Abstract
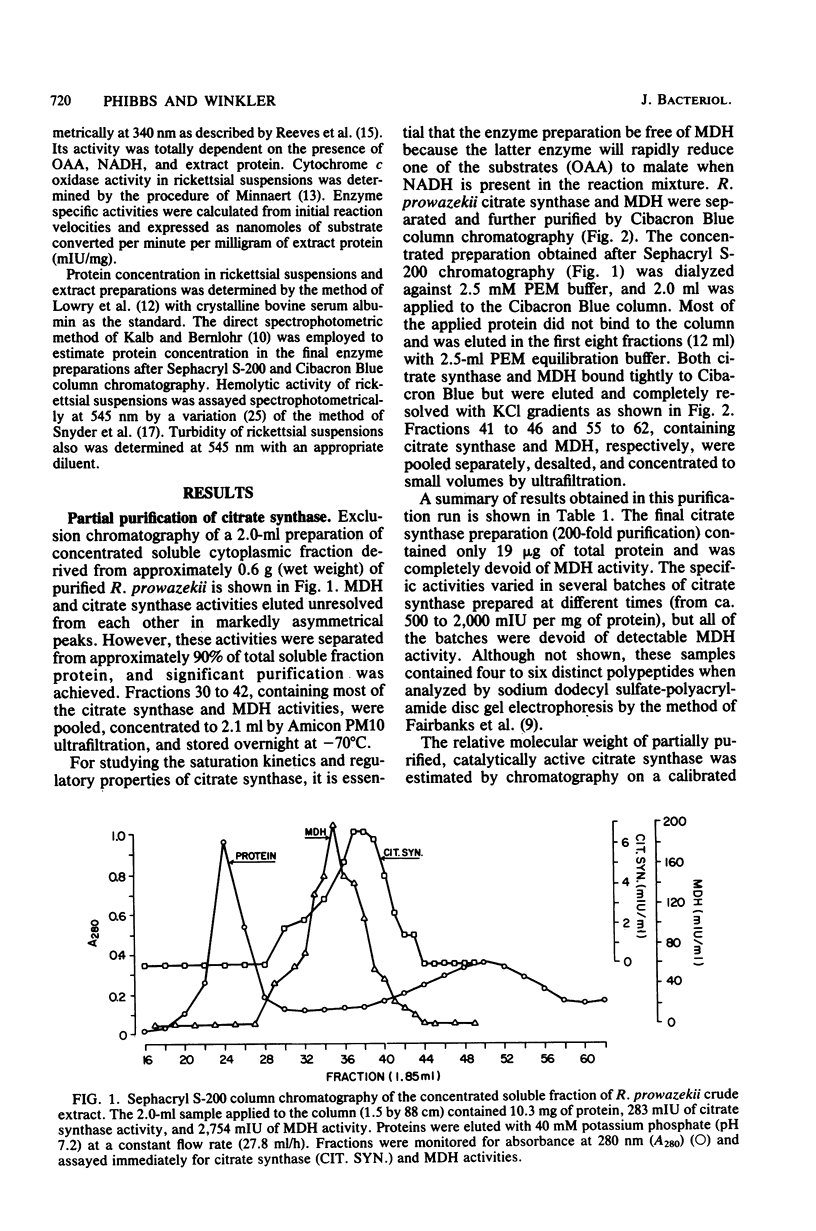
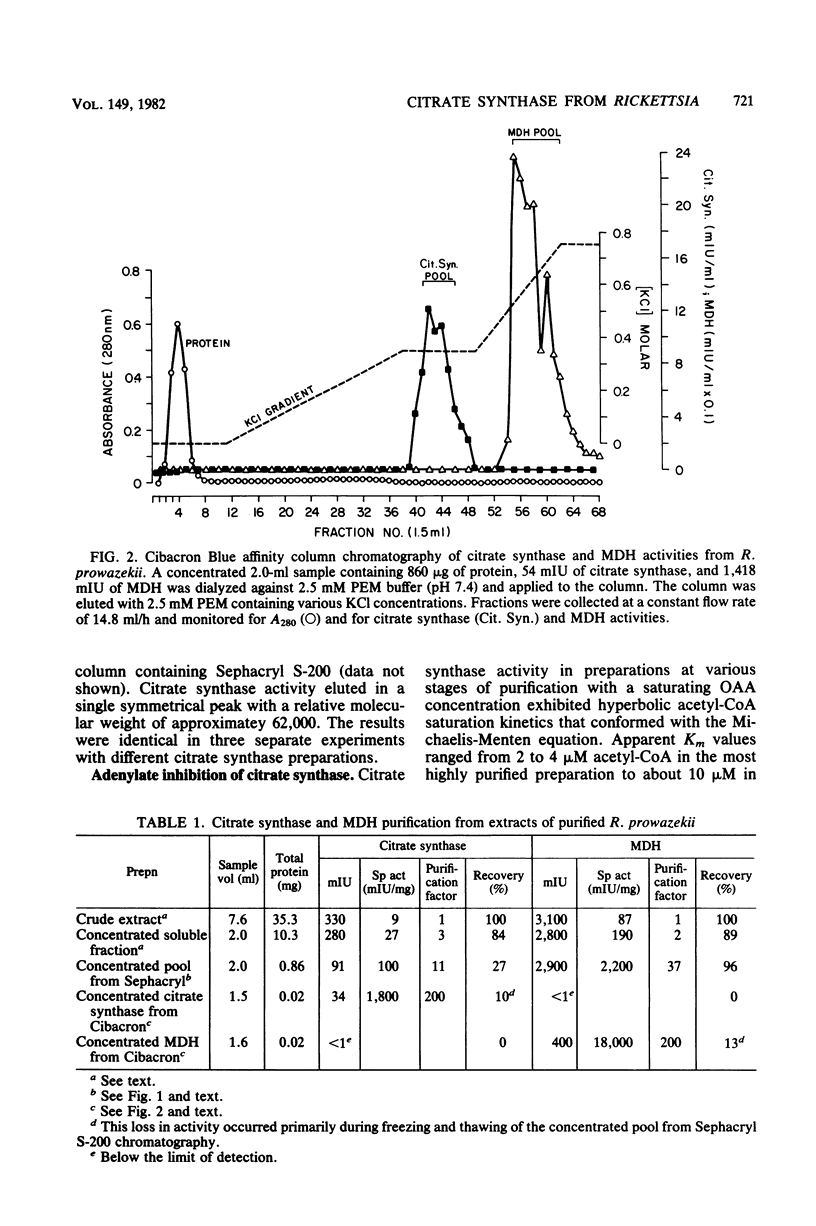
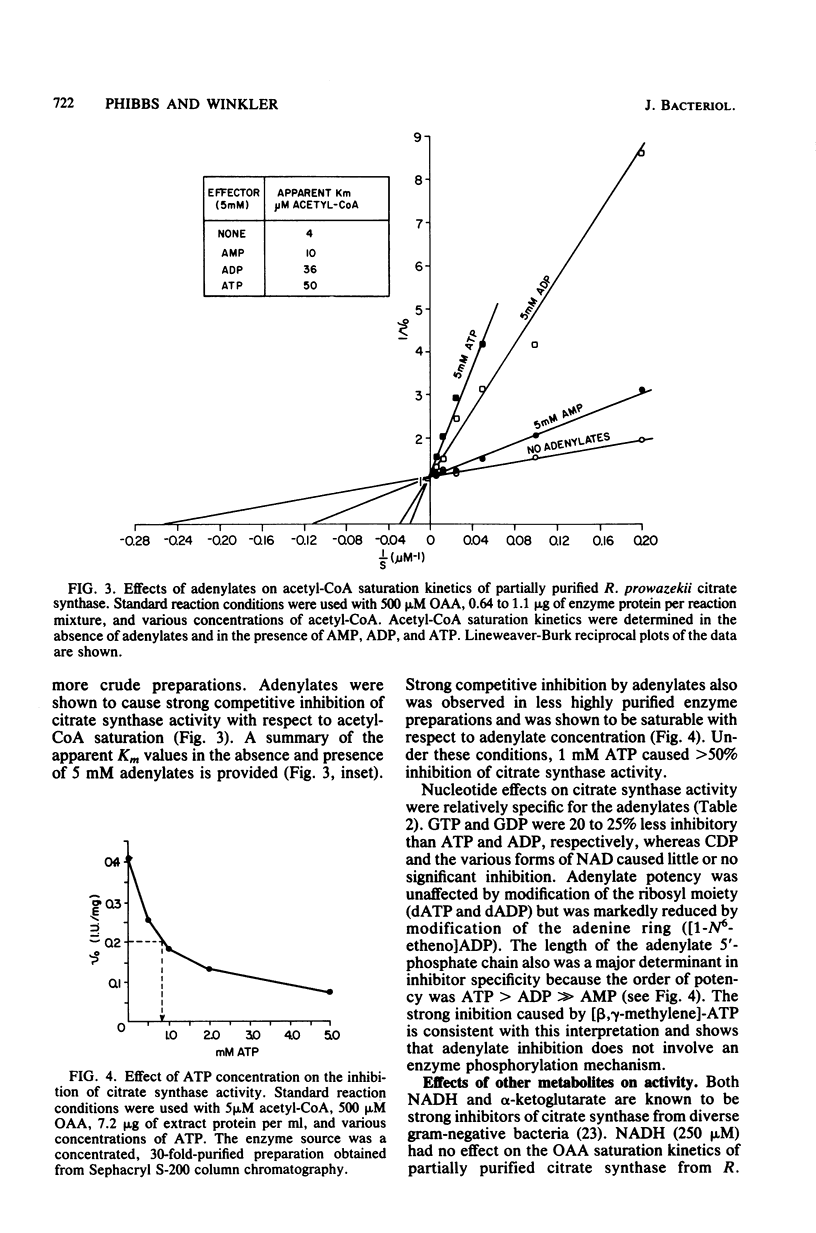
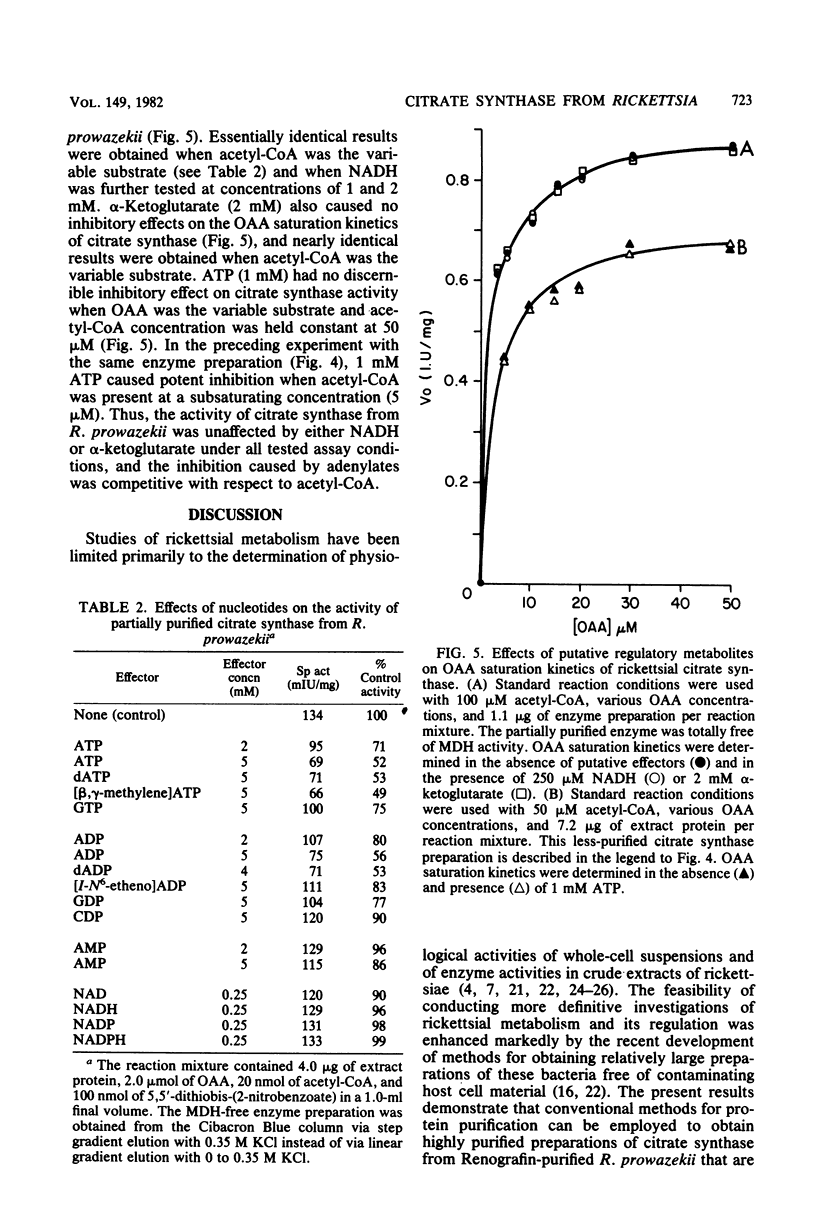
Citrate synthase [citrate (si)-synthase] (EC 4.1.3.7) was partially purified from extracts of highly purified typhus rickettsiae (Rickettsia prowazekii). Molecular exclusion and affinity column chromatography were used to prepare 200-fold-purified citrate synthase that contained no detectable malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) activity. Rickettsial malate dehydrogenase also was partially purified (200-fold) via this purification procedure. Catalytically active citrate synthase exhibited a relative molecular weight of approximately 62,000 after elution from a calibrated Sephacryl S-200 column. Acetyl coenzyme A saturation of partially purified enzyme was sensitive to strong competitive inhibition with adenylates (ATP greater than ADP much greater than AMP). [beta,gamma-methylene]ATP, dATP, and dADP also caused strong inhibition, but guanosine and cytosine nucleotides were significantly less inhibitory. Adenylates had no effect on oxalacetate saturation kinetics when acetyl coenzyme A was present in high concentration (greater than or equal to 50 microM). Neither NADH nor