Abstract
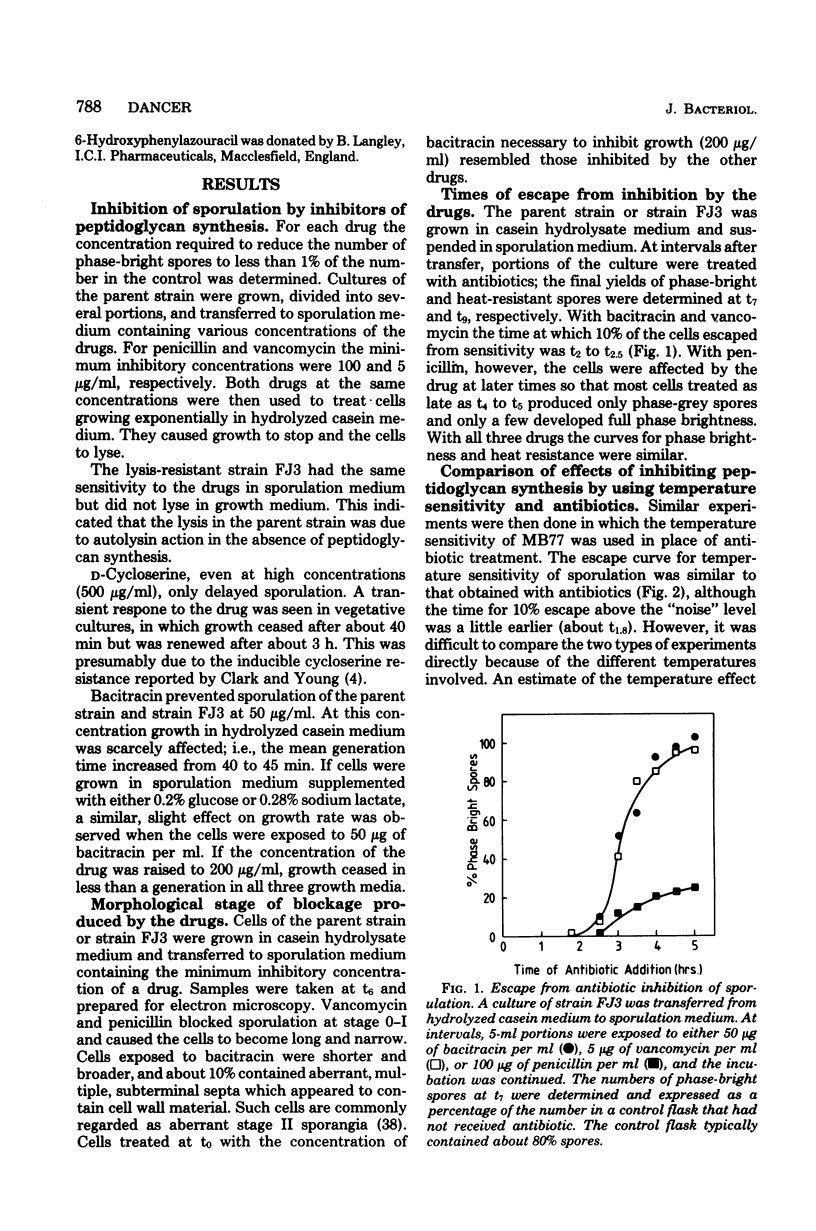
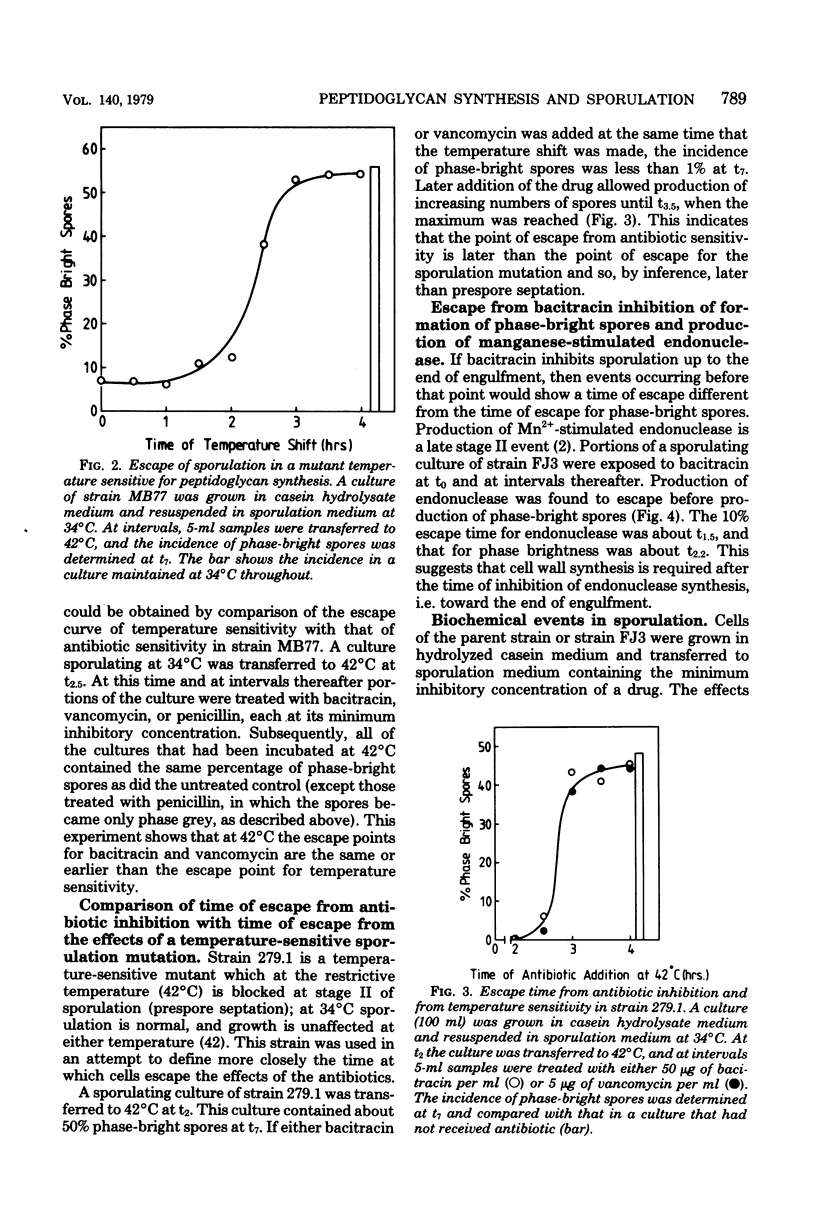
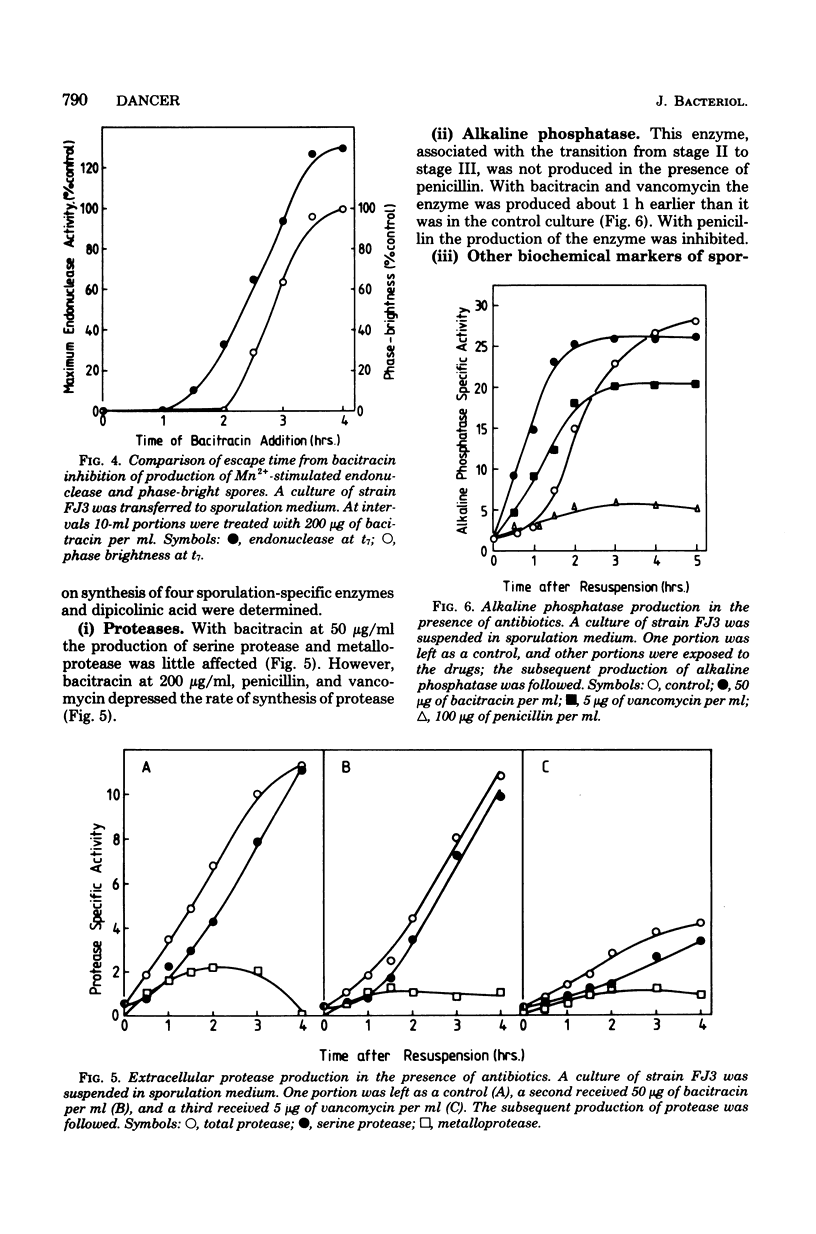
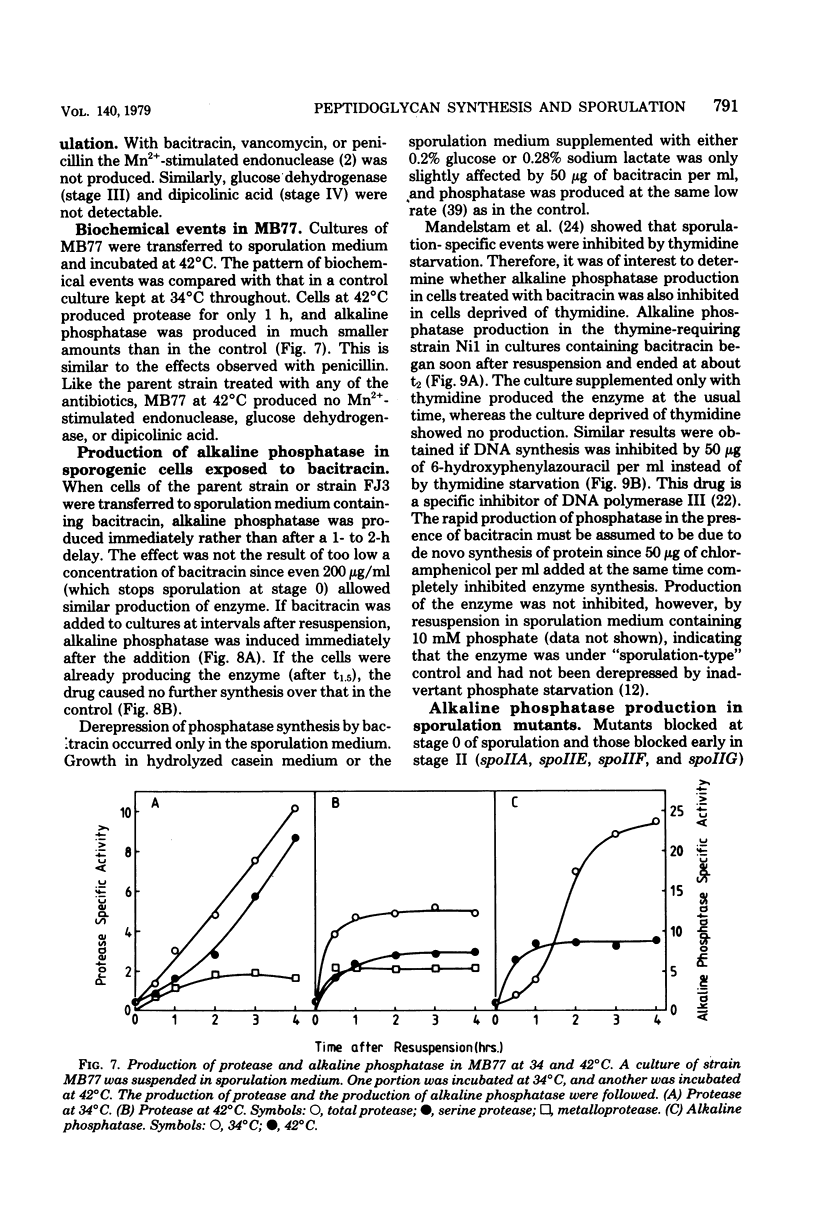
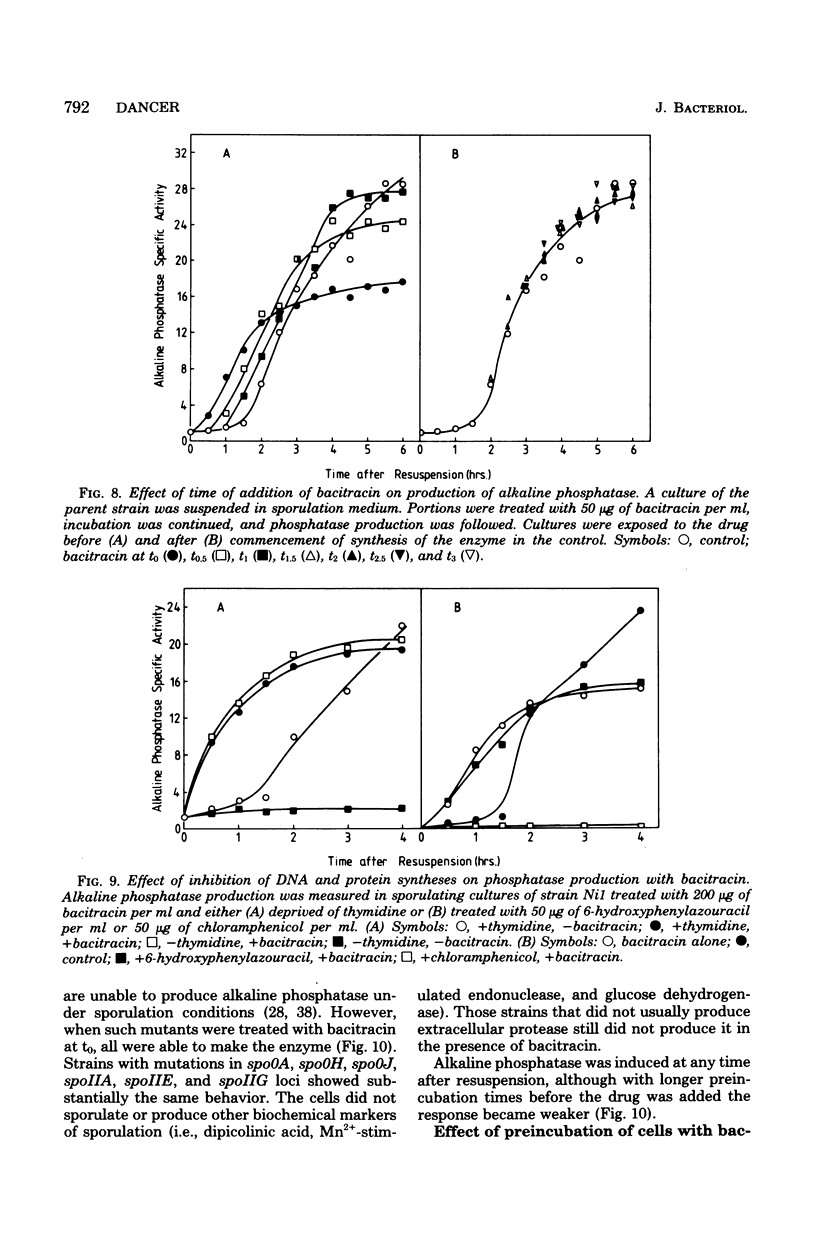
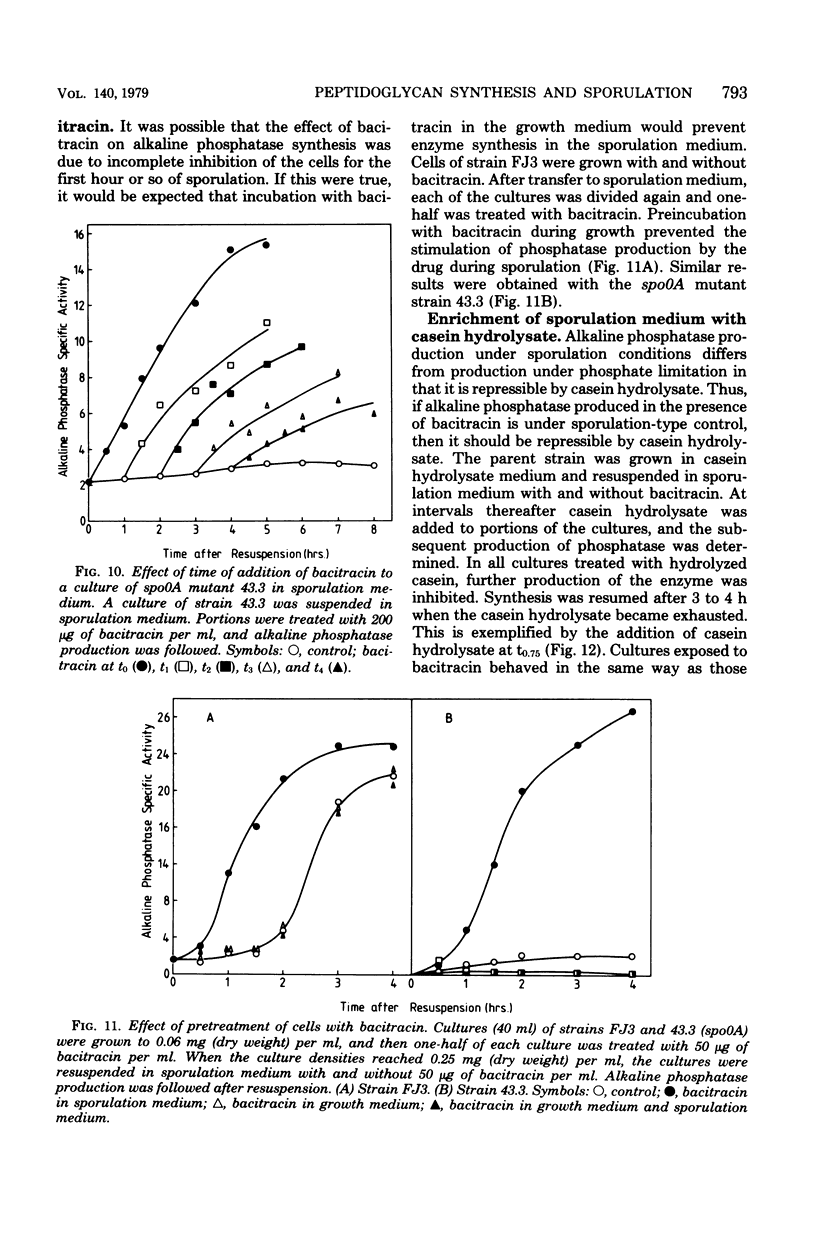
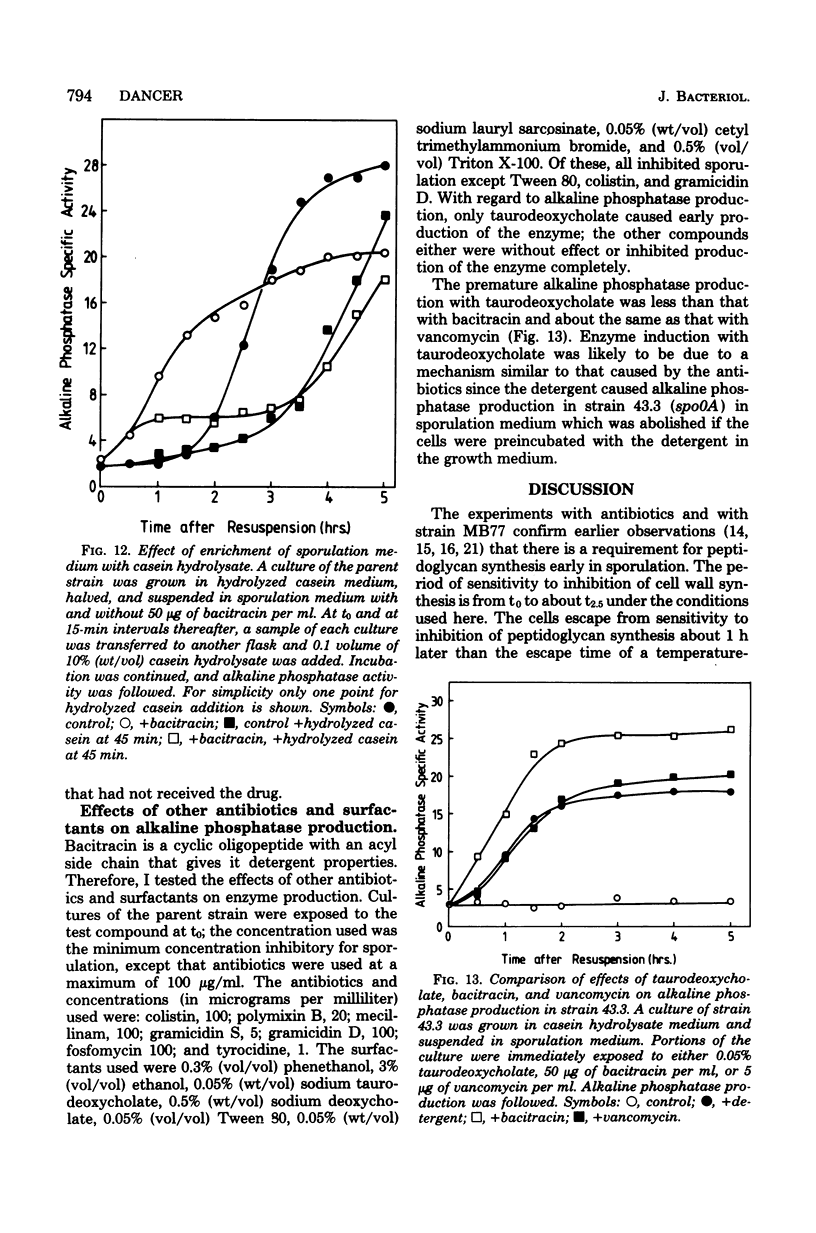
Cultures of Bacillus subtilis were treated during sporulation with antibiotics (bacitracin and vancomycin) that affect peptidoglycan synthesis. The cells were resistant to the effects of the antibiotics only when the drugs were added about 2 h after the beginning of sporulation. This was about 1 h later than the escape time of a temperature-sensitive sporulation mutant that is unable to complete prespore septation. Similar experiments were done with a mutant temperature sensitive for peptidoglycan synthesis. This showed an escape curve similar to that shown by the antibiotics. When sporulating cells were treated with antibiotics, they produced alkaline phosphatase earlier than normal. Enzyme production was unaffected by inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis but was inhibited by chloramphenicol. Sporulation mutants that are unable to make alkaline phosphatase under normal conditions were able to make it in the presence