Abstract
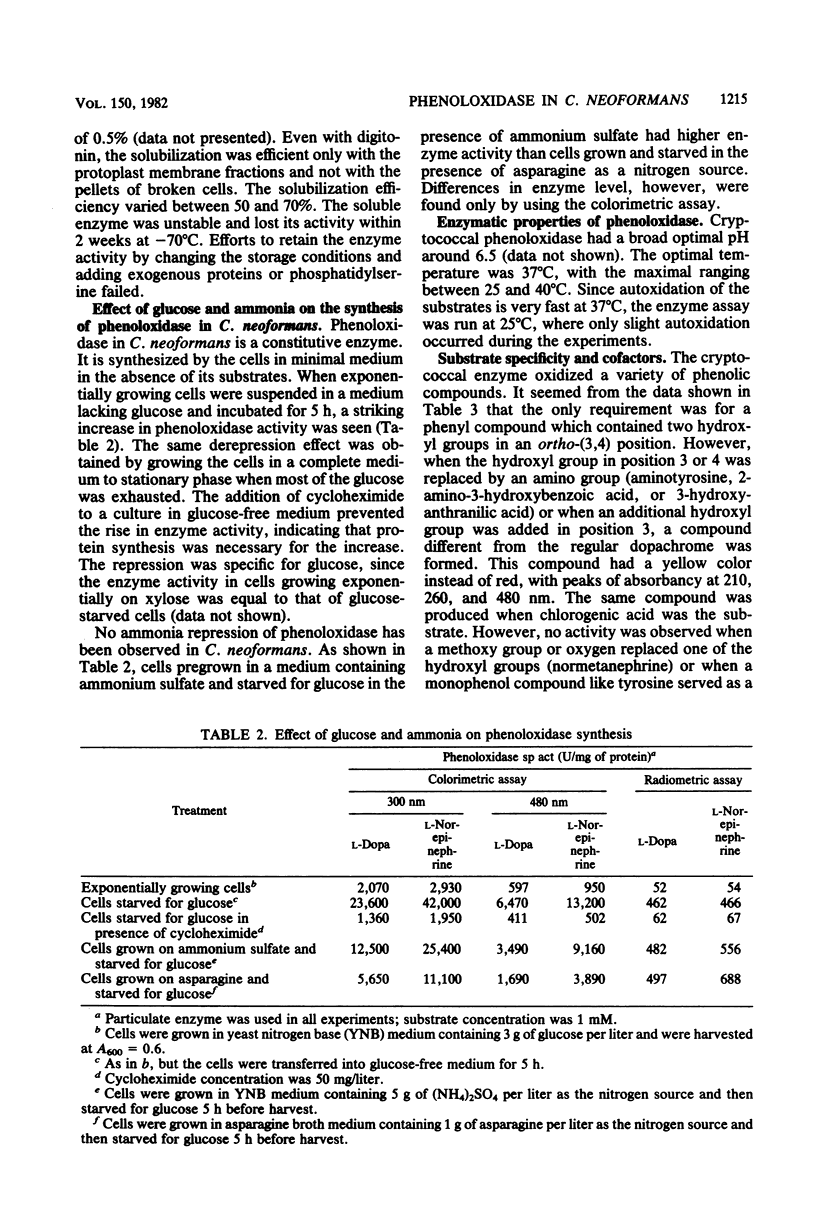
Protoplasts of Cryptococcus neoformans contain phenoloxidase as a membrane-bound enzyme. The enzyme appeared to be attached on the inner side of cytoplasmic membranes. Synthesis of the enzyme was derepressed by low levels of glucose but was not affected by the level of ammonium. Copper chelators which inhibited the phenoloxidase of other organisms did not affect cryptococcal enzymes. However, cyanide- or iron-chelating agents such as hydroximide derivates or 8-hydroxyquinoline were effective inhibitors, suggesting that cryptococcal phenoloxidase is an iron-containing enzyme. Phenoloxidase of C. neoformans catalyzed the oxidation of various diphenols via dopachrome and labile intermediates to melanin polymers. The kinetic constants (Km) of the phenoloxidase and the permease for dopamine and norepinephrine were low. The correlation between phenoloxidase and the preferential growth of C. neoformans in the host brain is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. THE DISTRIBUTION OF DOPAMINE AND DOPA IN VARIOUS ANIMALS AND A METHOD FOR THEIR DETERMINATION IN DIVERSE BIOLOGICAL MATERIAL. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Sep;145:326–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall S., Noack N., Wu M., Loewenberg J. R. A simple colorimetric method for determination of protein. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaskes S., Tyndall R. L. Pigment production by Cryptococcus neoformans and other Cryptococcus species from aminophenols and diaminobenzenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):146–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.146-152.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaskes S., Tyndall R. L. Pigment production by Cryptococcus neoformans from para- and ortho-Diphenols: effect of the nitrogen source. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.509-514.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth H. W., Coleman J. E. Physicochemical and kinetic properties of mushroom tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1613–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran A., Cabib E. Solubilization and partial purification of yeast chitin synthetase. Confirmation of the zymogenic nature of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4419–4425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durán A., Bowers B., Cabib E. Chitin synthetase zymogen is attached to the yeast plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3952–3955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Ekel T. M. Mammalian tyrosinase. A comparison of tyrosine hydroxylation and melanin formation. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1570549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jr, Ekel T. M., Montague P. M., Nicholson J. M. Mammalin tyrosinase. Stoichiometry and measurement of reaction products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 14;611(2):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeldtke R., Kaufman S. Bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase: purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3160–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Oka K., Nagatsu T., Sugimoto T., Matsuura S. Effects of structures of tetrahydropterin cofactors on tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 14;612(1):226–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth H., Pulverer G. Pigment formation for differentiating Cryptococcus neoformans from Candida albicans. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Mar;21(3):541–542. doi: 10.1128/am.21.3.541-542.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. J., Alexander M. Inhibition of the lysis of fungi by melanins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):624–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.624-629.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Polacheck I., Popkin T. J. Melanin-lacking mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans and their virulence for mice. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1414–1421. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1414-1421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEHLY A. C., CHANCE B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:357–424. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurudeen T. A., Ahearn D. G. Regulation of melanin production by Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):724–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.724-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal D. K., Randhawa H. S. Evaluation of a simplified Guizotia abyssinica seed medium for differentiation of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):346–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.346-348.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Hawley R. J., Calderone R. A. An ultrastructural analysis of protoplast-spheroplast induction in Cryptococcus neoformans. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1518–1521. doi: 10.1139/m76-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacheck I., Kwon-Chung K. J. Creatinine metabolism in Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus bacillisporus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.15-20.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter H. J., Alexander M. Susceptibility and resistance of several fungi to microbial lysis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1526–1532. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1526-1532.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakaran K., Harris E. B., Kirchheimer W. F. Effect of inhibitors on phenoloxidase of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):935–938. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.935-938.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakaran K., Harris E. B., Kirchheimer W. F. The nature of the phenolase enzyme in Mycobacterium leprae: structure-activity relationships of substrates and comparison with other copper proteins and enzymes. Microbios. 1972;5(20):273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. E., Kapica L. Production of diagnostic pigment by phenoloxidase activity of cryptococcus neoformans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):824–830. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.824-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan A. A., Yu R. J., Blank F. Pigment production of Cryptococcus neoformans grown with extracts of Guizotia abyssinica. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):478–479. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.478-479.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



