Abstract
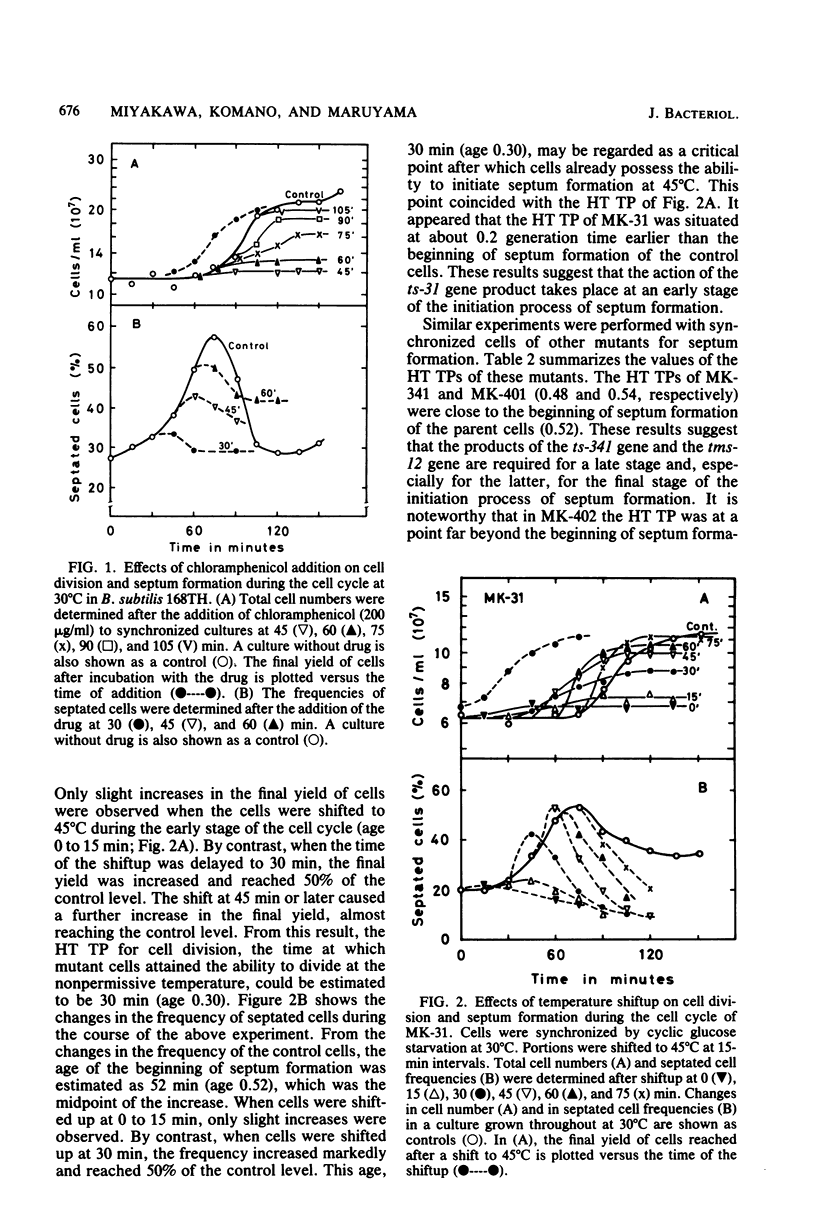
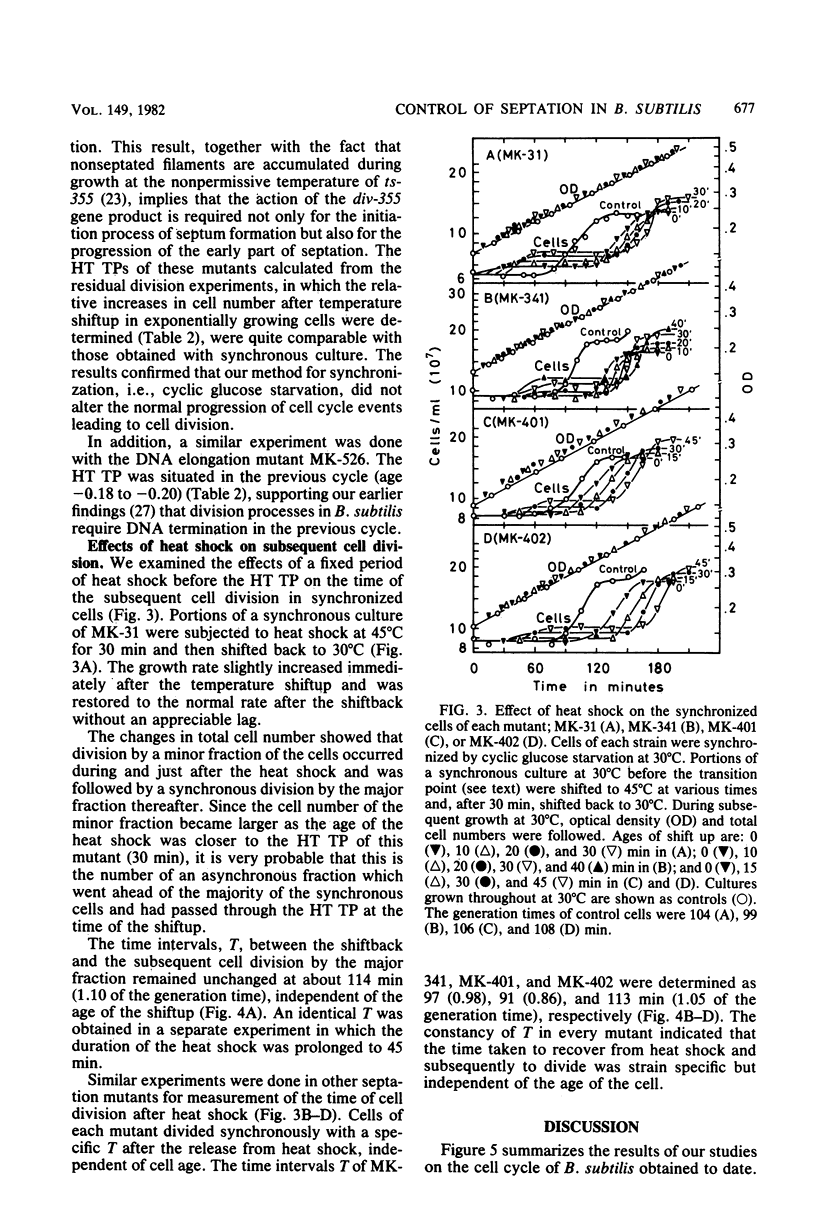
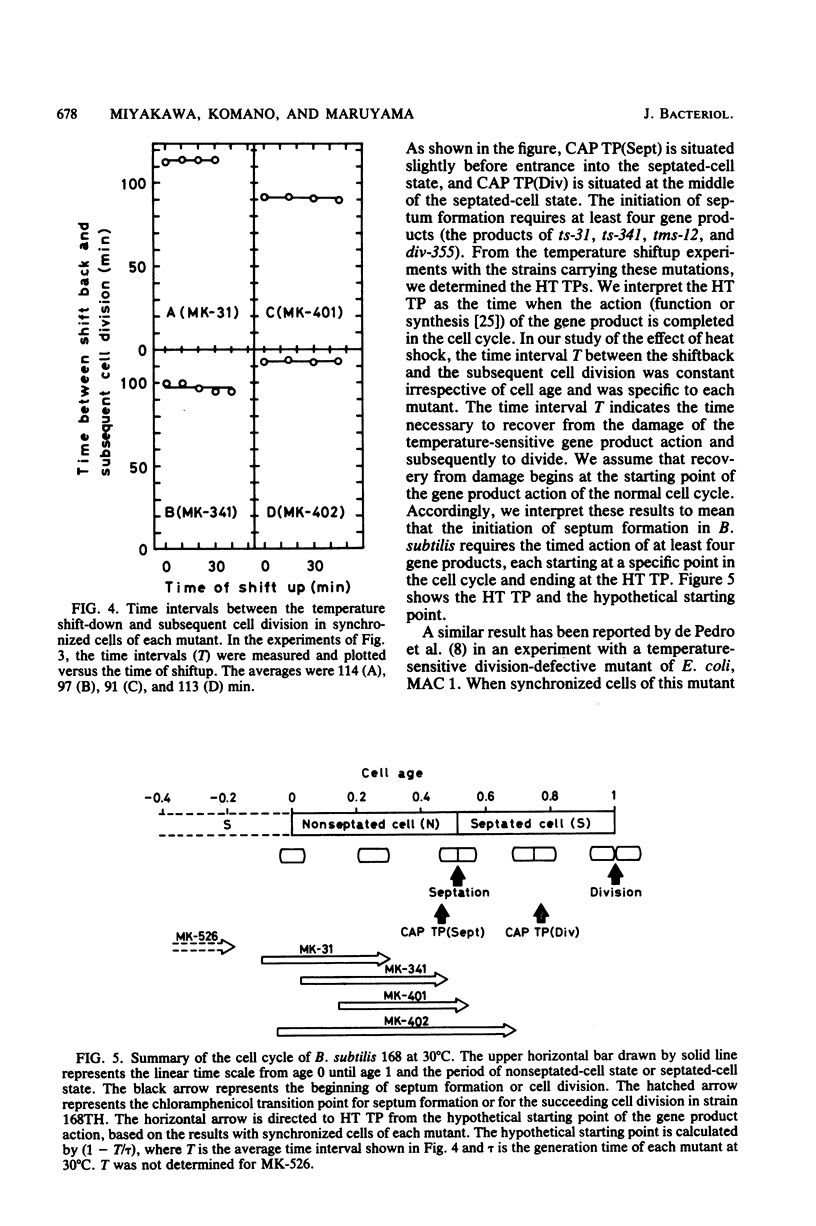
Four isogenic strains of temperature-sensitive septationless mutants, whose mutations are located on different genes, were used to study the periods of action of the gene products required for the initiation of septum formation during the cell cycle of Bacillus subtilis. The shift-up experiments, in which portions of a synchronous culture of each mutant were transferred to the nonpermissive temperature, showed that the transition point, at which cells attained the ability to divide at the nonpermissive temperature in the cell cycle, was strain specific. Furthermore, the heat shock experiments, in which portions of a synchronous culture were subjected to the nonpermissive temperature before the transition point for a fixed period and shifted back to the permissive temperature, showed that the time interval between the shift-back and the subsequent cell division was specific to each strain but was independent of the age of heat shock. These results led us to the idea that the initiation of septum formation in B. subtilis requires the timed action of the four gene products, each of which functions at a specific stage in the cell cycle. In addition, the result with DNA elongation mutant MK-526, which is also septation defective, supported our previous findings that the initiation of septum formation requires the termination of DNA replication in the previous cell cycle.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed N., Rowbury R. J. Temperature-sensitive cell division component in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jul;67(1):107–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-67-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. S., Filip C. C., Gustafson R. A., Allen R. G., Walker J. R. Regulation of bacterial cell division: genetic and phenotypic analysis of temperature-sensitive, multinucleate, filament-forming mutants of Escherichia. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):978–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.978-986.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breakefield X. O., Landman O. E. Temperature-sensitive divisionless mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in the initiation of septation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):985–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.985-998.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister H., Wake R. G. Characterization and mapping of temperature-sensitive division initiation mutations of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1042–1051. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1042-1051.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla Z., Bagdasarian M., Szczurkiewicz W., Przygońska M., Klopotowski T. Defective cell division in thermosensitive mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):107–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00582221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C., Marmur J. Identification of conserved genetic functions in Bacillus by use of temperature-sensitive mutants. