Abstract
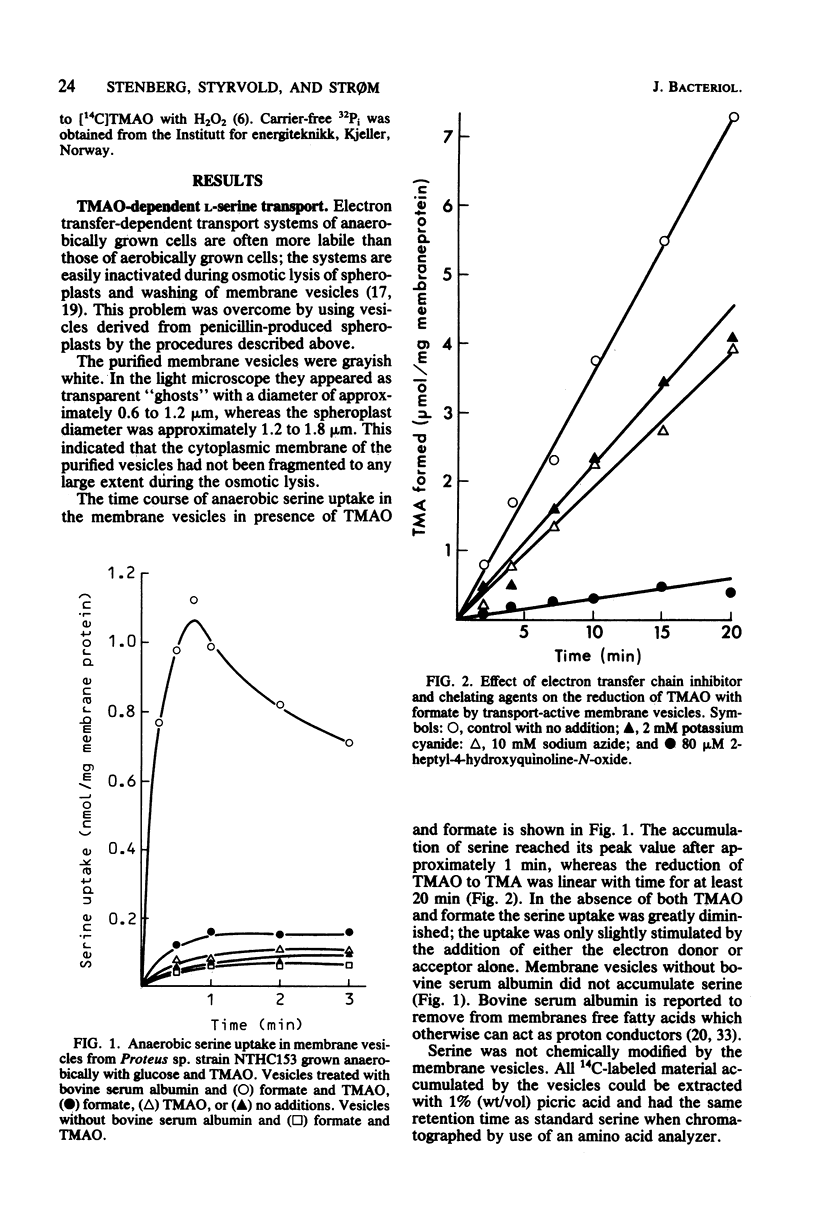
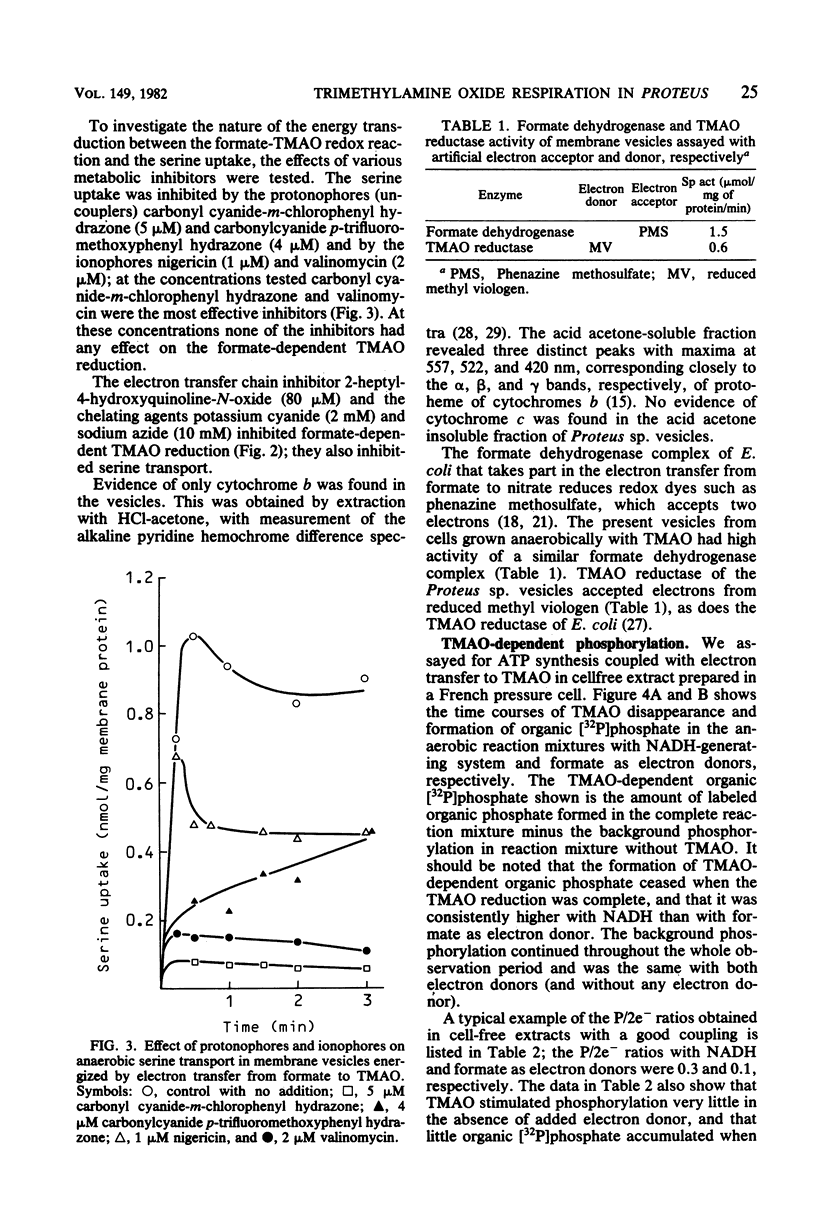
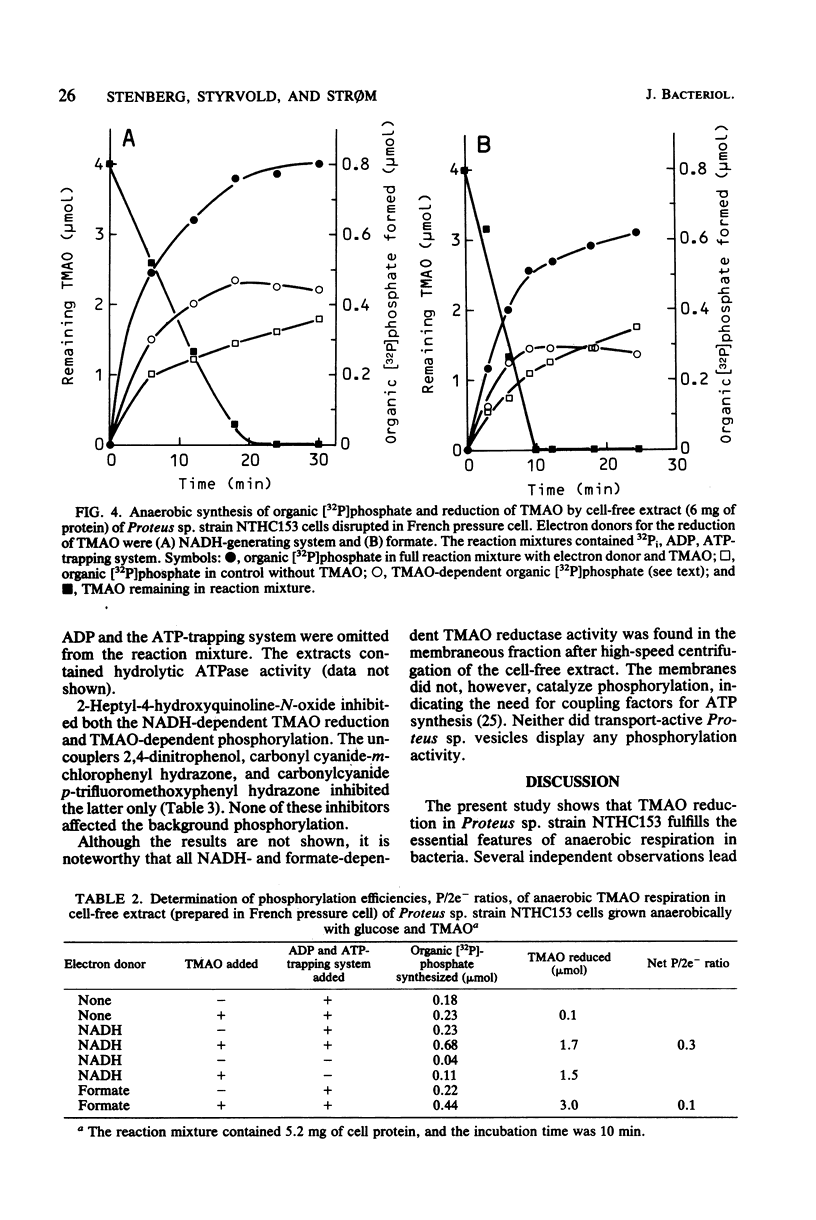
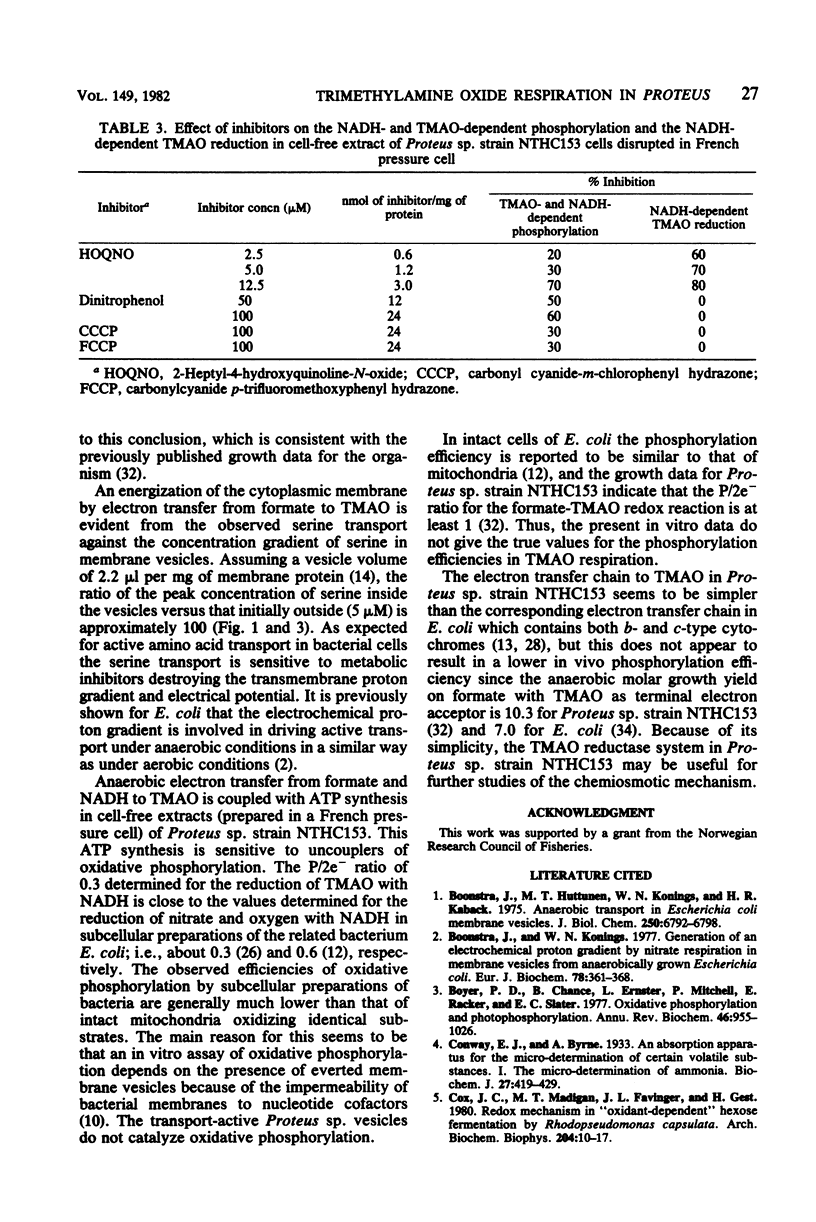
Cells of Proteus sp. strains NTHC153 grown anaerobically with glucose and trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) were converted to spheroplasts by the penicillin method. The spheroplasts were lysed by osmotic shock, and the membrane vesicles were purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Vesicles energized electron transfer from formate to TMAO displayed active anaerobic transport of serine. An anaerobic cell-free extract of Proteus sp. disrupted in a French pressure cell reduced TMAO with formate and NADH with the concomitant formation of organic phosphate. The net P/2e- ratios determined were 0.1 and 0.3, respectively. The NADH- and TMAO-dependent phosphorylation was sensitive to uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation (protonophores), and the formate- and TMAO-dependent serine transport was sensitive to ionophores and protonophores. We conclude that TMAO reduction in Proteus sp. fulfills the essential features of anaerobic respiration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conway E. J., Byrne A. An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances: The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem