Abstract
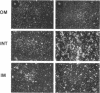
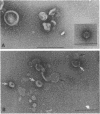
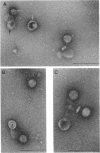
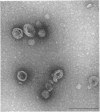
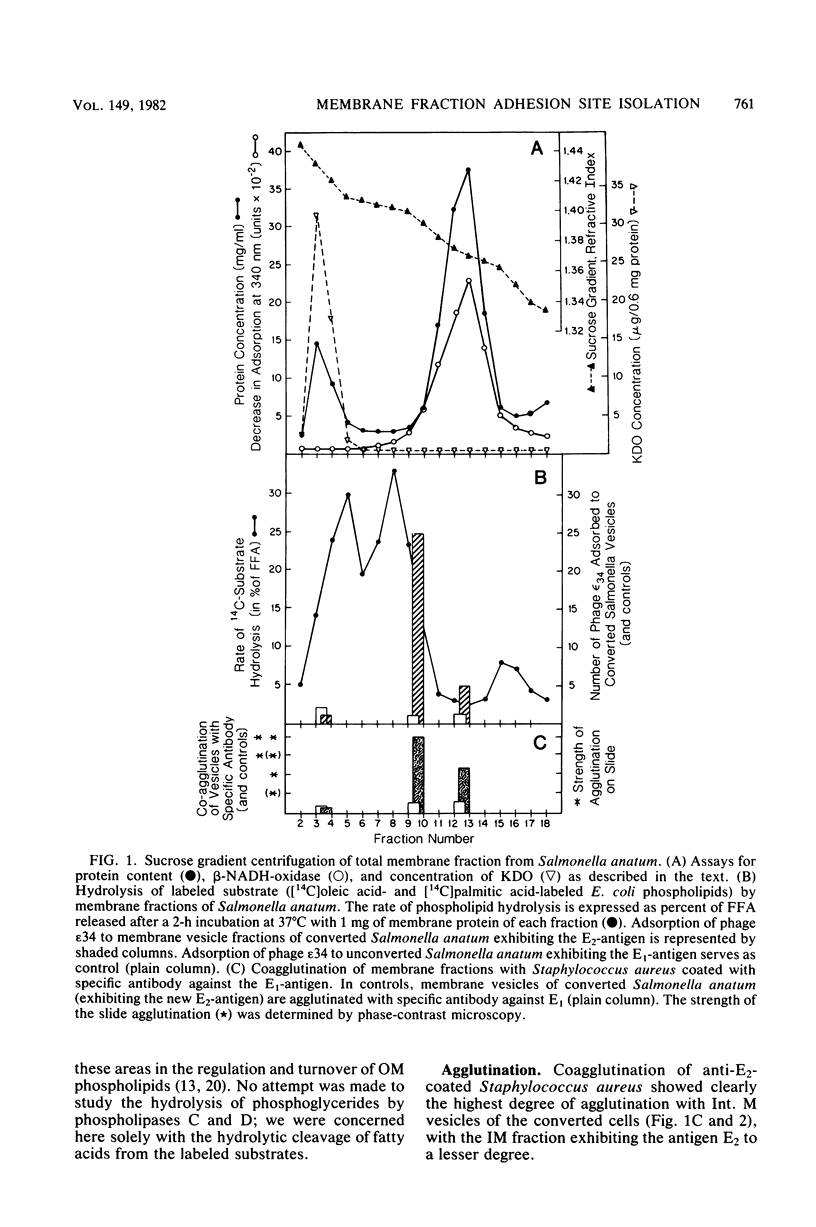
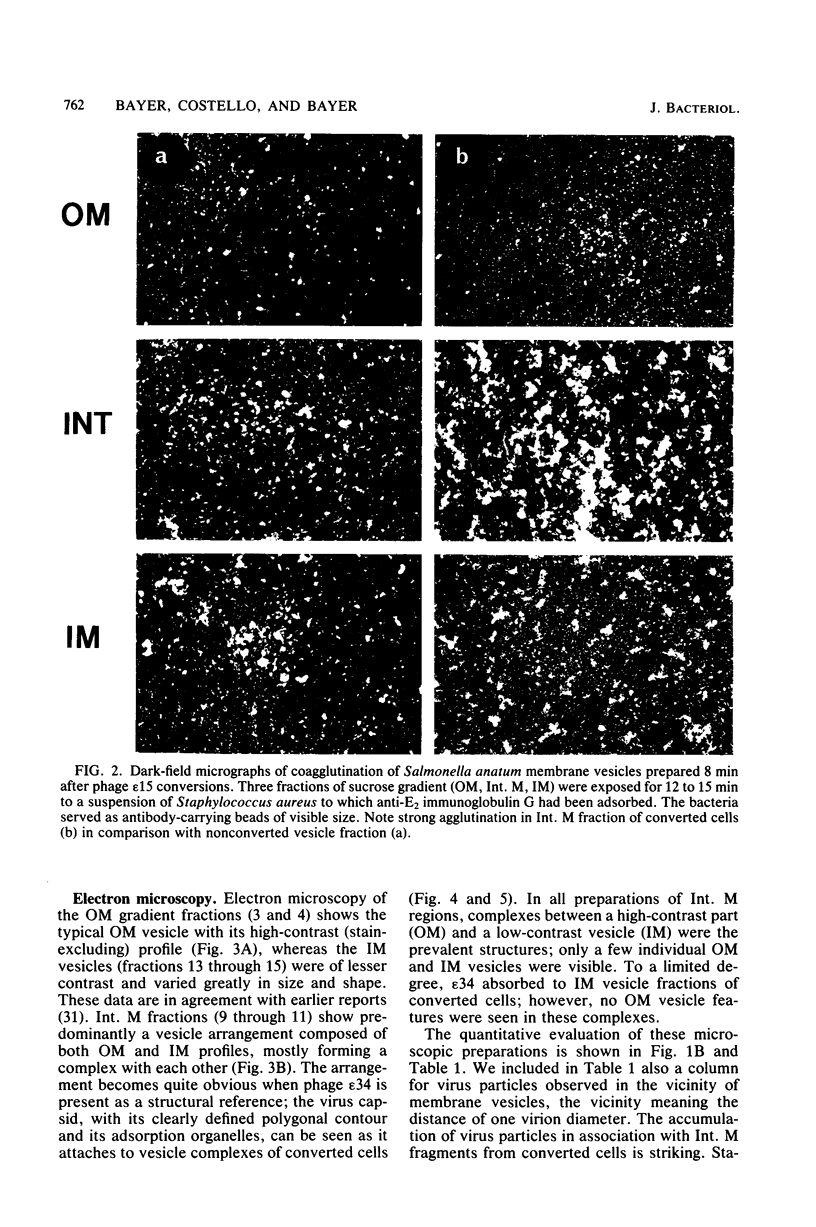
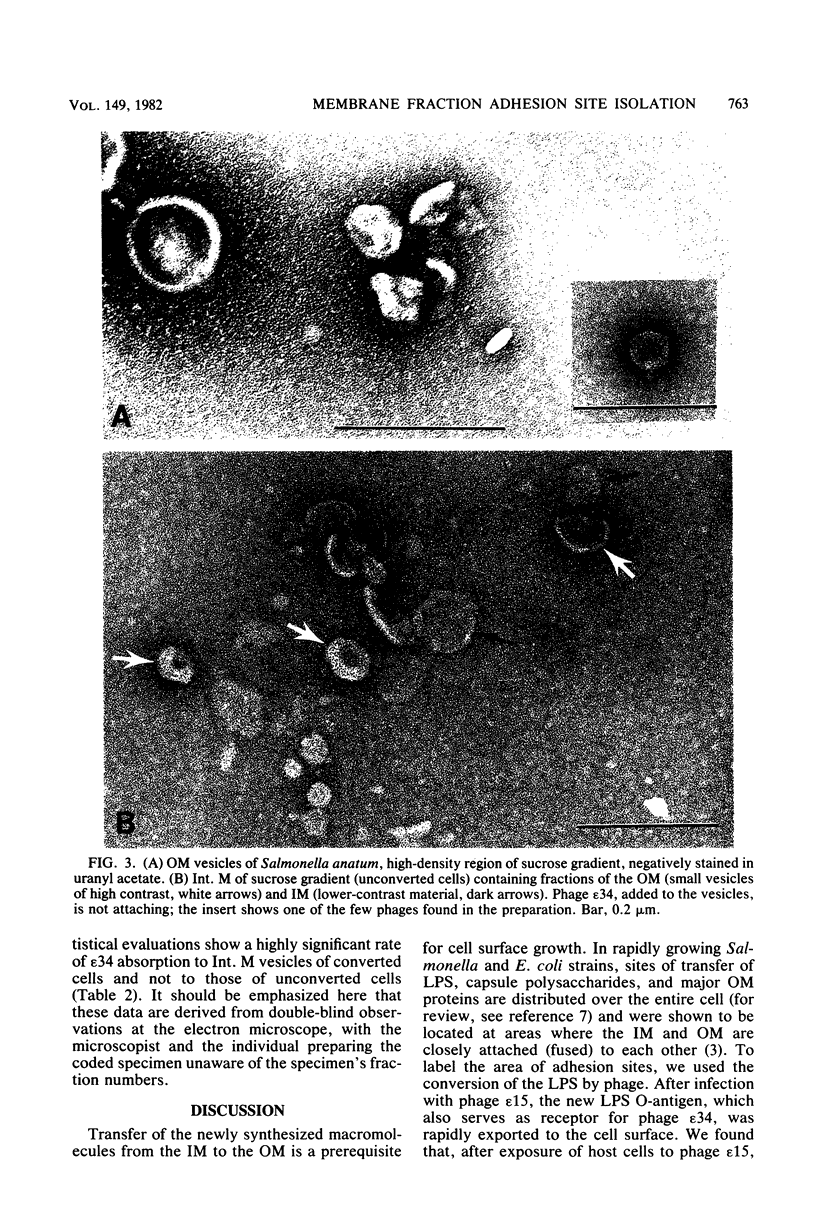
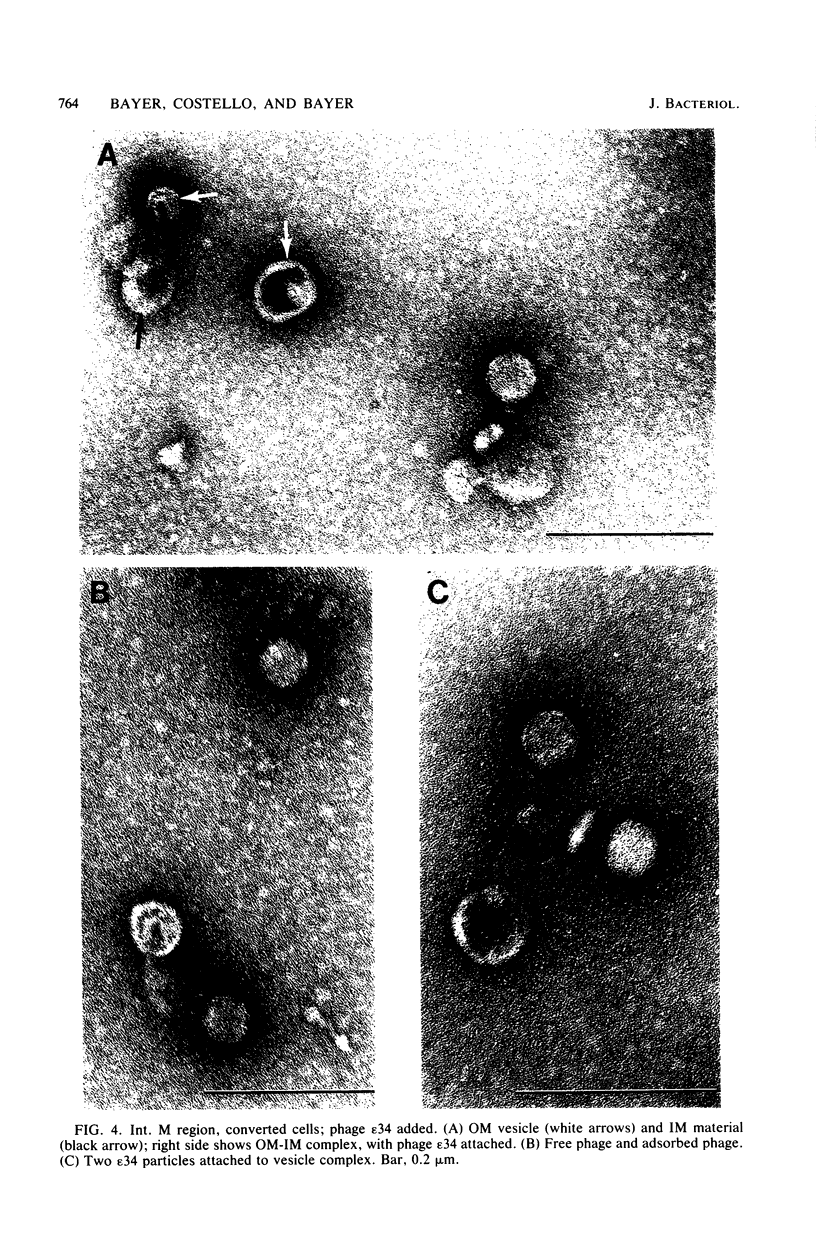
At areas of adhesion between outer membrane (OM) and inner membrane (IM) in gram-negative bacteria, newly synthesized membrane constituents are inserted, and bacteriophage infection occurs. We describe here the isolation of these sites from cell membrane fractions of Salmonella anatum. Sucrose density gradients yielded membrane vesicles of the OM and IM; their mutual cross-contamination was low, as measured by 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate and beta-NADH-oxidase activities. To mark the areas of lipopolysaccharide synthesis in the envelope (the adhesion sites), we infected S. anatum with phage epsilon 15, which causes a rapid change (conversion) in the cell's O-antigenic composition from serogroup E1 to E2; lipopolysaccharide of type E2 also serves as receptor for phage epsilon 34. We found that the fractions of intermediate density (Int. M) from briefly converted cells bound both phage epsilon 34 and E2-specific antibody. In the electron microscope, epsilon 34 was seen to have absorbed with a high degree of significance to the Int. M fraction of briefly converted cells, but not to the Int. M