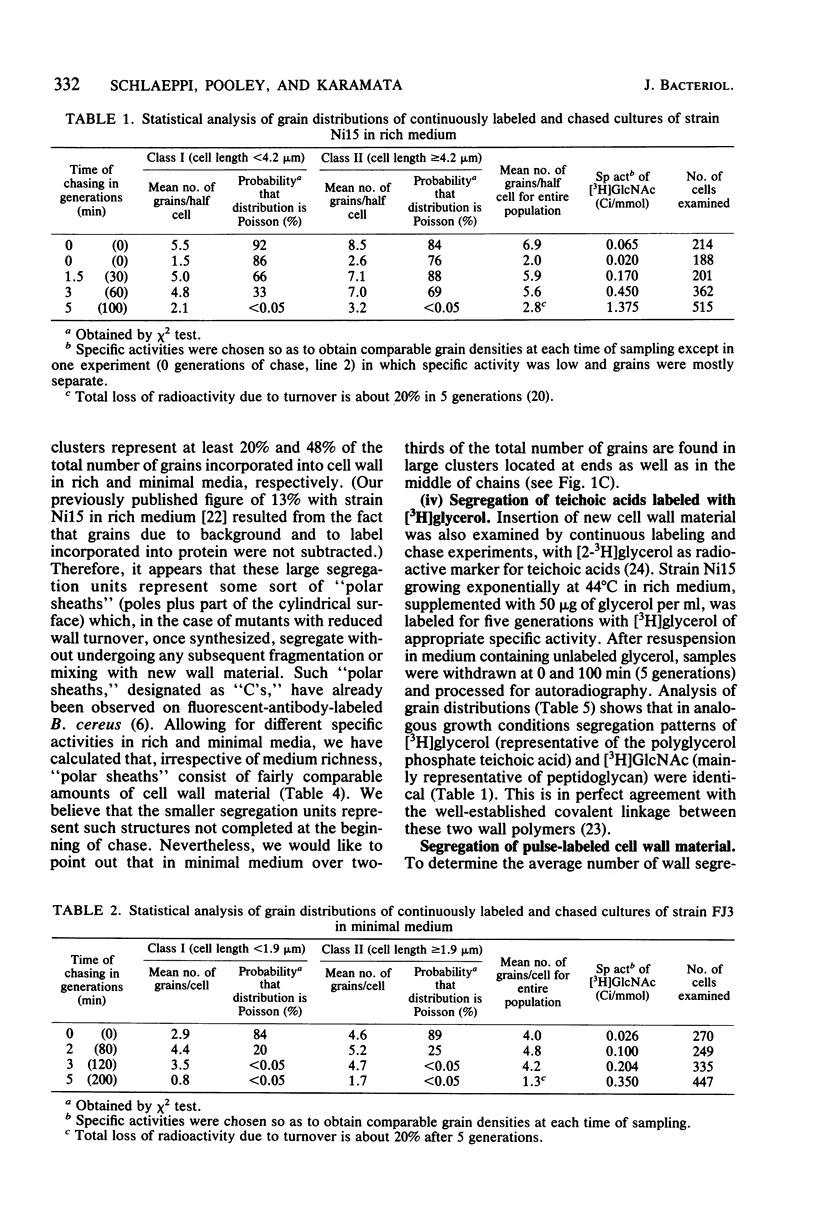
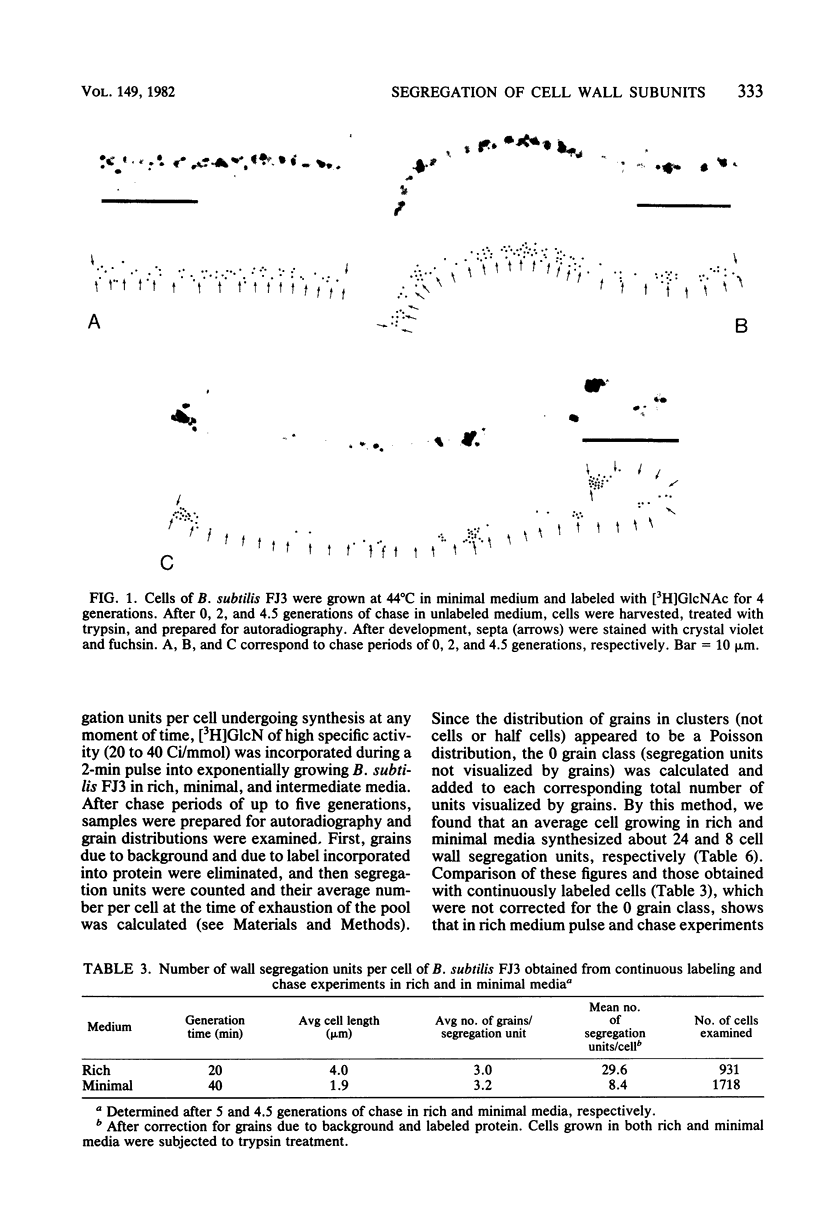
Abstract
Continuous as well as pulse-labeling and chase experiments with Bacillus subtilis demonstrated that the cell wall (both peptidoglycan and teichoic acid) is composed of a limited number of blocks which, once completed, segregate during subsequent growth without undergoing any mixing with newly synthesized blocks. This observation suggests that new wall material is inserted in a limited number of zones. Previously reported observations which suggested diffuse intercalation of new wall material are reinterpreted on the basis of our results. Experiments performed on different media showed that the number of segregation units per unit of cell length and thus the density of insertion zones increases with medium richness. This finding suggests analogies between the regulation of cell wall and DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. J., Green R. S., Sturman A. J., Archibald A. R. Cell wall assembly in Bacillus subtilis: location of wall material incorporated during pulsed release of phosphate limitation, its accessibility to bacteriophages and concanavalin A, and its susceptibility to turnover. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):886–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.886-899.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R. Cell wall assembly in Bacillus subtilis: development of bacteriophage-binding properties as a result of the pulsed incorporation of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):956–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.956-960.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Coapes H. E. Bacteriophage SP50 as a marker for cell wall growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1195-1206.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Higgins M. L. Study of pole assembly in Bacillus subtilis by computer reconstruction of septal growth zones seen in central, longitudinal thin sections of cells. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):959–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.959-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUNG K. L., HAWIRKO R. Z., ISAAC P. K. CELL WALL REPLICATION. I. CELL WALL GROWTH OF BACILLUS CEREUS AND BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Feb;10:43–48. doi: 10.1139/m64-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. 3. Bacterial cell-wall replication followed by immunofluorescence. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):326–344. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.326-344.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein J. E., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzyme-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1427–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1427-1442.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehel C., Ryter A. Peptidoglycan turnover during growth of a Bacillus megaterium Dap- Lys- mutant. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):947–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.947-955.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Study of cycle of cell wall assembly in Streptococcus faecalis by three-dimensional reconstructions of thin sections of cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1346–1358. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1346-1358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Stokes E. Cell wall growth in Bacillus licheniformis followed by immunofluorescence with mucopeptide-specific antiserum. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):694–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.694-696.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Chan L., Glaser L., Williamson J. Mode of cell wall growth of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):373–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.373-378.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. On the mode of in vivo assembly of the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1180–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L. Membrane synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. I. Isolation and properties of strains bearing mutations in glycerol metabolism. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):415–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF PENICILLINASES FROM TWO STRAINS OF BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS: A CHEMICAL, PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL COMPARISON. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:666–675. doi: 10.1042/bj0940666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley H. M., Schlaeppi J. M., Karamata D. Localised insertion of new cell wall in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):264–266. doi: 10.1038/274264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Layered distribution, according to age, within the cell wall of bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1139–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1139-1147.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Turnover and spreading of old wall during surface growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1127-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Membrane synthesis in synchronous cultures of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):397–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.397-409.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIKAWA H., O'SULLIVAN A., SUEOKA N. SEQUENTIAL REPLICATION OF THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS CHROMOSOME. 3. REGULATION OF INITIATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:973–980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chastellier C., Hellio R., Ryter A. Study of cell wall growth in Bacillus megaterium by high-resolution autoradiography. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1184–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1184-1196.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




