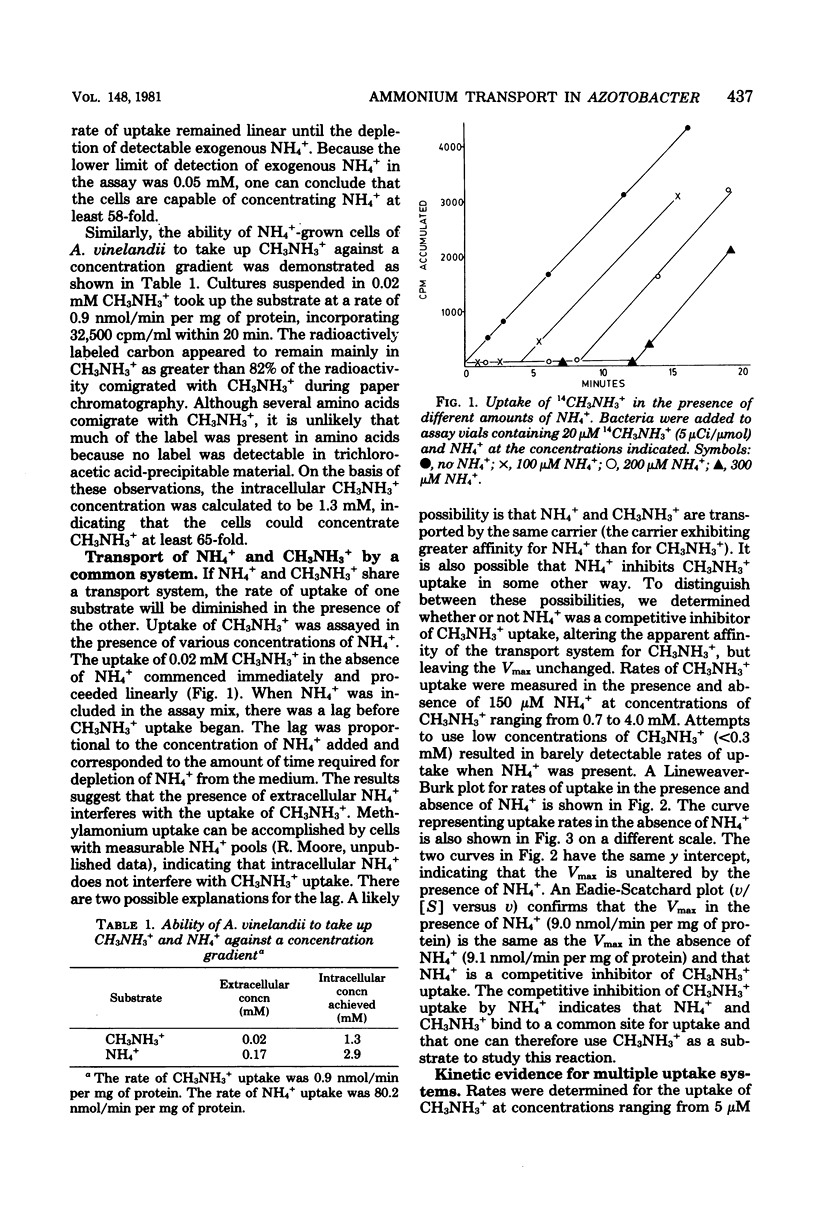
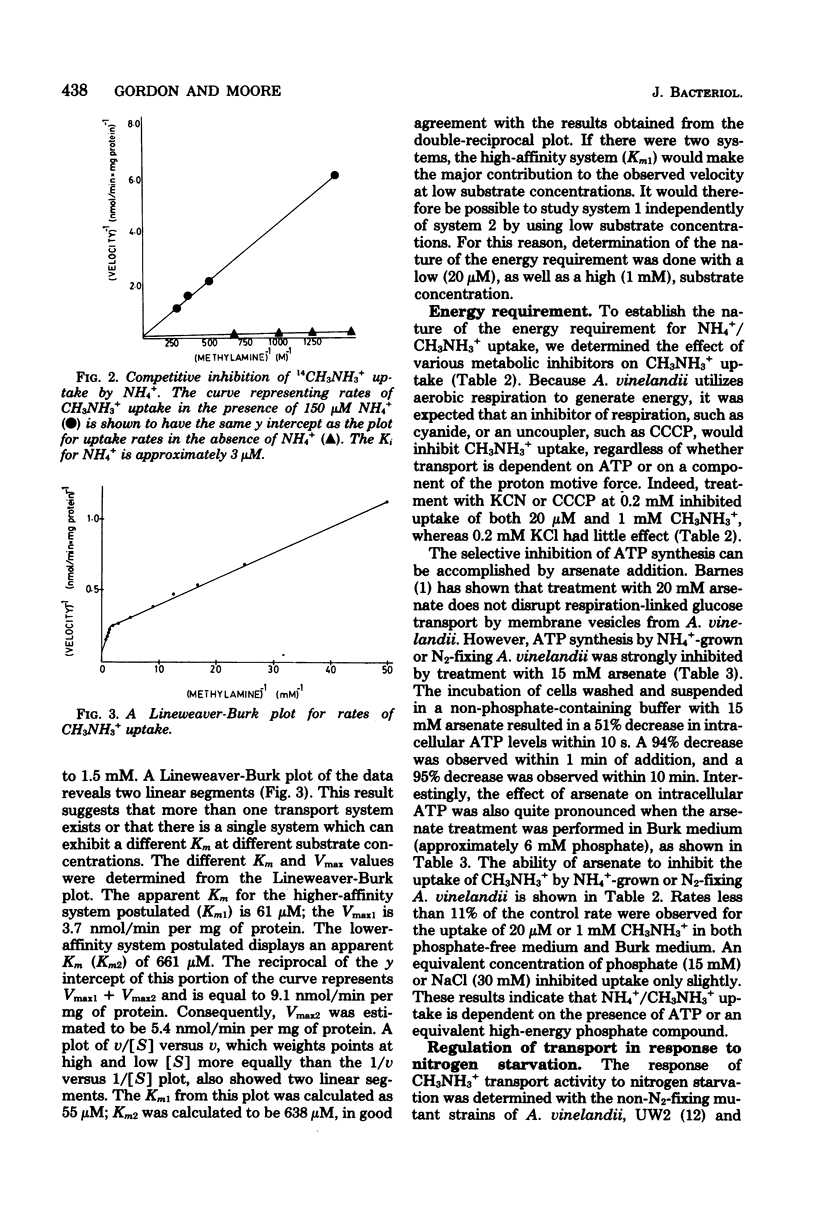
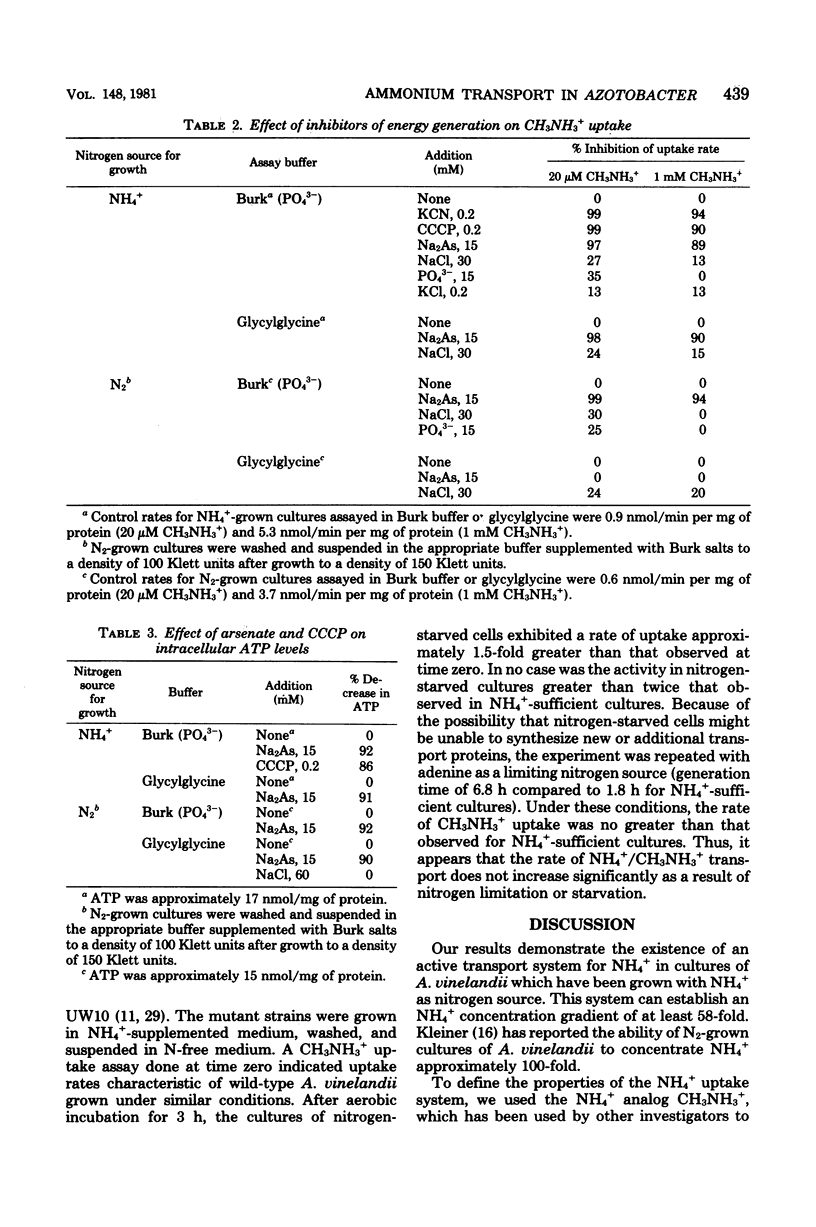
Azotobacter vinelandii, grown with NH4+ as nitrogen source, was shown to possess an active transport system which can take up NH4+ against a concentration gradient of 58-fold. The properties of the NH4+ uptake system were investigated with the NH4+ analog CH3NH3+. The use of this analog was justified on the basis of the conclusion that the uptake of NH4+ and CH3NH3 involves a common binding site, as shown by the competitive inhibition of CH3NH3+ uptake by NH4+ (Ki approximately 3 microM). A Lineweaver-Burk plot for CH3NH3+ uptake revealed a biphasic curve, suggesting the existence of two CH3NH3+ (NH4+) uptake systems with apparent Km's for CH3NH3+ equal to 61 microM and 661 microM. The uptake of CH3NH3+ was inhibited by arsenate, as well as by cyanide or carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenyl hydrazone, indicating that phosphate bond energy is required.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr Respiration-coupled glucose transport in membrane vesicles from Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):795–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Heppel L. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the shock-sensitive and shock-resistant amino acid permeases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7747–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E. The ATP pool in Escherichia coli. I. Measurement of the pool using modified luciferase assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L. Energetics of glycylglycine transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.139-146.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WITT C. W., ROWE J. A. N,O-Diacetylneuraminic acid and N-acetylneuraminic acid in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1959 Aug 1;184(Suppl 6):381–382. doi: 10.1038/184381b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Grenson M. Methylamine/ammonia uptake systems in saocharomyces cerevisiae: multiplicity and regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00267857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell J. W., Dobrogosz W. J. Cyclic AMP regulation of the hexose phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):1047–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.1047-1049.