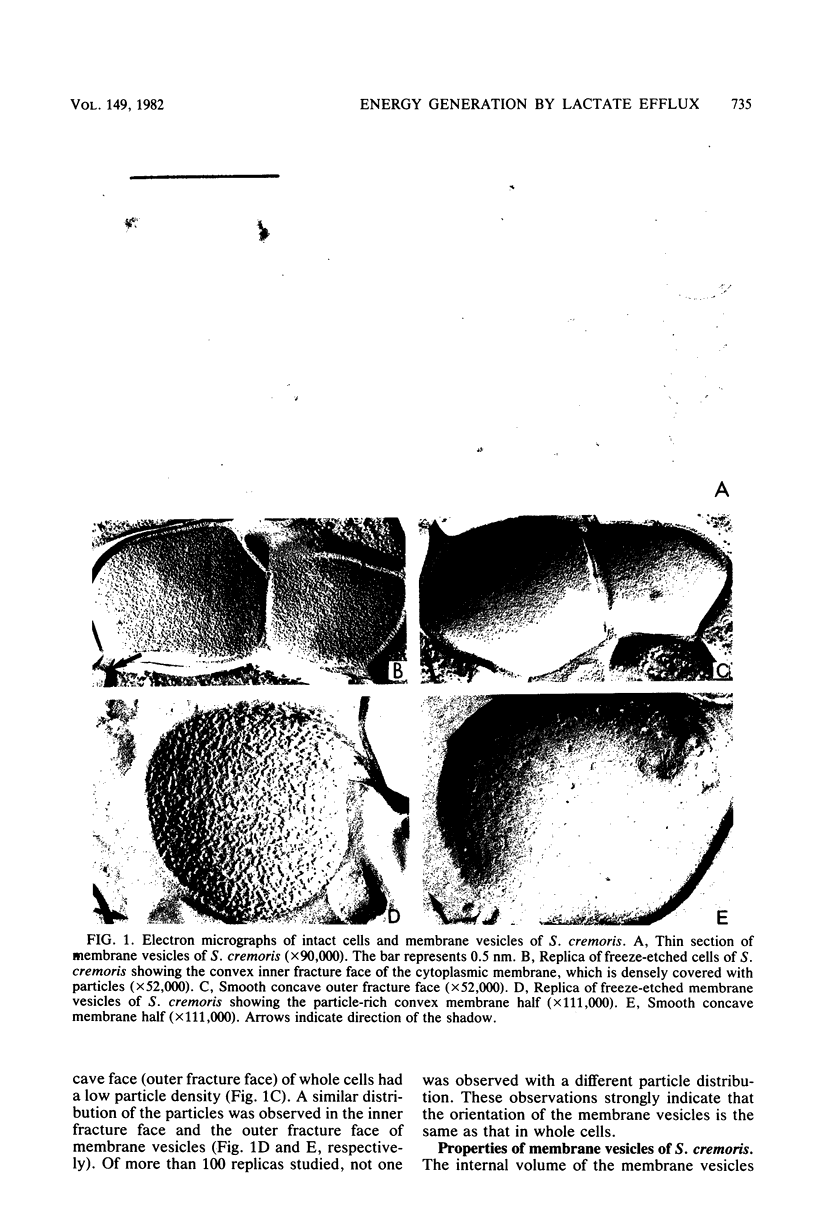
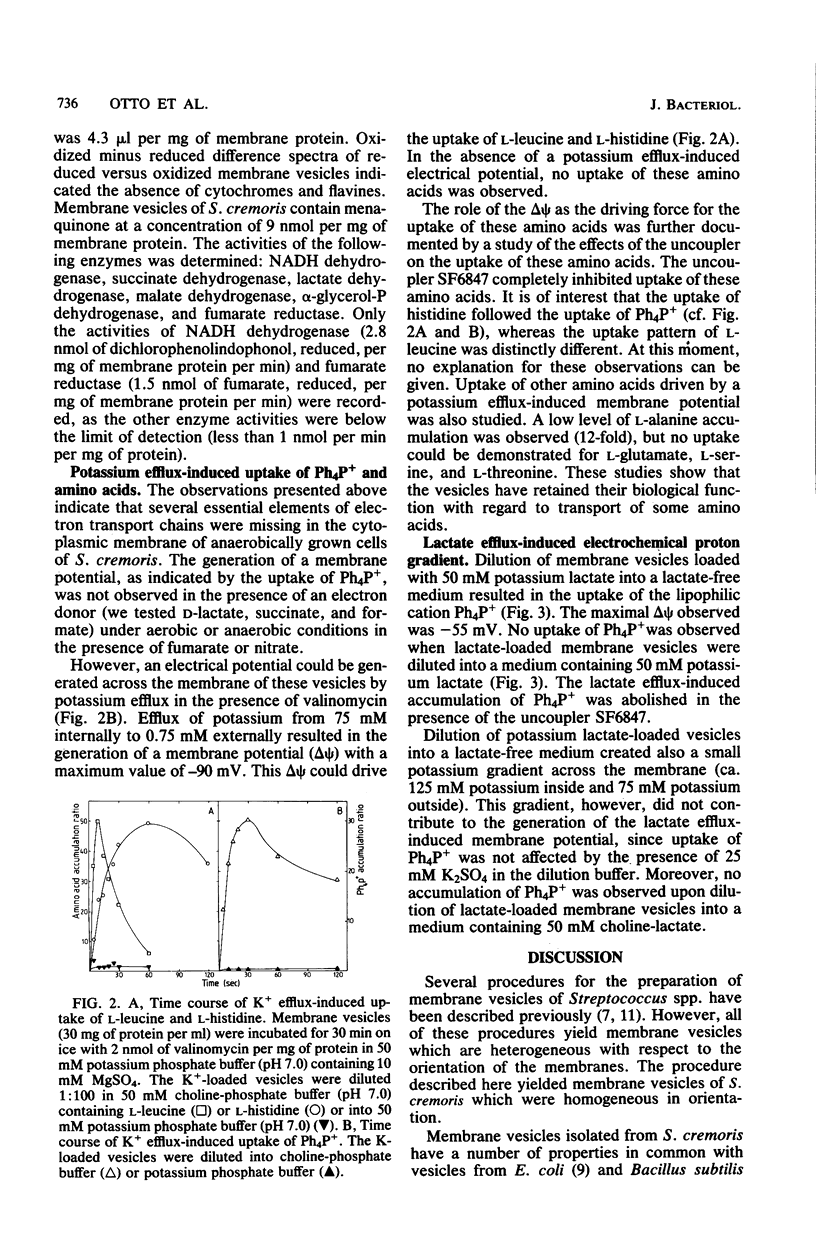
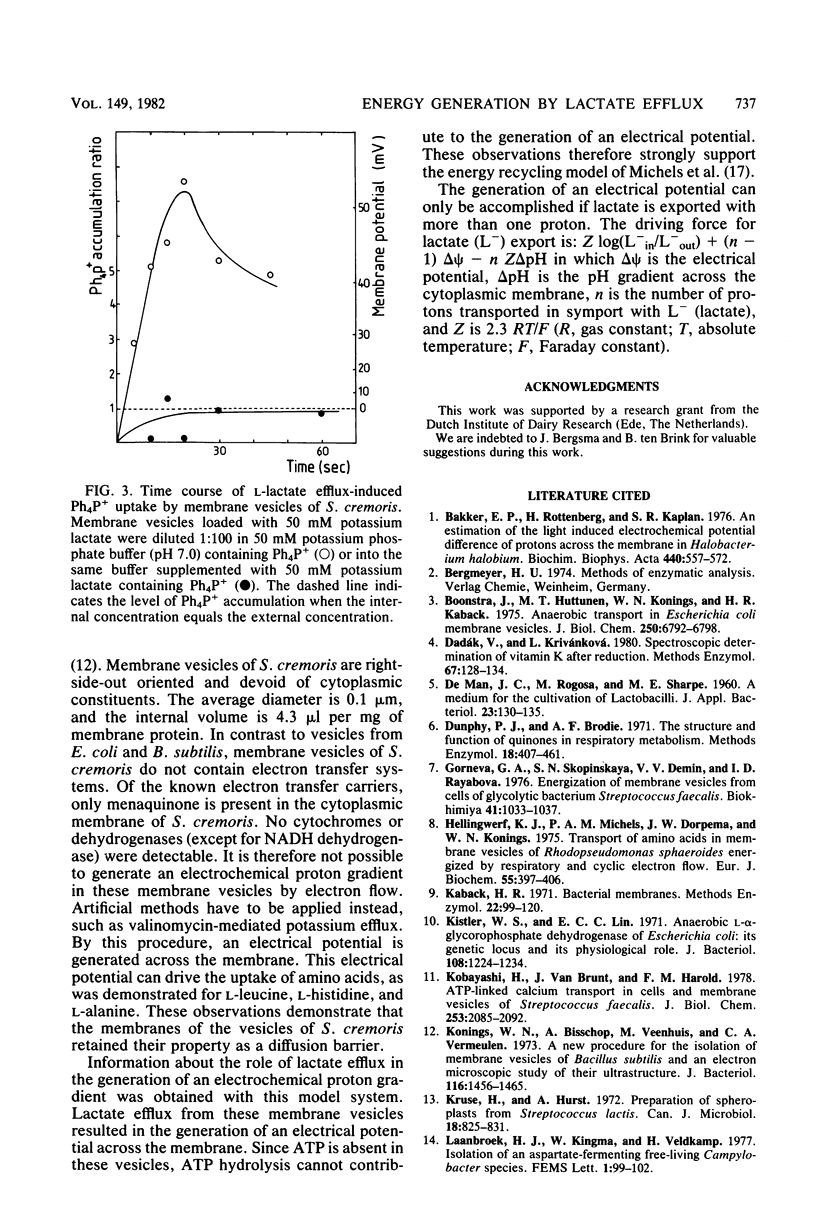
Abstract
We developed a procedure for isolating membrane vesicles from the homolactic fermentative bacterium Streptococcus cremoris. The membrane vesicles were shown to have a right-side-out orientation by freeze-etch electron microscopy and to be free of cytoplasmic constituents. The membrane vesicles retained their functional properties and accumulated the amino acids L-leucine, L-histidine, and L-alanine in response to a valinomycin-induced potassium diffusion gradient. Studies with these membrane vesicles strongly supported the possibility that there was a proton motive force-generating mechanism by end product efflux (Michels et al., FEMS Lett. 5:357-364, 1979). Lactate efflux from membrane vesicles which were loaded with L-lactate and diluted in a lactate-free medium led to the generation of an electrical potential across the membrane. The results indicate that lactate efflux is an electrogenic process by which L-lactate is translocated with more than one proton.