Abstract
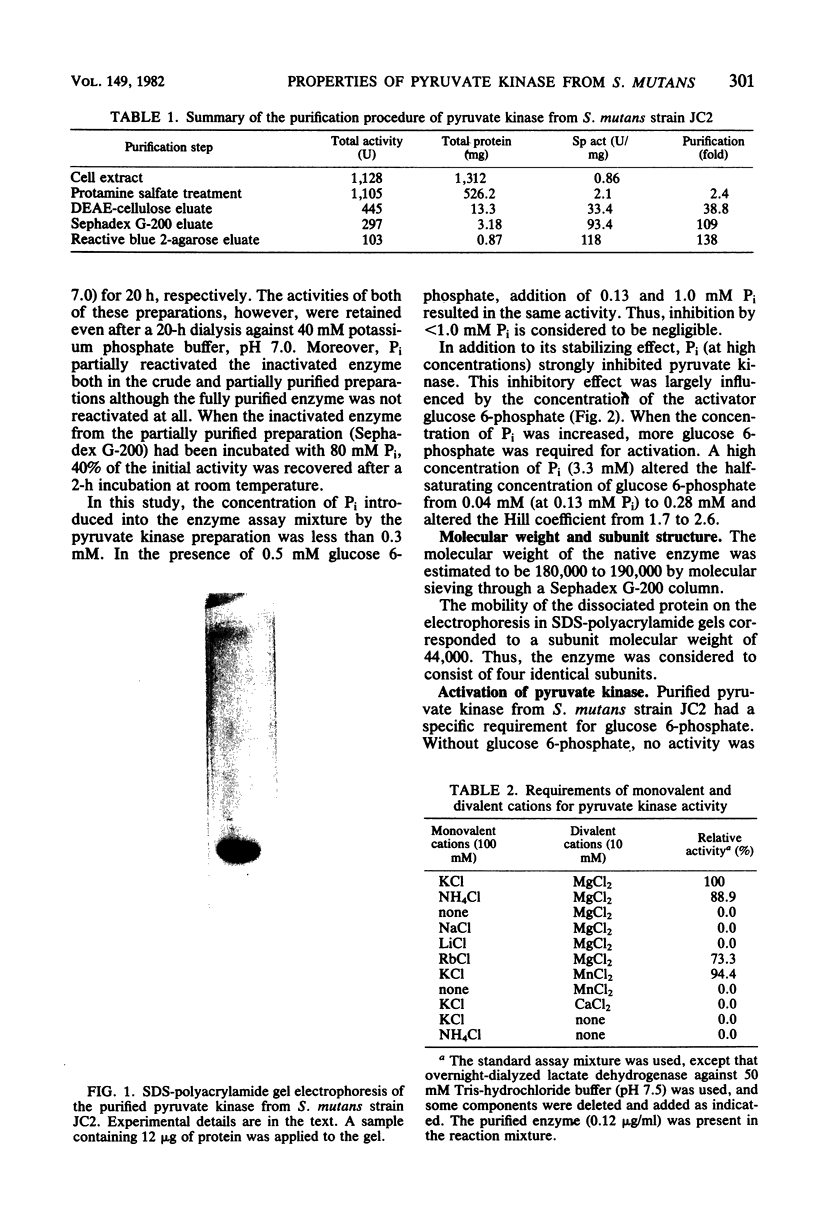
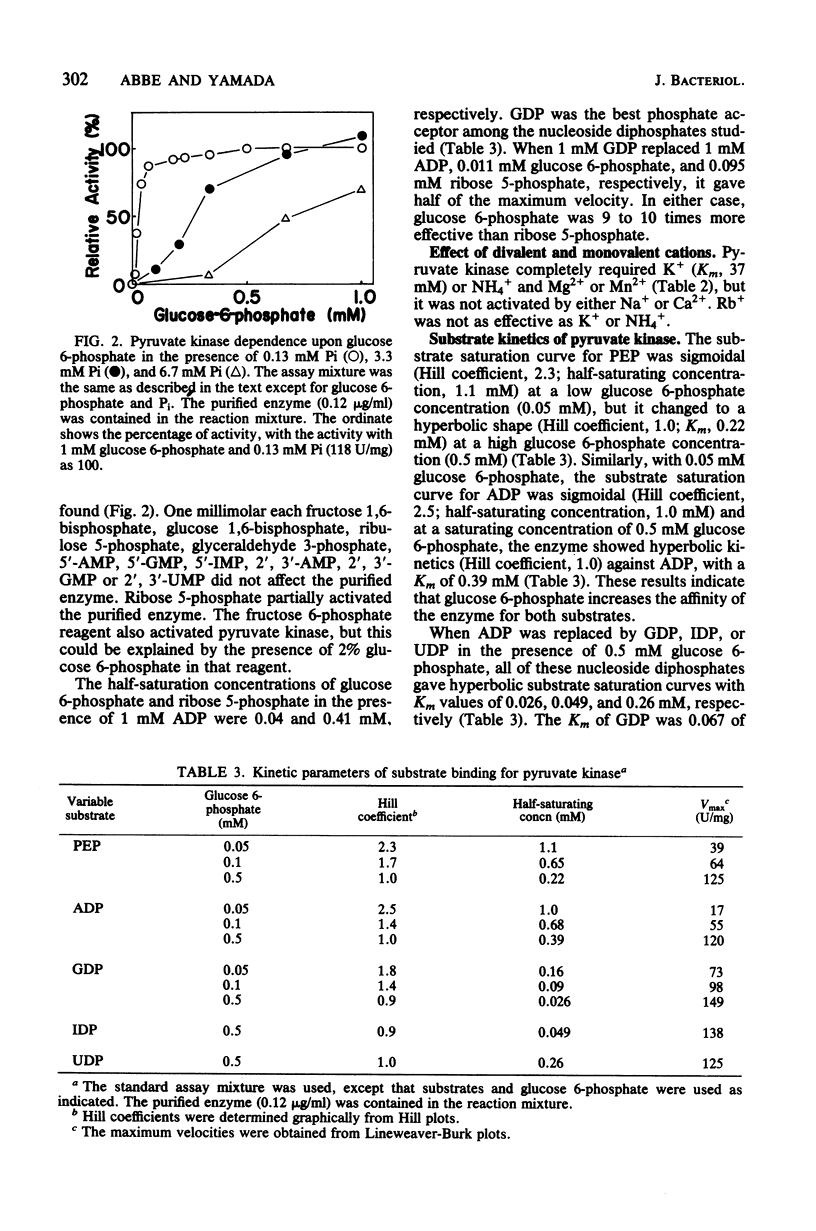
Pyruvate kinase (EC 2.7.1.40) from Streptococcus mutans strain JC2 was purified, giving a single band on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight of the native enzyme was 180,000 to 190,000, and the enzyme was considered to consist of four identical subunits. This enzyme was completely dependent on glucose 6-phosphate for activity, and the saturation curve for activation by glucose 6-phosphate was sigmoidal. In the presence of 0.5 mM glucose 6-phosphate, the saturation curves for the substrates phosphoenolpyruvate and ADP were hyperbolic, and the Km values were 0.22 and 0.39 mM, respectively. GDP, IDP, and UDP could replace ADP, and the Km for GDP (0.026 mM) was 0.067 of that for ADP. The enzyme required not only divalent cations, Mg2+ or Mn2+, but also monovalent cations, K+ or NH4+, for activity, and it was strongly inhibited by Pi. When the concentration of Pi was increased, the half-saturating concentration and Hill coefficient for glucose 6-phosphate increased. However, the enzyme was immediately inactivated in a solution without Pi. The intracellular concentration of glucose 6-phosphate, in cooperation with that of Pi, may regulate pyruvate kinase activity in S. mutans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. T., Ruh R., Jr Negative interaction of orthophosphate with glycolytic metabolism by Streptococcus mutans as a possible mechanism for dental caries reduction. Arch Oral Biol. 1977;22(8-9):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(77)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Wittenberger C. L. The occurrence of multiple glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases in cariogenic streptococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A numerical taxonomic study of human oral streptococci. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(2):137–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. T., Utter M. F. Structural and regulatory properties of pyruvate kinase from Pseudomonas citronellolis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8434–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. A. A biochemical approach to the control of dental caries. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):1232–1239. doi: 10.1042/bst0051232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. B., Thomas T. D. Pyruvate kinase of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.52-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow V. L., Pritchard G. G. Purification and properties of pyruvate kinase from Streptococcus lactis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 7;438(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardsson S. Characteristics of caries-inducing human streptococci resembling Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):637–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibriel A. Y., Doelle H. W. Investigation into pyruvate kinases from Escherichia coli K-12 grown under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Microbios. 