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):302–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Begg K. J., Lutkenhaus J. F., Salmond G. P., Martinez-Salas E., Vincente M. Role of the ftsA gene product in control of Escherichia coli cell division. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.388-394.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckman B. E. Structural difference between walls from hemispherical caps and partial septa of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.790-797.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher G., Irwin C. A., Henson J. M., Fillingim C., Malone M. M., Walker J. R. Identification of the Escherichia coli cell division gene sep and organization of the cell division-cell envelope genes in the sep-mur-ftsA-envA cluster as determined with specialized transducing lambda bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):91–100. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.91-100.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita H., Komano T., Maruyama Y. Dynamic aspects of membrane-bound DNA in Bacillus subtilis during the course of synchronous growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1361–1367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90651-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Ryter A., Jacob F. Thermosensitive mutants of E. coli affected in the processes of DNA synthesis and cellular division. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:677–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Messer W., Schwarz U. Regulation of polar cap formation in the life cycle of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe W. E., Mount D. W. Analysis of cell division in single clones of the Escherichia coli K-12 lexA mutant. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1278–1281. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1278-1281.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. Pleiotropic effect of the rec A gene of Escherichia coli: uncoupling of cell division from deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):539–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.539-542.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Donachie W. D. Chromosome replication, transcription and control of cell division in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F., Donachie W. D. Identification of the ftsA gene product. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1088–1094. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1088-1094.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson N. H., Cole R. M. Genetic regulation of cell division initiation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.994-1003.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa J., Schierenberg E., Miwa S., von Ehrenstein G. Genetics and mode of expression of temperature-sensitive mutations arresting embryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1980 Apr;76(1):160–174. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Komano T., Maruyama Y. Cell-cycle-specific inhibition by chloramphenicol of septum fromation and cell division in synchronized cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.502-507.