Abstract
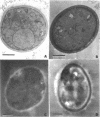
A double mutant of Cryptococcus neoformans which lacked the ability to produce melanin (Mel-) on media containing diphenols and failed to grow at 37 degrees C (temperature sensitive, Tem-) was obtained by UV irradiation and subsequent cloning. The mutant showed two lesions in melanogenesis in that it lacked the active transport system for diphenolic compounds and also lacked phenoloxidase. Ultrastructures of the mutant and wild-type cells grown on a medium with or without L-dopa showed that only the wild-type cells grown on L-dopa medium formed a dark cell wall layer, presumably containing melanin. The mutant was crossed with a wild type, and the phenotypes of the progeny were analyzed. The analysis showed no linkage between the mating type and either Mel or Tem loci, but loose linkage was seen between Mel and Tem loci. The progeny, Mel+ Tem+, Mel+ Tem-, Mel- Tem+, and Mel- Tem-, were studied for their virulence in mice. Only Mel+ Tem+ types killed mice with an inoculum of 5 X 10(5) cells within 50 days.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. THE DISTRIBUTION OF DOPAMINE AND DOPA IN VARIOUS ANIMALS AND A METHOD FOR THEIR DETERMINATION IN DIVERSE BIOLOGICAL MATERIAL. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Sep;145:326–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER W. T., ALLING D. W., SPICKARD A., UTZ J. P. DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY FINDINGS IN CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS, A FOLLOW-UP STUDY OF FORTY PATIENTS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Jan 9;270:59–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196401092700201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield B. J., Alexander M. Melanins and resistance of fungi to lysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1276-1280.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaskes S., Tyndall R. L. Pigment production by Cryptococcus neoformans from para- and ortho-Diphenols: effect of the nitrogen source. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.509-514.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman K. J., Powell K. E., Tosh F. E. The incidence of hospitalized cases of systemic mycotic infections. Sabouraudia. 1974 Mar;12(1):33–45. doi: 10.1080/00362177485380061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Ekel T. M. Mammalian tyrosinase. A comparison of tyrosine hydroxylation and melanin formation. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1570549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jr, Ekel T. M., Montague P. M., Nicholson J. M. Mammalin tyrosinase. Stoichiometry and measurement of reaction products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 14;611(2):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamalam A., Yesudian P., Thambiah A. S. Cutaneous infection by Cryptococcus laurentii. Br J Dermatol. 1977 Aug;97(2):221–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb15070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. J., Alexander M. Inhibition of the lysis of fungi by melanins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):624–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.624-629.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Morphogenesis of Filobasidiella neoformans, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):821–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Popkin T. J. Ultrastructure of septal complex in Filobasidiella neoformans (Cryptococcus neoformans). J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):524–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.524-528.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon K. J., Raper K. B. Heterokaryon formation and genetic analyses of color mutants in Aspergillus heterothallicus. Am J Bot. 1967 Jan;54(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER A. B., FITZPATRICK T. B. Biochemistry of melanin formation. Physiol Rev. 1950 Jan;30(1):91–126. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1950.30.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. P., 3rd, Schaberg D. R., Kissner D. G., Kauffman C. A. Cryptococcus laurentii lung abscess. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):135–138. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. C., Srinivasan S., Scott M. L., Raff M. J. Cryptococcus albidus meningitis. J Infect. 1980 Mar;2(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(80)91865-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacheck I., Hearing V. J., Kwon-Chung K. J. Biochemical studies of phenoloxidase and utilization of catecholamines in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1212–1220. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1212-1220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacheck I., Kwon-Chung K. J. Creatinine metabolism in Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus bacillisporus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.15-20.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popkin T. J., Theodore T. S., Cole R. M. Electron microscopy during release and purification of mesosomal vesicles and protoplast membranes from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):907–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.907-917.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter H. J., Alexander M. Susceptibility and resistance of several fungi to microbial lysis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1526–1532. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1526-1532.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer G., Korth H. Cryptococcus neoformans: pigmentbildung aus verschiedenen Polyphenolen. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1971;157(1):46–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02121290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. E., Kapica L. Production of diagnostic pigment by phenoloxidase activity of cryptococcus neoformans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):824–830. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.824-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. B., Ajello L. Medium for selective isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):208–209. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Zeimis R. T., Roberts G. D. Evaluation of a caffeic acid-ferric citrate test for rapid identification of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.445-449.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cunha T., Lusins J. Cryptococcus albidus meningitis. South Med J. 1973 Nov;66(11):1230–passim. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]