J. 1933;27(2):419–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. The proton-translocating pumps of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1079–1113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIHARA B., LARDY H. A. A method for the separation of orthophosphate from other phosphate compounds. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempfling W. P., Hertzberg E. L. Techniques for measurement of oxidative phosphorylation in intact bacteria and in membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Barnes E. M., Jr Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. II. The mechanism of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5523–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen M. D., Horio T. Bacterial cytochromes. I. Structural aspects. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:673–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. E., Chang G. W. Trimethylamine oxide reduction by Salmonella. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Dec;20(12):1745–1748. doi: 10.1139/m74-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N. Energization of solute transport in membrane vesicles from anaerobically grown bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:378–388. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., DeMoss J. A. Effects of molybdate and selenite on formate and nitrate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1006-1014.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki K., Lin E. C. Anaerobic energy-yielding reaction associated with transhydrogenation from glycerol 3-phosphate to fumarate by an Escherichia coli system. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1282–1287. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1282-1287.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki K., Lin E. C. Electron transport chain from glycerol 3-phosphate to nitrate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1288–1294. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1288-1294.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTA A., YAMANAKA T., OKUNUKI K. OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION COUPLED WITH NITRATE RESPIRATION. II. PHOSPHORYLATION COUPLED WITH ANAEROBIC NITRATE REDUCTION IN A CELL-FREE EXTRACT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota A. Oxidative phosphorylation coupled with nitrate respiration. 3. Coupling factors and mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biochem. 1965 Aug;58(2):137–144. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C. Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:1015–1026. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry J. F., Wilkins T. D. Cytochrome spectrum of an obligate anaerobe, Eubacterium lentum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):905–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.905-909.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strøm A. R., Larsen H. Anaerobic fish spoilage by bacteria. I. Biochemical changes in herring extracts. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;46(3):531–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strøm A. R., Olafsen J. A., Larsen H. Trimethylamine oxide: a terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration of bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):315–320. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOJTCZAK L., LEHNINGER A. L. Formation and disappearance of an endogenous uncoupling factor during swelling and contraction of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:442–456. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90600-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Ishimoto M. Anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on formate by reduction of nitrate, fumarate, and trimethylamine N-oxide. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1977;17(3):235–242. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630170309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



