Abstract
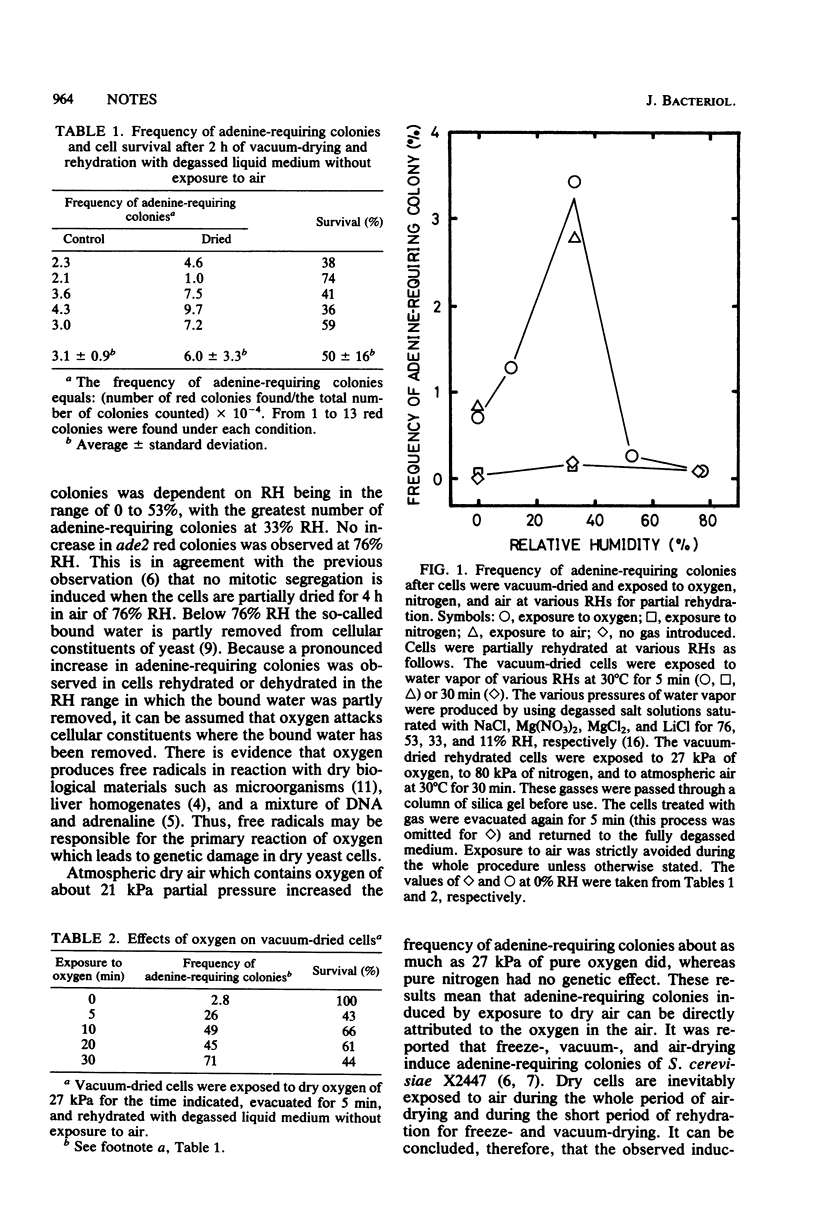
Cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae were dried in vacuum, exposed to oxygen, nitrogen, air, and water vapor, and rehydrated with degassed medium without exposure to air. Drying per se caused few genetic changes, but the exposure of dry cells to oxygen increased the frequency of adenine-requiring colonies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando Y., Fukada E. Effects of drying on deoxyribonucleic acids. J Radiat Res. 1974 Dec;15(4):212–218. doi: 10.1269/jrr.15.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asada S., Takano M., Shibasaki I. Deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks during drying of Escherichia coli on a hydorohobic filter membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):266–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.266-273.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwood-Smith M. J., Grant E. Mutation induction in bacteria by freeze-drying. Cryobiology. 1976 Apr;13(2):206–213. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(76)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckly R. J., Dimmick R. L. Correlations between free radical production and viability of lyophilized bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jul;16(7):1081–1085. doi: 10.1128/am.16.7.1081-1085.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckly R. J., Dimmick R. L. Electron paramagnetic resonance in frozen and dried biological materials. Nature. 1967 Dec 9;216(5119):1003–1004. doi: 10.1038/2161003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieda K. Induction of genetic changes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by partial drying in air of constant relative humidity and by UV. Mutat Res. 1981 Nov;84(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Echigo A., Nunomura K. Physical properties of cell water in partially dried Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biophys J. 1966 Sep;6(5):665–674. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86685-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LION M. B., BERGMANN E. D. The effect of oxygen on freeze-dried Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Feb;24:191–200. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LION M. B., KIRBY-SMITH J. S., RANDOLPH M. L. Electronspin resonance signals from lyophilized bacterial cells exposed to oxygen. Nature. 1961 Oct 7;192:34–36. doi: 10.1038/192034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servin-Massieu M. Effects of freeze-drying and sporulation on microbial variation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1971;54:119–150. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65123-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J. BOUND WATER, METABOLITES AND GENETIC CONTINUITY. Nature. 1964 Jul 25;203:374–377. doi: 10.1038/203374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamenhof S., Eichhorn H. H., Rosenbaum-Oliver D. Mutability of stored spores of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1968 Nov 23;220(5169):818–819. doi: 10.1038/220818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