alpha-ketoglutarate affected the saturation kinetics of rickettsial citrate synthase. Thus, citrate synthase from R. prowazekii exhibits greater similarity to the eucaryotic and gram-positive procaryotic enzymes than to citrate synthase from free-living gram-negative bacteria. These results represent the first characterization of a highly purified key regulatory enzyme from these obligate intracellular parasitic bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Pickens E. G., Lackman D. B. Details of the ultrastructure of Rickettsia prowazekii grown in the chick yolk sac. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):260–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.260-262.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., ALLEN E. G. Reversible inactivation of the toxicity and hemolytic activity of typhus rickettsiae by starvation. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):637–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.637-645.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R. Phosphorylation accompanying the oxidation of glutamate by the Madrid E strain of typhus rickettsiae. J Biol Chem. 1956 May;220(1):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton L. P., Burgdorfer W. Fine structure of Rickettsia canada in tissues of Dermacentor andersoni Stiles. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1149-1159.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coolbaugh J. C., Progar J. J., Weiss E. Enzymatic activities of cell-free extracts of Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):298–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.298-305.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Harford S., Weitzman P. D. Studies on a mutant form of Escherichia coli citrate synthase desensitised to allosteric effectors. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):515–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MINNAERT K. The kinetics of cytochrome c oxidase. I. The system: cytochrome c-cytochrome oxidase-oxygen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 10;50:23–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER J. C., BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., CHANG R. S. M. Observations on the hemolytic properties of typhus rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.724-730.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Separation of inner and outer membranes of Rickettsia prowazeki and characterization of their polypeptide compositions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):963–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.963-971.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stork E., Wisseman C. L., Jr Growth of Rickettsia prowazeki in enucleated cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1743–1748. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1743-1748.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, HAHN F. E., JACKSON E. B., BOZEMAN M. F., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. II. Studies on the pathway of glutamate oxidation by purified suspensions of Rickettsia mooseri. J Immunol. 1952 Mar;68(3):251–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Growth and physiology of rickettsiae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):259–283. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.259-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman P. D., Danson M. J. Citrate synthase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:161–204. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Weiss E. Energy metabolism of Rickettsia typhi: pools of adenine nucleotides and energy charge in the presence and absence of glutamate. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.884-892.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