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Brill W. J. Mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii unable to fix nitrogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Brill W. J. Mutants that produce nitrogenase in the presence of ammonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3501–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackette S. L., Skye G. E., Burton C., Segel I. H. Characterization of an ammonium transport system in filamentous fungi with methylammonium-14C as the substrate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4241–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Winkler H. H. Energy coupling for methionine transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.985-991.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake and metabolism by mitrogen fixing bacteria. II. Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Dec 1;111(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00446553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake by nitrogen fixing bacteria I. Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):163–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00447319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Fitzke E. Evidence for ammonia translocation by Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Fitzke E. Some properties of a new electrogenic transport system: the ammonium (methylammonium) carrier from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Burton D., Garcia E., McCarter L., McFarland N. Nitrogen control in Salmonella: regulation by the glnR and glnF gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4576–4580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laane C., Krone W., Konings W., Haaker H., Veeger C. Short-term effect of ammonium chloride on nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii and by bacteroids of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland N., McCarter L., Artz S., Kustu S. Nitrogen regulatory locus "glnR" of enteric bacteria is composed of cistrons ntrB and ntrC: identification of their protein products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase complex: regulation by the proton electrochemical gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. The Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase complex: activation by phosphoenolpyruvate. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(2):219–230. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A. Requirement for membrane potential in active transport of glutamine by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.221-225.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Even H. L., Dunlop P., Larimore F. L. Methylamine and ammonia transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):502–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.502-509.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis I. C., Gordon J. K., Orme-Johnson W. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. 3. Nitrogenaseless mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii: activities, cross-reactions and EPR spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. I. Repression and derepression of the iron-molybdenum and iron proteins of nitrogenase in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):498–511. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R., Silver S. Methylammonium uptake by Escherichia coli: evidence for a bacterial NH4+ transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):1133–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Shanmugam K. T., Ausubel F., Morandi C., Goldberg R. B. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae: evidence for a role of glutamine synthetase as a regulator of nitrogenase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):815–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.815-821.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubb R. S. Glutamine synthetase and ammonium regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in Klebsiella. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):481–485. doi: 10.1038/251481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Source of energy for the Escherichia coli galactose transport systems induced by galactose. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):866–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.866-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. The regulation and properties of the galactose transport system in Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



