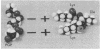Abstract
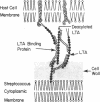
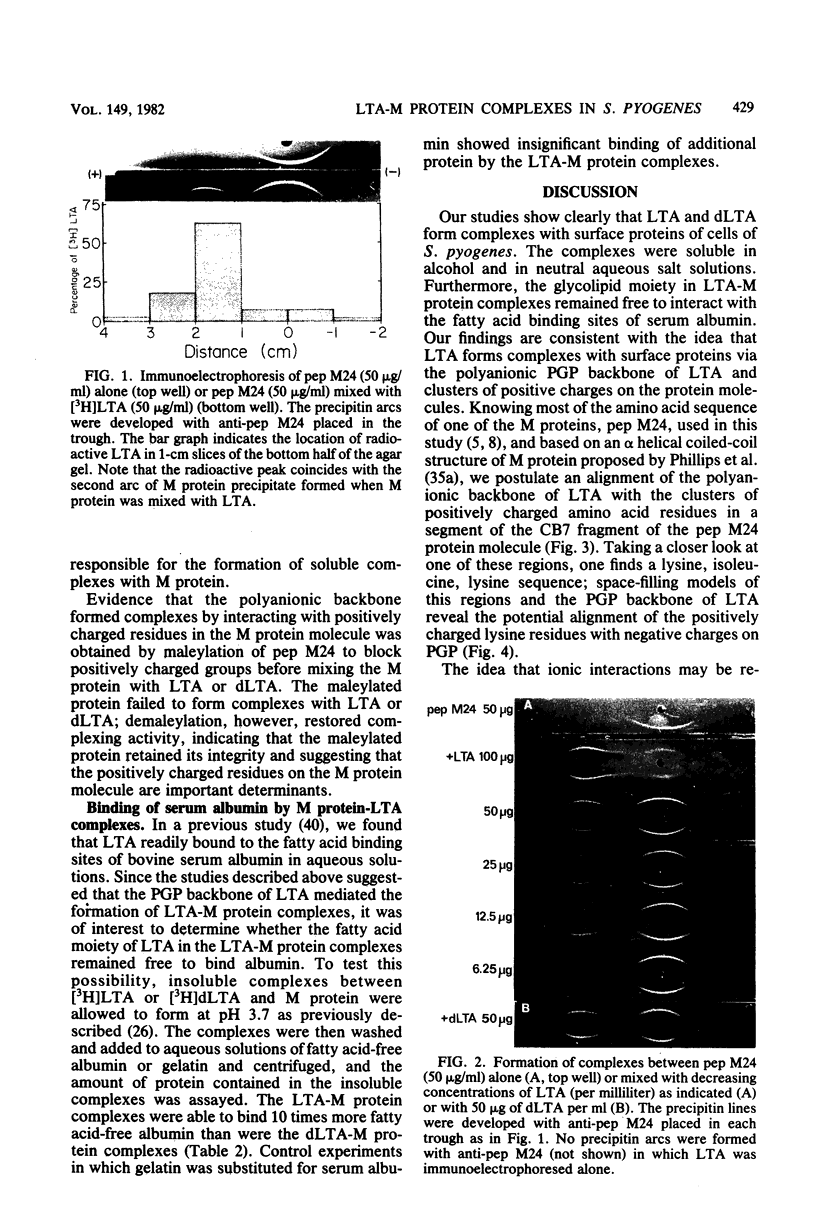
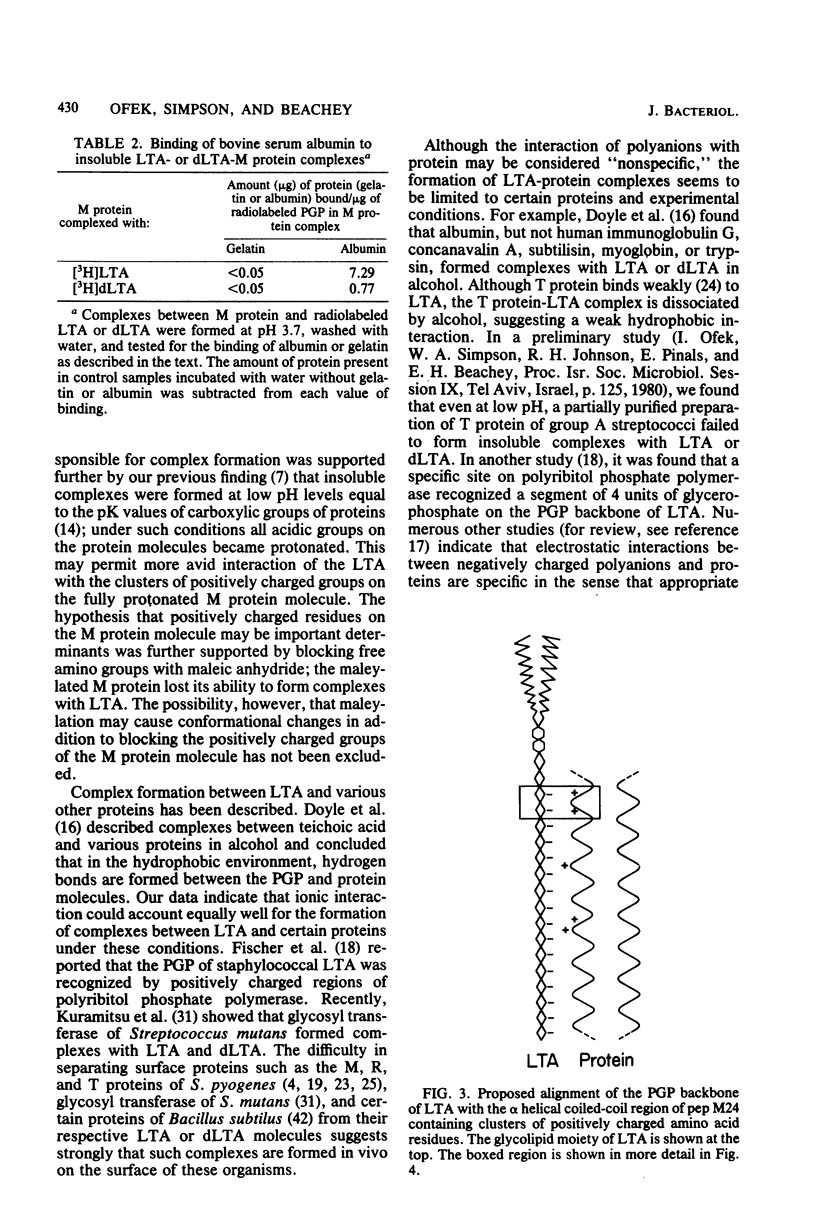
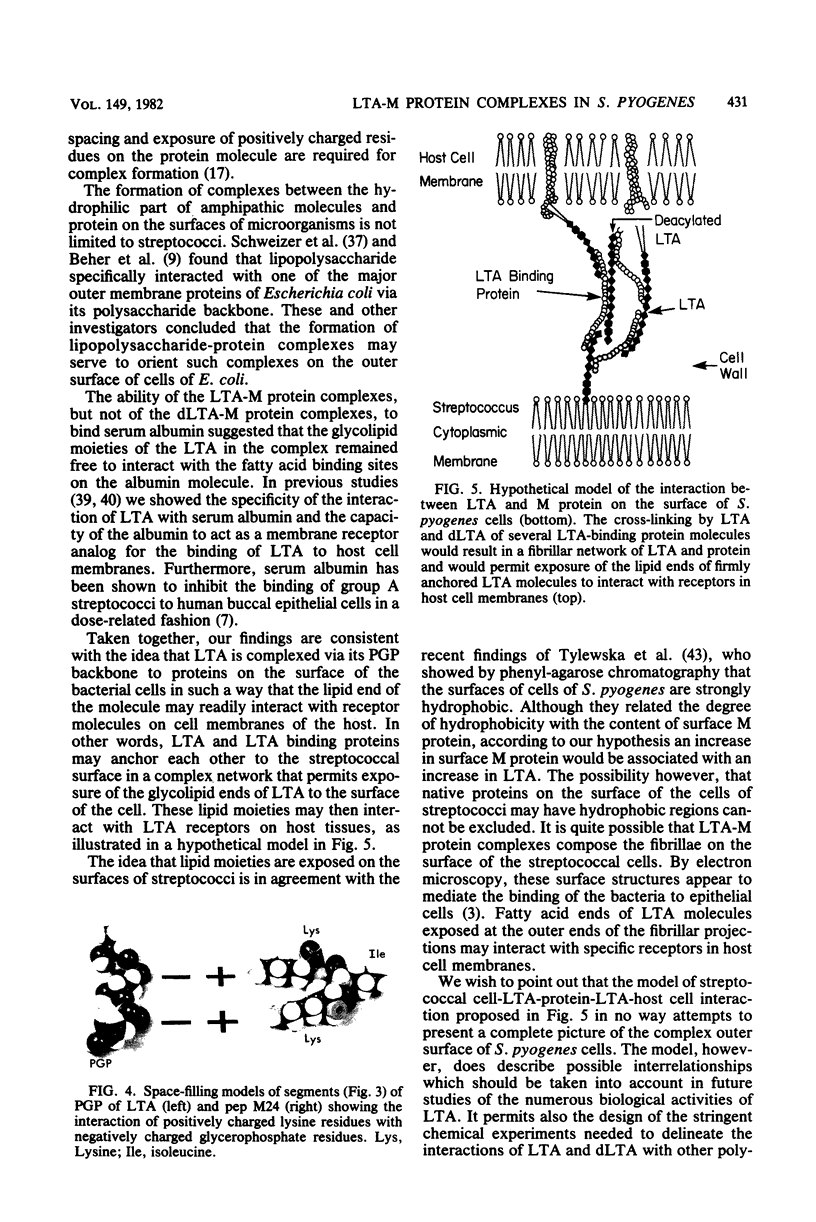
The orientation of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) molecules on the surface of bacterial cells undoubtedly is determined by the ability of the LTA, during its transit through the cell wall, to bind via its polyglycerophosphate backbone or its glycolipid moieties to other constituents of the cytoplasmic membrane and the cell wall. We have investigated the possibility that LTA may become anchored to the cell surface by binding through its polyanionic backbone to positively charged regions of cell wall proteins. LTA was found to prevent the precipitation of partially purified HCl extracts of several strains of streptococci as well as a structurally defined streptococcal M protein molecule (pep M24) in 83% solutions of ethanol. The formation of complexes between LTA and M protein was demonstrated further by immunoelectrophoresis of pep M24 protein with increasing concentrations of radiolabeled LTA and by using antiserum against pep M24 to develop precipitin arcs. Pep M24 electrophoresed alone produced a single precipitin arc close to the origin. In contrast, when electrophoresed as a mixture with LTA or deacylated LTA, the M protein produced a second precipitin arc toward the anode coinciding with the area of migration of the radioactive LTA. Increasing concentrations of LTA or deacylated LTA shifted increasing amounts of the pep M24 antigen to the region of the second arc. Maleylation of M protein to block the positively charged free amino groups before mixing it with LTA prevented the formation of complexes. The complexes formed by the M protein with LTA, but not with deacylated LTA, showed the capacity to bind bovine serum albumin; LTA had been shown previously to bind to the fatty acid binding sites on bovine serum albumin. These results indicate that the LTA molecule is able to bind via its polyanionic backbone to positively charged residues of surface proteins of cells of S. pyogenes. The implications of such interaction as to the orientation of LTA molecules on the surface of cells of S. pyogenes are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkan M. L., Beachey E. H. Excretion of lipoteichoic acid by group A streptococci. Influence of penicillin on excretion and loss of ability to adhere to human oral mucosal cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):671–677. doi: 10.1172/JCI108979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Binding of group A streptococci to human oral mucosal cells by lipoteichoic acid. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975;88:285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I., Bismo A. L. Studies of antibodies to non-type-specific antigens associated with streptococcal M protein in the sera of patients with rheumatic fever. