Abstract
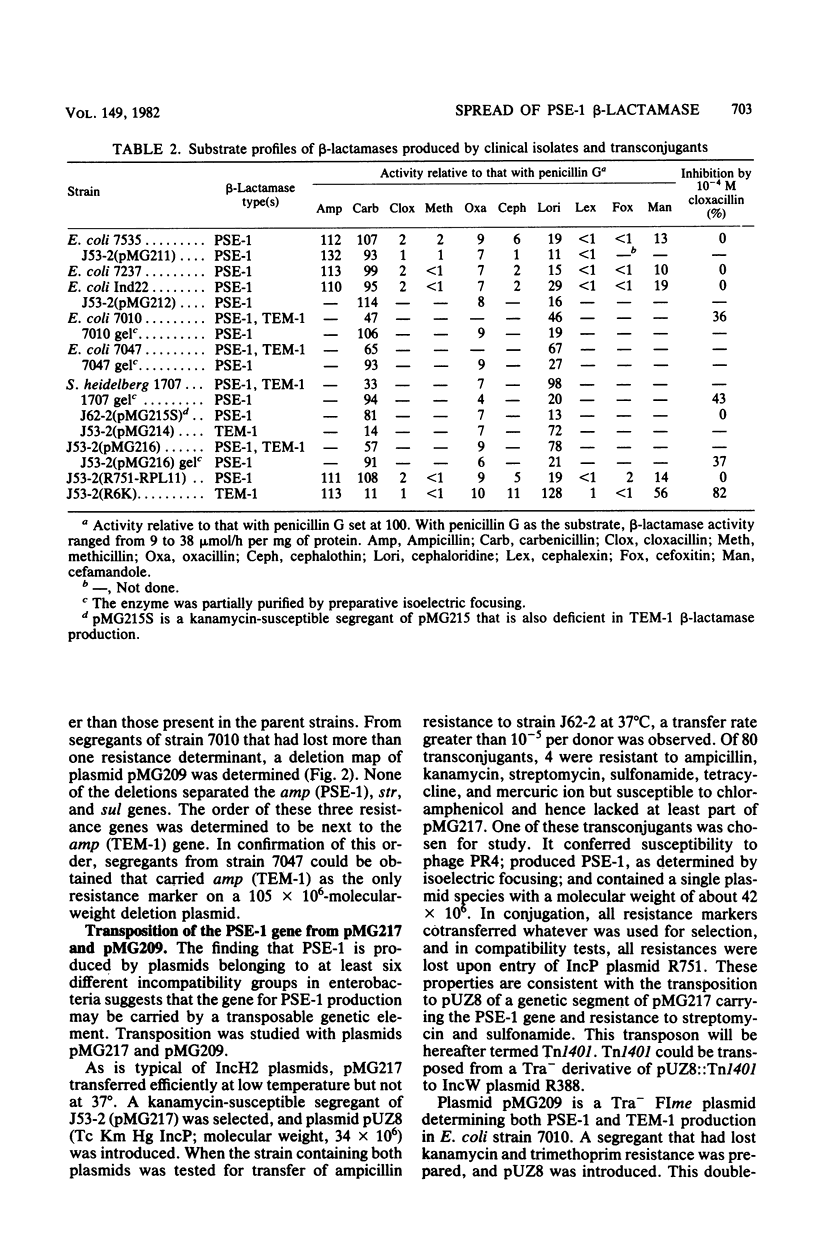
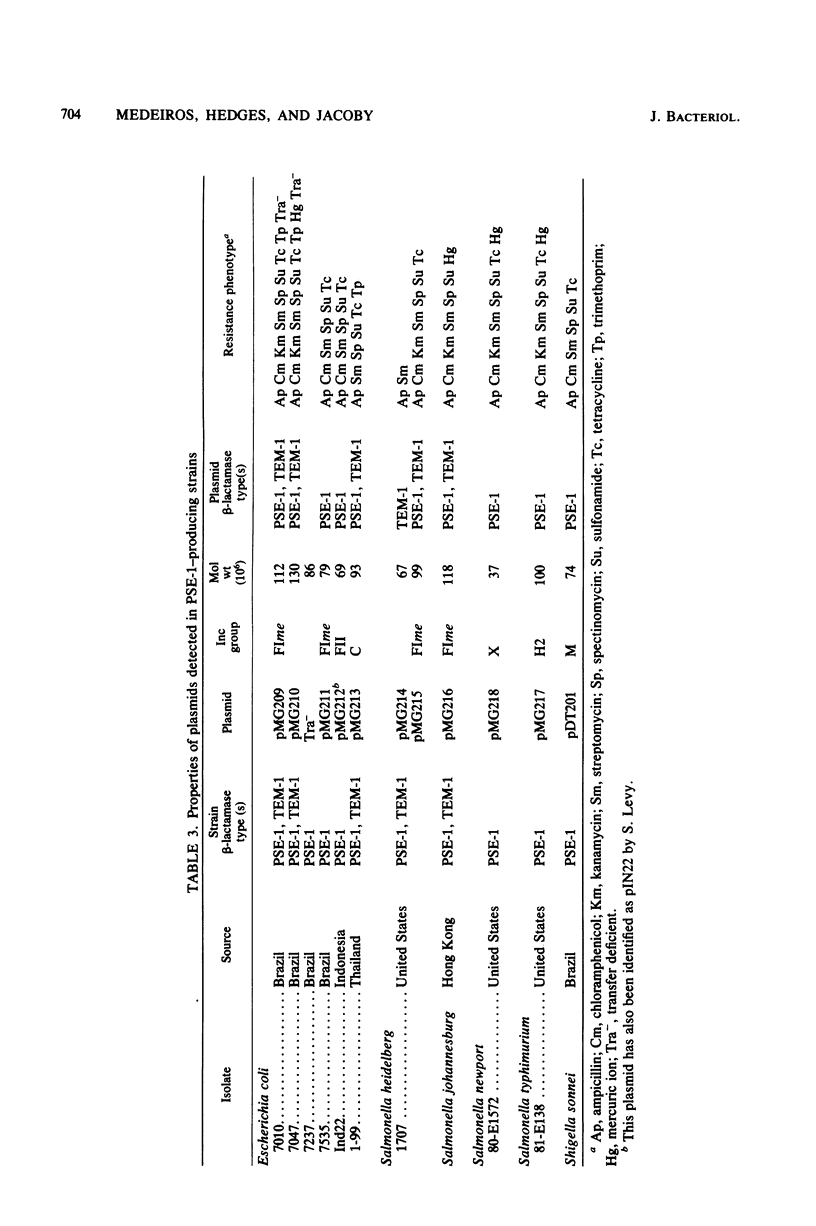
Eleven isolates including Escherichia coli, Salmonella enteritidis, and Shigella sonnei, obtained in Brazil, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Thailand, and the United States, were found to produce beta-lactamase of the PSE-1 type, which was previously considered to be Pseudomonas specific. The enterobacterial strains produced a beta-lactamase with the same isoelectric point, immunological reactions, and substrate profile as those of the prototype PSE-1 enzyme determined by Pseudomonas plasmid RPL11. The producer strains were resistant to multiple antibiotics, and all contained plasmids, ranging in size from 37 x 10(6) to 130 x 10(6), that belonged to at last six incompatibility groups. Plasmids of IncH2 and IncFIme were shown to contain 8 x 10(6)-molecular-weight transposons Tn1401 and Tn1402 that encoded PSE-1 beta-lactamase production, resistance to streptomycin and spectinomycin via AAD(3"), and resistance to sulfonamide. PSE-1 beta-lactamase was not Pseudomonas specific and appeared to have spread among plasmids found in enterobacteria by transposition.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthelemy M., Guionie M., Labia R. Beta-lactamases: determination of their isoelectric points. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):695–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Datta N., Hedges R. W. R factors from Proteus rettgeri. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):543–552. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Trimethoprim resistance conferred by W plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hughes V. M., Nugent M. E., Richards H. Plasmids and transposons and their stability and mutability in bacteria isolated during an outbreak of hospital infection. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):182–196. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Smith D. I. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:469–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Matthew M. Acquisition by Escherichia coli of plasmid-borne beta-lactamases normally confined to Pseudomonas spp. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., ADELBERG E. A. Transfert de caractéres génétiques par incorporation au facteur sexuel d'Escherichia coli. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Jul 6;249(1):189–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Recombination between plasmids of incompatibility groups P-1 and P-2. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1278-1285.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Matthew M. The distribution of beta-lactamase genes on plasmids found in Pseudomonas. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A. Properties of R plasmids determining gentamicin resistance by acetylation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):239–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Datta N. Trimethoprim R factors in enterobacteria from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontomichalou P., Mitani M., Clowes R. C. Circular R-factor molecules controlling penicillinase synthesis, replicating in Escherichia coli under either relaxed or stringent control. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):34–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.34-44.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Brevet J., Cohen S. N. Involvement of multiple translocating DNA segments and recombinational hotspots in the structural evolution of bacterial plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):333–360. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfhagen T. R., Loper J. C. RPL11, an R factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa determining carbenicillin and gentamicin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):69–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases of Gram-negative bacteria: properties and distribution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):349–358. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Sykes R. B. Properties of the beta-lactamase specified by the Pseudomonas plasmid RPL11. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):341–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.341-345.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Tai M., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of a penicillinase from Escherichia coli carrying Rms 298. Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Oct 20;21(10):545–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Yaginuma S., Tai M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Plasmid-mediated penicillin beta-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E., Van Den Elizen H. M. Further properties of P-2 R-factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their relationship to other plasmid groups. Can J Microbiol. 1975 May;21(5):592–605. doi: 10.1139/m75-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. N., Harper P. B., O'Callaghan C. H. Principal beta-lactamases responsible for resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):929–936. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A. The properties and host range of male-specific bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):332–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Keystone J. S., Devlin H. R. Resistance to trimethoprim and other antibiotics in Ontario shigellae. Lancet. 1980 Feb 23;1(8165):426–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tanaka M., Nohara C., Fukunaga Y., Yamagishi S. Transposition of the oxacillin-hydrolyzing penicillinase gene. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.808-813.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]