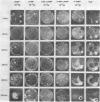
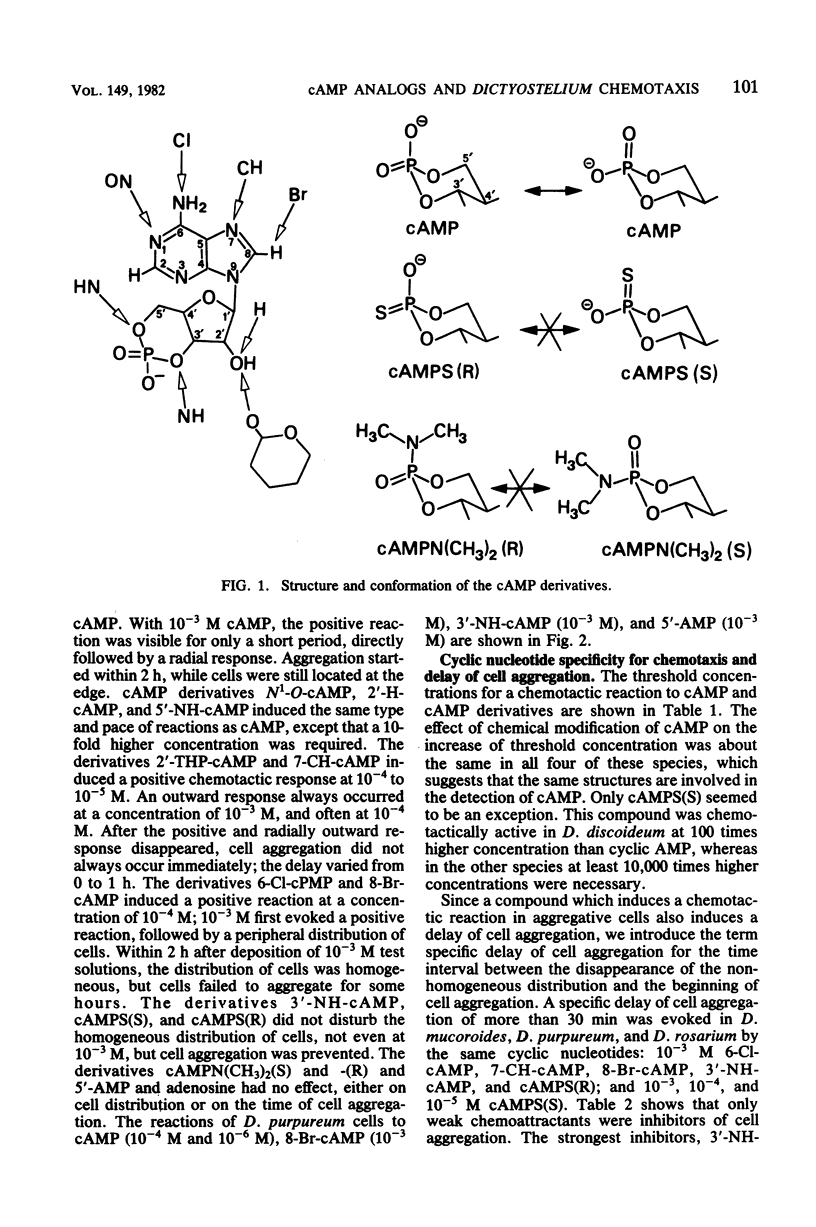
Abstract
Aggregative amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum, D. mucoroides, D. purpureum, and D. rosarium react chemotactically to cyclic AMP (cAMP). We measured the chemotactic activity of 14 cAMP analogs and found that these four species have a similar sensitivity to chemical modifications of cAMP; this suggests that the cAMP receptor is identical in all of these species. Besides the induction of a chemotactic response, cAMP analogs also may delay or prevent cell aggregation. cAMP analogs like N1-O-cAMP, 2'-H-cAMP, and 5'NH-cAMP are chemotactically nearly as active as cAMP and induced no, or only a short, delay of cell aggregation. Other cAMP derivatives, such as 6-Cl-cPMP and 8-Br-cAMP, are chemotactically active only at high concentrations and delayed cell aggregation for several hours. Still other cAMP analogs, which do not induce a chemotactic reaction in D. mucoroides, D. purpureum, and D. rosarium, either prevented cell aggregation [cAMPS(S), cAMPS(R), and 3'-NH-cAMP[ or had no effect on cell aggregation [cAMPN(CH3)2(S) and cAMPN(CH3)2(R)]. cAMP analog 3'-NH-cAMP prevented cell aggregation by the inhibition of chemotaxis, whereas cell locomotion was not affected. Although we cannot provide a satisfactory explantation for these observations, our data suggest that occupation and activation of the cAMP receptors do not always induced a chemotactic response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Erneux C., Couchie D., Dumont J. E., Baraniak J., Stec W. J., Abbad E. G., Petridis G., Jastorff B. Specificity of cyclic GMP activation of a multi-substrate cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):503–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. A., Newell P. C. Evidence for the existence of two types of cAMP binding sites in aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. J. The cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Binding characteristics of aggregation-competent cells and variation of binding levels during the life cycle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4730–4736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIJN T. M., RAPER K. B. Cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1961 Dec;3:725–756. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(61)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M. Microbiological assay of cyclic 3',5'-AMP. Experientia. 1970 Apr 15;26(4):367–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01896891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Fuchila J., Jastorff B. Correlation of substrate specificity of cAMP-phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium discoideum with chemotactic activity of cAMP-analogues. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80690-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Gerisch G. Short-term binding and hydrolysis of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate by aggregating Dictyostelium cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Jastorff B., Morr M., Konijn T. M. A model for cyclic AMP-chemoreceptor interaction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 1;544(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Konijn T. M. Chemotaxis and binding of cyclic AMP in cellular slime molds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Rhijnsburger E. H., Dobbe F. C., Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP and folic acid mediated cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80814-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama A., Jastorff B., Cramer F., Hettler H. 5'-amido analogs of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. J Org Chem. 1971 Oct 8;36(20):3029–3033. doi: 10.1021/jo00819a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Folic acid as second chemotactic substance in the cellular slime moulds. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):181–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio237181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier C., Gerisch G., Malchow D. Action of a slowly hydrolysable cyclic AMP analogue on developing cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:321–338. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van Der Meer R. C., Konijn T. M. Evidence that the rate of association of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate to its chemotactic receptor induces phosphodiesterase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):170–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.170-175.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Butz U. Reversible binding of the chemoattractant folic acid to cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):613–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yathindra N., Sundaralingam M. Conformations of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotides. Effect of the base on the synanti conformer distribution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]