Abstract
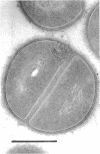
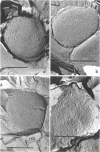
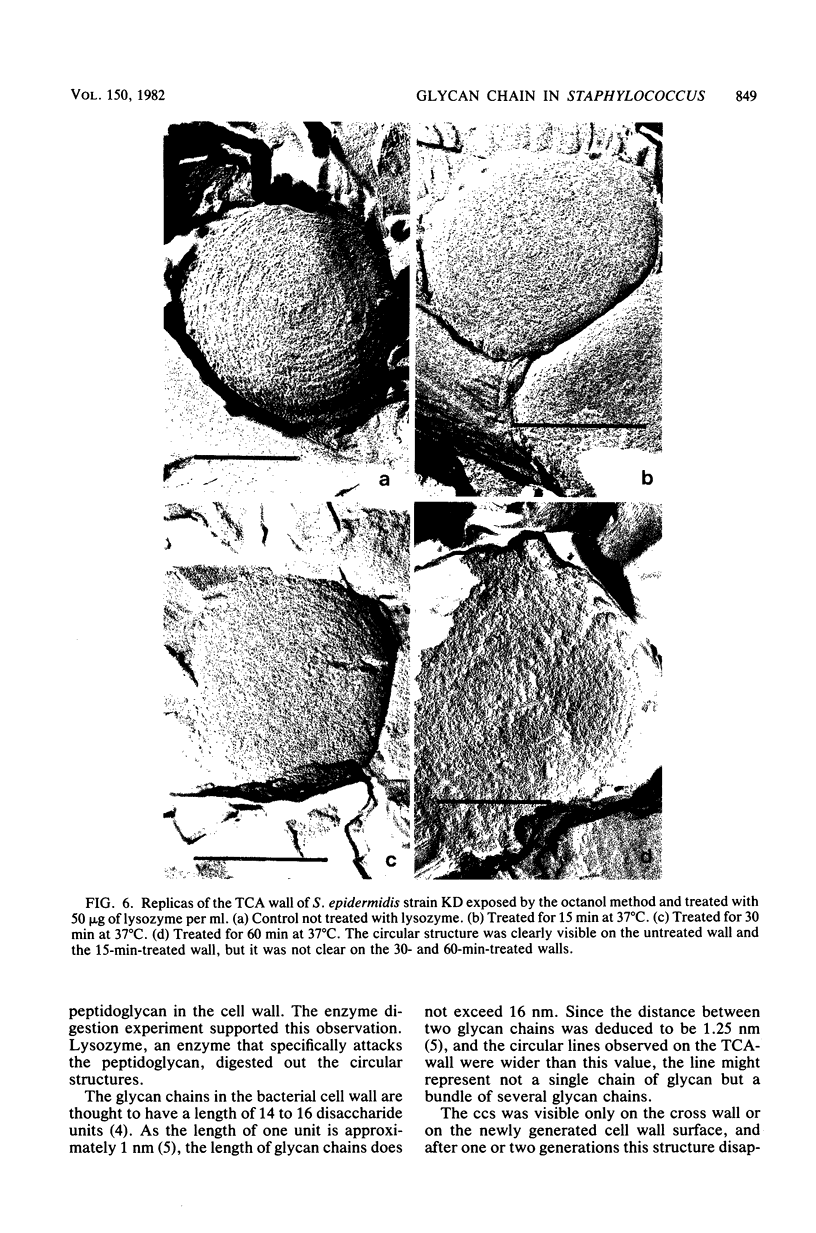
The arrangement of peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Staphylococcus was observed with the newly developed freeze-fracture technique, using n-octanol instead of water as the freezing medium. The replica of the trichloroacetic acid-extracted cell wall (TCA-wall) showed two areas. One of them has a concentric circular structure, a characteristic surface structure of the staphylococcal cell wall, and the other showed an irregular and rough surface. The chemical analysis of the wall revealed that the TCA-wall consisted of mostly peptidoglycan. By digesting the TCA-wall with lysozyme, the circular structures were greatly disturbed, and they disappeared after 60 min of treatment. From these observations it can be expected that the peptidoglycan is arranged in a concentric circular manner in the newly generated cell wall of Staphylococcus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Umeda A. Regular arrangement of wall polymers in staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):421–424. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Umeda A. Scanning electron microscopy of Staphylococcus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Jan;58(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)80005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Tarelli E., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The linkage between teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesbrecht P., Wecke J., Reinicke B. On the morphogenesis of the cell wall of staphylococci. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;44:225–318. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preusser H. J. Strukturveränderungen am "Murein-Sacculus" von Spirillum serpens nach Einwirkung von Uranylacetat. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969 Oct;68(2):150–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRI RAM J., TAWDE S. S., PIERCE G. B., Jr, MIDGLEY A. R., Jr Preparation of antibody-ferritin conjugates for immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:673–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda A., Ikebuchi T., Amako K. Localization of bacteriophage receptor, clumping factor, and protein A on the cell surface of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.838-844.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwer R. W., Nanninga N. Electron microscopy of isolated cell walls of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):195–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00425135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwer R. W., Nanninga N., Keck W., Schwarz U. Arrangement of glycan chains in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):723–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.723-729.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]