Abstract
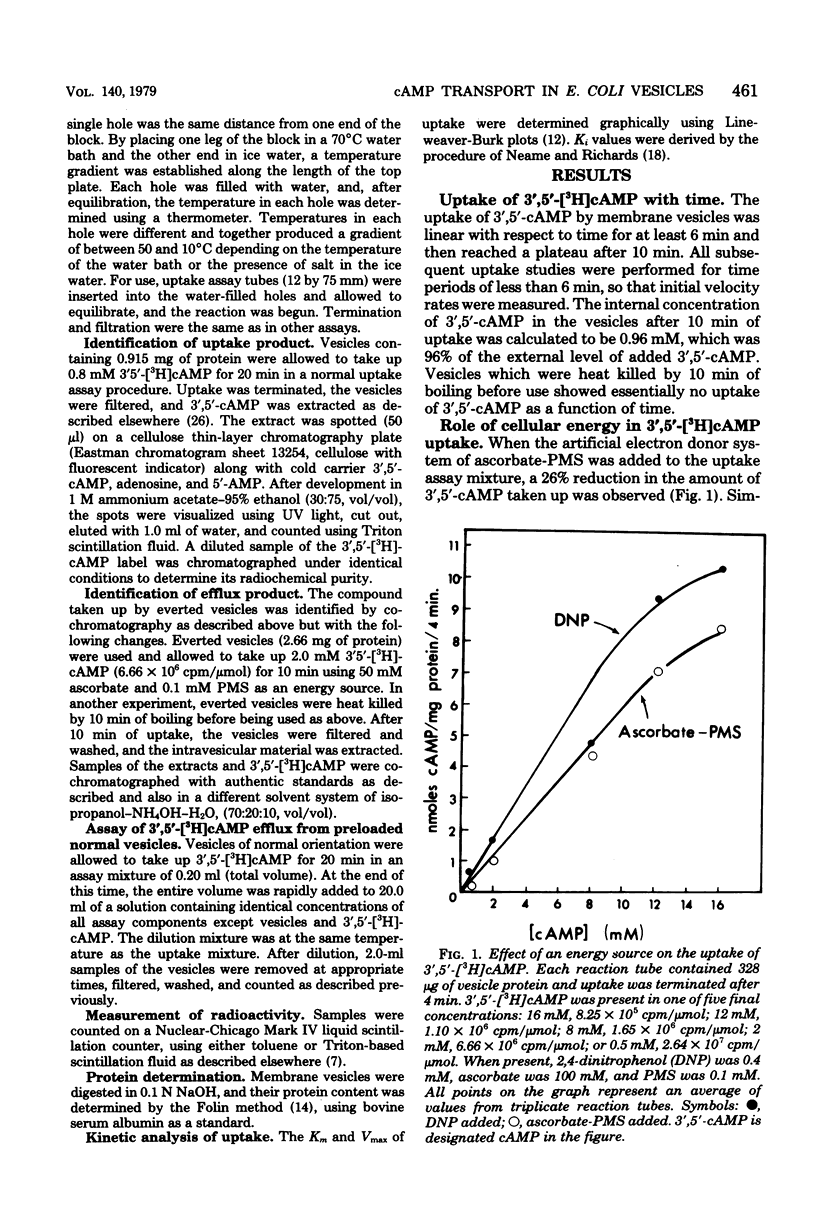
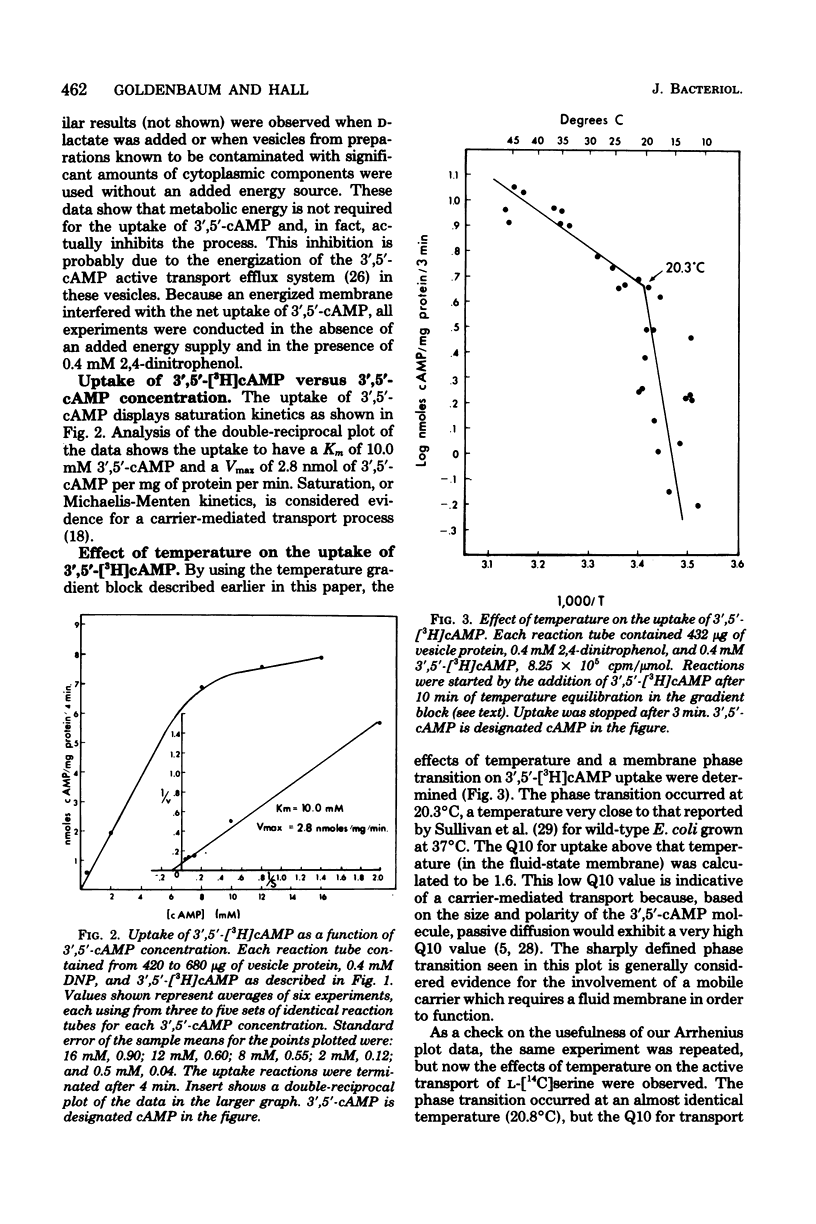
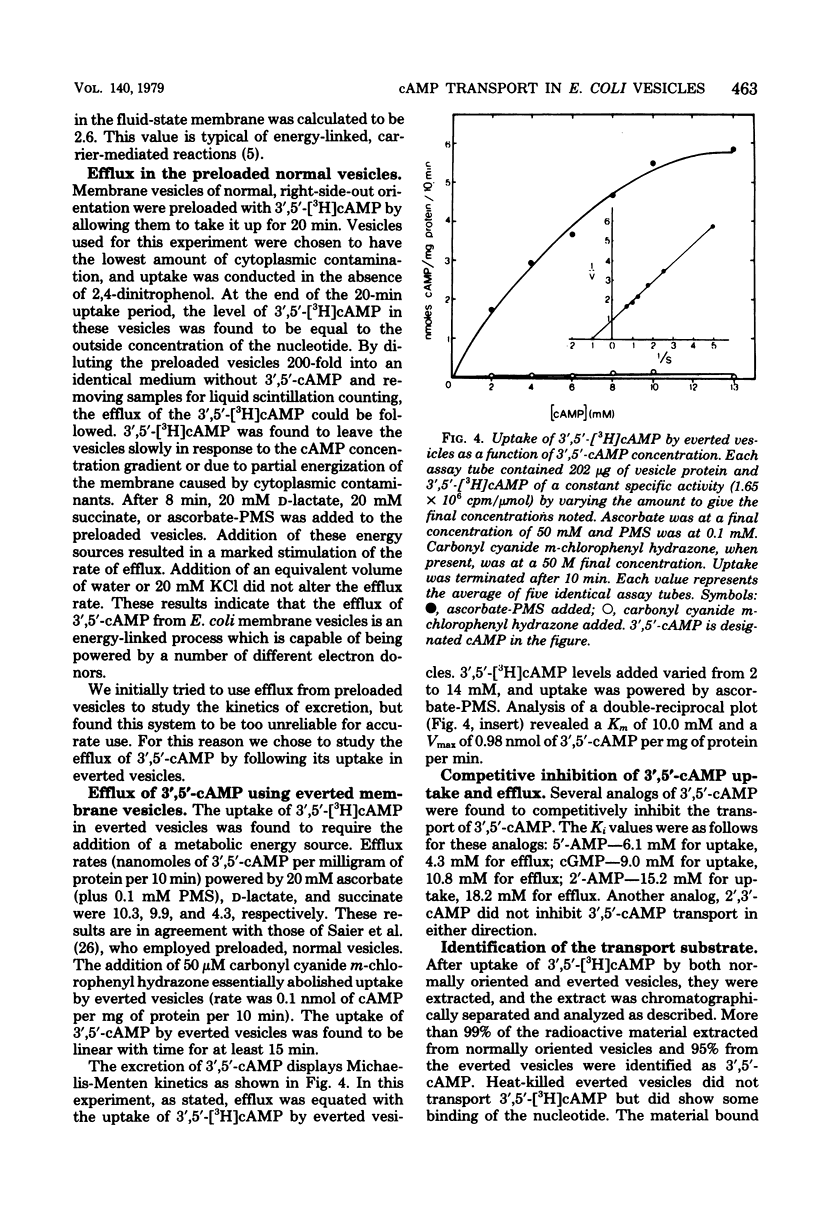
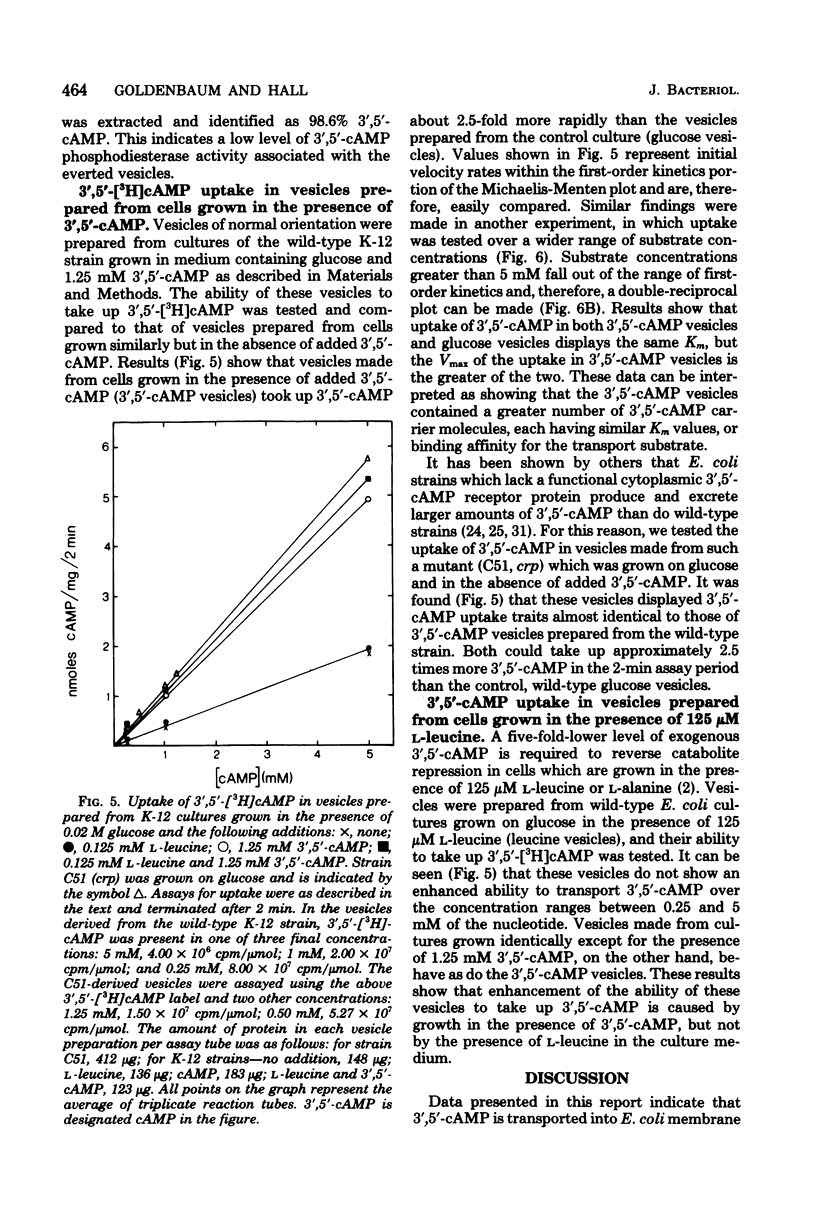
The uptake and efflux of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (3',5'-cAMP) by Escherichia coli membrane vesicles were studied. Metabolic energy was not required for the uptake process and was found to actually decrease the amount of 3',5'-cAMP found in the vesicles. 3',5'-cAMP uptake exhibits saturation kinetics (Km = 10 mM, Vmax = 2.8 nmol/mg of protein per min) and was competitively inhibited by a number of 3',5'-cAMP analogs. The uptake of 3',5'-cAMP was found to be sharply affected by a membrane phase transition. The excretion of 3',5'-cAMP was studied by using everted membrane vesicles. Efflux in this system was dependent upon metabolic energy and was reduced or abolished by uncouplers. Different energy sources powered efflux at different rates, showing a relationship between the degree of membrane energization and rate of excretion of 3',5'-cAMP. The efflux process also displayed saturation kinetics (Km = 10.0 mM, Vmax = 0.98 nmol/mg of protein per min) and was competitively inhibited by the same 3',5'-cAMP analogs and to the same degree as was the uptake process. 3',5'-cAMP was found to be chemically unaltered by both the uptake and excretion processes. These data are interpreted as showing that the uptake and excretion of 3',5'-cAMP in E. coli membrane vesicles are carrier-mediated phenomena, possibly employing the same carrier system. Uptake is by facilitated diffusion whereas efflux is via an energy-dependent, active transport process. Evidence is presented showing that cells can regulate the number of 3',5'-cAMP transport carriers. The rate of 3',5'-cAMP excretion is possibly regulated by both the degree of membrane energization and the number of carriers present per cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K. H., Staehelin L. A. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli as detected by freeze-cleave electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.888-899.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broman R. L., Goldenbaum P. E., Dobrogosz W. J. The effect of amino acids on the ability of cyclic AMP to reverse catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Tseng Y., Dobrogosz W. J. Regulation of membrane functions and fatty acid composition in Escherichia coli by cyclic AMP receptor protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Rothman-Denes L. B., Hesse J. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate as mediator of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenbaum P. E., Broman R. L., Dobrogosz W. J. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate and N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate as regulatory signals in catabolite repression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):663–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.663-670.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenbaum P. E., Dobrogosz W. J. The effect of cyclic 3',5'-AMP on catabolite repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):828–833. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport studies in bacterial membrane vesicles. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):882–892. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 8. The transport of amino acids by membranes prepared from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7844–7857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M., Yamamoto T. Conversion of active transport vesicles of Escherichia coli into oxidative phosphorylation vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 25;357(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Náprstek J., Janecek J., Spizek J., Dobrová Z. Culic 3', 5', -adenosine monophosphate and catabolic repression in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., De Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP regulates catabolite and transient repression in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):810–812. doi: 10.1038/223810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Pastan I. Cyclic 3'5-AMP: stimulation of beta-galactosidase and tryptophanase induction in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):656–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90563-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Measurements of rates of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate synthesis in intact Escherichia coli B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2149–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter K., Chaloner-Larsson G., Yamazaki H. Abnormally high rate of cyclic AMP excretion from an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in cyclic AMP receptor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90941-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A. W., Saier M. H., Jr Effects of crp mutations on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate metabolism in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.120-127.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., McCaman M. T. Regulation of intracellular adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate levels in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Evidence for energy-dependent excretion of the cyclic nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7593–7601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Nagata Y., Maruo B. Effect of glucose and its analogues on the accumulation and release of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in a membrane fraction of Escherichia coli: relation to beta-galactosidase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):669–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.669-675.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. H., Jain M. K., Koch A. L. Activation of the beta-galactoside transport system in Escherichia coli ML-308 by n-alkanols. Modification of lipid-protein interaction by a change in bilayer fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne P. K., Fetell J., Rosen O. M. Measurement of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate synthesis in growing Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne P. K., Rosen O. M. Cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate in Escherichia coli during transient and catabolite repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1436–1440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J. Control of amino sugar metabolism in Escherichia coli and isolation of mutants unable to degrade amino sugars. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):847–858. doi: 10.1042/bj1060847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