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1361–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Primary structure of protective antigens of type 24 streptococcal M protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6284–6289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Repeating covalent structure of streptococcal M protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3163–3167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H., Chiang E. Y., Chiang T. M., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Purification and properties of M protein extracted from group A streptococci with pepsin: covalent structure of the amino terminal region of type 24 M antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1469–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beher M., Pugsley A., Schnaitman C. Correlation between the expression of an Escherichia coli cell surface protein and the ability of the protein to bind to lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):403–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.403-410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Emdur L. I., Platt D. Lipoteichoic acids from Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):471–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.471-479.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M., Beachey E. H. Immunochemical properties of streptococcal M protein purified by isoelectric focusing. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1002–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Chatterjee A. N., Streips U. N., Young F. E. Soluble macromolecular complexes involving bacterial teichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.341-347.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Interactions of polynucleotides and other polyelectrolytes with enzymes and other proteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;40(0):29–64. doi: 10.1002/9780470122853.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Schlecht S. Molecular organization of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):609–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Release of lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus sanguis: stimulation of release during penicillin treatment. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1180–1184. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1180-1184.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N. A., Hardy L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by Streptococcus mutans BHT. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.75-84.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Beachey E. H. Purification and immunobiological properties of R antigen and its relation to M protein of type 3 group A Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1051–1059. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1051-1059.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Simpson W. A., Dale J. B., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Lipoteichoic acid-binding and biological properties of T protein of group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):791–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.791-798.