1975;12(50):179–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeckel R., Hess B., Lauterborn W., Wüster K. H. Purification and allosteric properties of yeast pyruvate kinase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 May;349(5):699–714. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1968.349.1.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelman S. L., Kreinces G. H. Effect of phosphate and pH on Streptococcus mutans acid production and growth. J Dent Res. 1973 Jul-Aug;52(4):651–657. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520040301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwami Y., Yamada T. Rate-limiting steps of the glycolytic pathway in the oral bacteria Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis and the influence of acidic pH on the glucose metabolism. Arch Oral Biol. 1980;25(3):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(80)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyes P. H. Research in dental caries. J Am Dent Assoc. 1968 Jun;76(6):1357–1373. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1968.0186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Malcovati M. Control in situ of the pyruvate kinase activity of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):257–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80846-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B., Jordan H. V., Edwardsson S., Svensson I., Trell L. The occurrence of certain "caries-inducing" streptococci in human dental plaque material with special reference to frequency and activity of caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Aug;13(8):911–918. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. L., Atkinson D. E. Regulation at the phosphoenolpyruvate branchpoint in Azotobacter vinelandii: pyruvate kinase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):37–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.37-44.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton N. W., McCabe R. M., Carter C. H. Studies of oral health in persons nourished by stomach tube. II. Acidogenic properties and selected bacterial components of plaque material. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 May;12(5):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcovati M., Kornberg H. L. Two types of pyruvate kinase in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;178(2):420–423. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcovati M., Valentini G., Kornberg H. L. Two forms of pyruvate kinase in E. coli: their properties and regulation. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol. 1973;27(1):96–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinases of Escherichia coli: further studies of the enzyme activated by ribose-5-phosphate. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):647–653. doi: 10.1139/o78-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. K., Hamilton I. R. Purification and regulatory properties of pyruvate kinase from Veillonella parvula. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1274–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1274-1282.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gonzalez J. E., Gazdar C. The Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase complex. Regulation by enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 May;188(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F. Glucose transport in Streptococcus mutans: preparation of cytoplasmic membranes and characteristics of phosphotransferase activity. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Mayo J. A. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose transport in oral streptococci. J Dent Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;52(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520060801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somani B. L., Valentini G., Malcovati M. Purification and molecular properties of the AMP-activated pyruvate kinase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):52–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Activator specificity of pyruvate kinase from lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1240–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1240-1242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Mort J. S., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinase of Escherichia coli. Binding of substrate and allosteric effectors to the enzyme activated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):277–282. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Rayman M. K., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinases of Escherichia coli. II. Effectors and regulatory properties of the enzyme activated by ribose 5-phosphate. Can J Biochem. 1975 Apr;53(4):444–454. doi: 10.1139/o75-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinases of Escherichia coli. I. Physicochemical and regulatory properties of the enzyme activated by fructose 1,6-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Glucose-6-phosphate-dependent pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):562–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.562-563.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and ammonium metabolism in oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jul;18(7):799–812. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and change of fermentation products in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.55-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]