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Tamura G. Mutant of Escherichia coli with thermosensitive protein in the process of cellular division. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):959–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.959-966.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanninga N., Koppes L. J., de Vries-Tijssen F. C. The cell cycle of Bacillus subtilis as studied by electron microscopy. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Nov;123(2):173–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00446817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Takeda Y., Nishimura A., Suzuki H., Inouye M., Hirota Y. Synthetic ColE1 plasmids carrying genes for cell division in Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulton R. J. Analysis of the multiseptate potential of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):762–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.762-767.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Groves D. J., Clark D. J. Regulation of Cell Division in Escherichia coli: Characterization of Temperature-Sensitive Division Mutants. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1052–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1052-1064.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Control of cell length in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):7–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.7-19.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M., Schaechter M. Control of cell division in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):199–221. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.199-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. S., Helmstetter C. E. Coordination between chromosome replication and cell division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1148–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1148-1156.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Martínez-Salas E., Vicente M. Involvement of the ftsA gene product in late stages of the Escherichia coli cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):806–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.806-813.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alstyne D., Simon M. I. Division mutants of Bacillus subtilis: isolation and PBS1 transduction of division-specific markers. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1366–1379. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1366-1379.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. R., Kovarik A., Allen J. S., Gustafson R. A. Regulation of bacterial cell division: temperature-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli that are defective in septum formation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):693–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.693-703.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R., Inouye M., Pardee A. B. Cell division in Escherichia coli: evidence for regulation of septation by effector molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro M. A., Llamas J. E., Cánovas J. L. A timing control of cell division in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):307–314. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