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Vosti K. L. Purification and characterization of group A streptococcal T-1 antigen. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.867-875.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H. Studies on the location of intermolecular cross-links in collagen. Isolation of a CNBr peptide containing -hydroxylysinonorleucine. Biochemistry. 1972 May 9;11(10):1828–1835. doi: 10.1021/bi00760a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Shockman G. D. Precursor-product relationship of intracellular and extracellular lipoteichoic acids of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.869-877.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., van de Rijn I., McCarty M. Characterization and localization of the enzymatic deacylation of lipoteichoic acid in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1498–1509. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Wondrack L., McGuinness M. Interaction of Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases with teichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):376–382. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.376-382.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwerys R. R. Colorimetric determination of free fatty acids. Anal Biochem. 1969 Nov;32(2):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Flicker P. F., Cohen C., Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: alpha-helical coiled-coil structure and arrangement on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer M., Hindennach I., Garten W., Henning U. Major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Interaction of protein II with lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Kessler R., Corentt J. B., Mychajlonka M. Turnover and excretion of streptococcal surface components. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:803–814. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to the fatty acid binding sites on serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6092–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Fatty acid binding sites of serum albumin as membrane receptor analogs for streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):119–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.119-122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabyj B. M., Panos C. Membrane lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus pyogenes and its stabilized L-form and the effect of two antibiotics upon its cellular content. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):855–862. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.855-862.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel D., Wicken A. J., Dickson M. R., Knox K. W. Cellular location of the lipoteichoic acids of Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991 and Lactobacillus casei NCTC 6375. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Jun;43(5):483–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]