of bacitracin. The alkaline phosphatase made under these conditions was under "sporulation-type" control since its synthesis was repressible by casein hydrolysate and unaffected by inorganic phosphate. When cells were treated with bacitracin in the growth medium as well as in the sporulation medium, alkaline phosphatase synthesis was at the same level as in an untreated control. A number of other antibiotics and surfactants were tested for the ability to cause premature production of the phosphatase of those tested, only taurodeoxycholate whowed this behavior. Moreover, incubation of cells with taurodeoxycholate in the growth medium as well as in the sporulation medium prevented premature enzyme production.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Mandelstam J. Extracellular manganese-stimulated deoxyribonuclease as a marker event in sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):63–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1720063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akrigg A. Purification and properties of a manganese-stimulated deoxyribonuclease produced during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):69–76. doi: 10.1042/bj1720069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti A. R., DeVoe I. W., Ingram J. M. Cell division in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: participation of alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):400–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.400-409.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Young F. E. Inducible resistance to D-cycloserine in Bacillus subtilis 168. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):871–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G. Interference by bromodeoxyuridine with differentiation in a prokaryote. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):635–637. doi: 10.1038/267635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G., Mandelstam J. Use of constructed double mutants for determining the temporal order of expression of sporulation genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1254–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1254-1263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancer B. N., Mandelstam J. Production and possible function of serine protease during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):406–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.406-410.