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Rottenberg H., Caplan S. R. An estimation of the light-induced electrochemical potential difference of protons across the membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):557–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Huttunen M. T., Konings W. N. Anaerobic transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6792–6798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadák V., Krivänková L. Spectroscopic determination of vitamin K after reduction. Methods Enzymol. 1980;67:128–134. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)67019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorneva G. A., Skopinskaia S. N., Demin V. V., Riabova I. D. Energizatsiia membrannykh pyzyr'kov iz kletok glikoliziruiushchei bakterii Streptococcus faecalis. Biokhimiia. 1976 Jul;41(6):1033–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Dorpema J. W., Konings W. N. Transport of amino acids in membrane vesicles of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides energized by respiratory and cyclic electron flow. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):397–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler W. S., Lin E. C. Anaerobic L- -glycerophosphate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli: its genetic locus and its physiological role. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1224–1234. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1224-1234.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. ATP-linked calcium transport in cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Bisschop A., Veenhuis M., Vermeulen C. A. New procedure for the isolation of membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis and an electron microscopy study of their ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1456–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1456-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse H., Hurst A. Preparation of spheroplasts from Streptococcus lactis. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):825–831. doi: 10.1139/m72-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Konings W. N. Transport of lactate and succinate by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and a pseudomonas species. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):58–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Sonnenberg A. S., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient in Streptococcus cremoris by lactate efflux. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by lactate efflux in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]