Full text
PDF
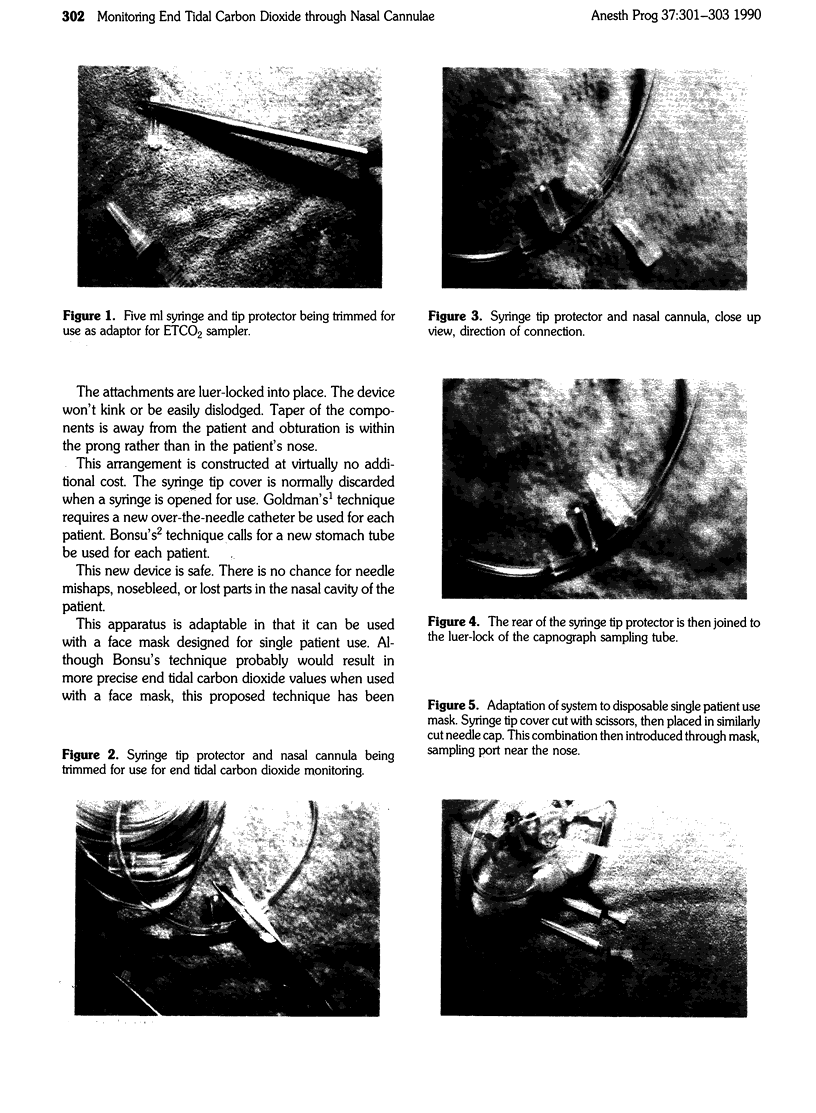

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonsu A. K., Tamilarasan A., Bromage P. R. A nasal catheter for monitoring tidal carbon dioxide in spontaneously breathing patients. Anesthesiology. 1989 Aug;71(2):318–318. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198908000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. M. A simple, easy, and inexpensive method for monitoring ETCO2 through nasal cannulae. Anesthesiology. 1987 Oct;67(4):606–606. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198710000-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]