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. C. SPORULATION IN PROTOPLASTS AND ITS DEPENDENCE ON PRIOR FORESPORE DEVELOPMENT. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.667-675.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein J. E., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzyme-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1427–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1427-1442.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. B., Cole R. M., Klofat W., Freese E. Growth, sporulation, and enzyme defects of glucosamine mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1046–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1046-1062.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn A. R., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase from sporulating and vegetative cells. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1230129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. D. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Control of synthesis of alkaline phosphatase. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):363–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D. Polarity and topology of DNA segregation and septation in cells and sporangia of the bacilli. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Oct;24(10):1104–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D., Slepecky R. A. Antibiotic inhibition of the septation stage in sporulation of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1513-1515.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Gauther J. J., Tipper D. J. Ultrastructural studies of sporulation in Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1322–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1322-1338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J. Penicillin: reversible inhibition of forespore septum development in Bacillus megaterium cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):815–820. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love E., D'Ambrosio D., Brown N. C. Mapping of the gene specifying DNA polymerase III of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00341730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Sterlini J. M., Kay D. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Effect of medium on the form of chromosome replication and on initiation to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):635–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1250635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J. The Leeuwenhoek lecture, 1975: bacterial sporulation: a problem in the biochemistry and genetics of a primitive developmental system. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Apr 13;193(1111):89–106. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., LYNCH J. L. Studies on the inhibition of D-alanyl-D-alanine synthetase by the antibiotic D-cycloserine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Aug 7;8:377–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J. Mapping of asporogenous mutations of Bacillus subtilis: a minimum estimate of the number of sporeulation operons. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1241–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1241-1253.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Taylor S. Y. New types of mutation affecting formation of alkaline phosphatase by Bacillus subtilis in sporulation conditions. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):69–80. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A. ETUDE MORPHOLOGIQUE DE LA SPORULATION DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jan;108:40–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Control of cell length in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):7–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.7-19.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert G., Strominger J. L. Bacitracin: an inhibitor of the dephosphorylation of lipid pyrophosphate, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):767–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites W. M., Kay D., Dawes I. W., Wood D. A., Warren S. C., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Correlation of biochemical events with morphological changes in asporogenous mutants. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1180667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochemical changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj1090811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warth A. D., Strominger J. L. Structure of the peptidoglycan from spores of Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1389–1396. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Use of temperature-sensitive mutants to study gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):928–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.928-936.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