fraction of unconverted cells. Furthermore, the Int. M fractions of briefly converted cells coagglutinated anti-E2-coated Staphylococcus aureus, whereas the OM and IM fractions showed comparatively little agglutination. In addition, Int. M material exhibited elevated phospholipase A1 and A2 activities comparable to those of the OM fraction; the IM was essentially phospholipase free. Our data indicate that this membrane fractionation allows one to isolate from Int. M regions a variety of activities associated with adhesion sites.
Full text
PDF


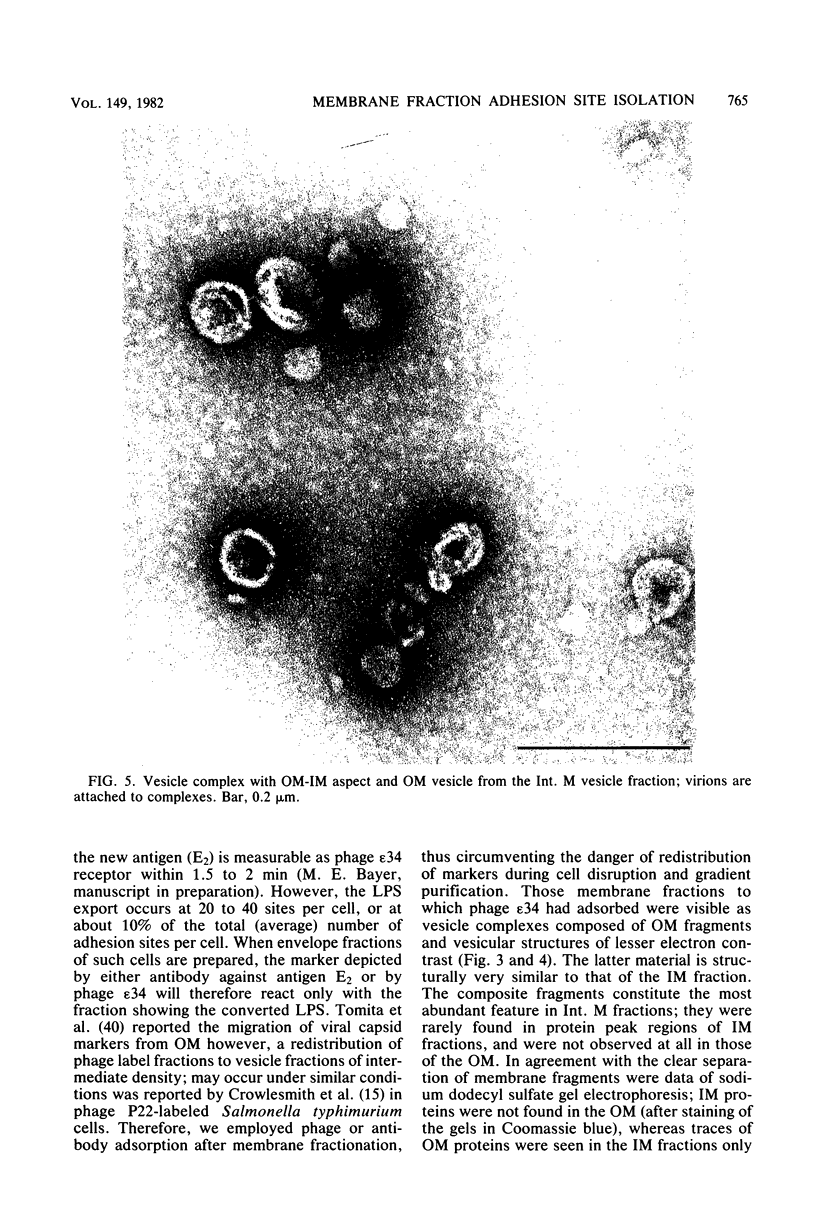


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLUM F. J. DEGRADATION OF THE HOMOPOLYMER COMPLEXES POLYDEOXYADENYLATE-POLYDEOXYTHYMIDYLATE, POLYDEOXYINOSINATE-POLYDEOXYCYTIDYLATE, AND POLYDEOXYGUANYLATE-POLYDEOXYCYTIDYLATE BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE I. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2599–2601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Adsorption of bacteriophages to adhesions between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):346–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.346-356.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Starkey T. W. The adsorption of bacteriophage phi X174 and its interaction with Escherichia coli; a kinetic and morphological study. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):236–256. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Takeda K., Uetake H. Effects of receptor destruction by Salmonella bacteriophages epsilon 15 and c341. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):328–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Ultrastructure and organization of the bacterial envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):6–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Mavis R. D., Osborn M. J., Vagelos P. R. Enzymes of phospholipid metabolism: localization in the cytoplasmic and outer membrane of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):628–635. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. K., Lueking D. R., Kaplan S. Intermembrane phospholipid transfer mediated by cell-free extracts of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):721–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowlesmith I., Schindler M., Osborn M. J. Bacteriophage P22 is not a likely probe for zones of adhesion between the inner and outer membranes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):259–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.259-269.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Nojima S. Detergent-resistant phospholipase A1 and A2 in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1973 Oct;74(4):667–674. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K. B. Lipolytic activity copurified with the outer membrane of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1120–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1120-1122.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Osborn M. J. Translocation of phospholipids between the outer and inner membranes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7405–7412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., Peters R. Distribution of lipids in cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 20;441(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Mizushima S. Separation and properties of outer and cytoplasmic membranes in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):268–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Menzel J., Golecki J. R., Speth V. Lateral mobility and surface density of lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Menzel J., Golecki J. R., Speth V. Outer membrane of salmonella. Sites of export of newly synthesised lipopolysaccharide on the bacterial surface. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun 15;35(3):471–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Nakaike S., Tamori Y., Nojima S. Detergent-resistant phospholipase A of Escherichia coli K-12. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):115–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS P. W., UCHIDA T. Studies on the chemical basis of the phage conversion of O-antigens in the E-group Salmonellae. Biochemistry. 1962 Mar;1:323–335. doi: 10.1021/bi00908a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. C., Makula S. R., Finnerty W. R. Isolation and characterization of membranes from a hydrocarbon-oxidizing Acinetobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):469–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.469-480.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenungsson B., Linberg A. A. Identification of Salmonella bacteria by co-agglutination, using antibodies against synthetic disaccharide-protein antigens O2, O4 and O9, adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1978 Oct;86B(5):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel T., Astrachan L. Absence of phospholipase activity in bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):835–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.835-837.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Iwashita S., Kanegasaki S. Role of cell surface mobility on bacteriophage infection: translocation of Salmonella phages to membrane adhesions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UETAKE H., LURIA S. E., BURROUS J. W. Conversion of somatic antigens in Salmonella by phage infection leading to lysis or lysogeny. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):68–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Leij L., Kingma J., Witholt B. Nature of the regions involved in the insertion of newly synthesized protein into the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 17;553(2):224–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]