Abstract
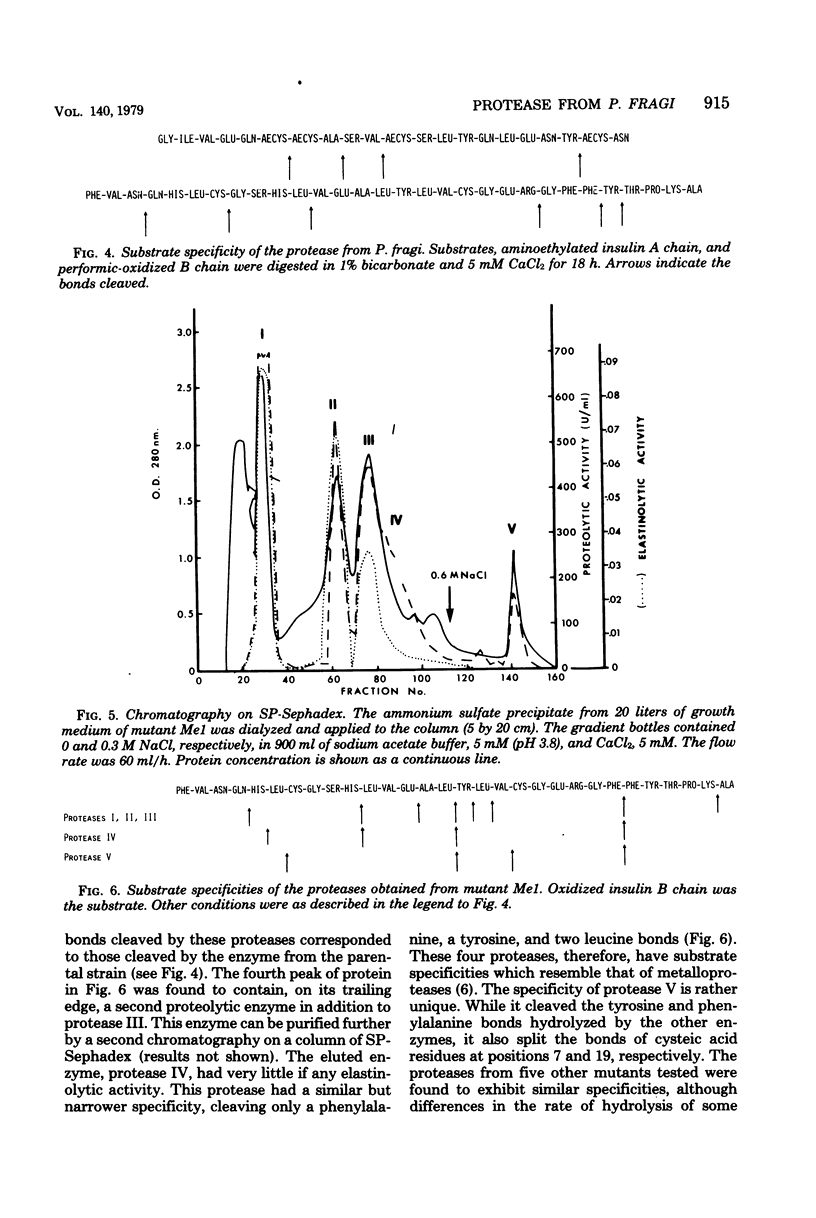
A simplified procedure for the purification of the extracellular protease of Pseudomonas fragi was developed. The enzyme was isolated from a derepressed mutant producing 40 times the enzyme level of the parental organism. It was collected from culture filtrates by ammonium sulfate precipitation, and it was obtained in pure form by single chromatography on a column of diethylaminoethyl cellulose. The protease had a molecular weight of 52,000 as estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis and had properties of a classical neutral endopeptidase with the exception of its substrate specificity. Mutants of P. fragi producing proteases of altered substrate specificities were isolated from plates containing elastin as the sole carbon source. The SP-Sephadex elution patterns of enzymes extracted from each mutant examined were complex, suggesting that either the enzyme was autodigested or several active forms could be generated from a common precursor. The substrate specificities of the mutant enzymes were different from that produced by the parental strain.
Full text
PDF
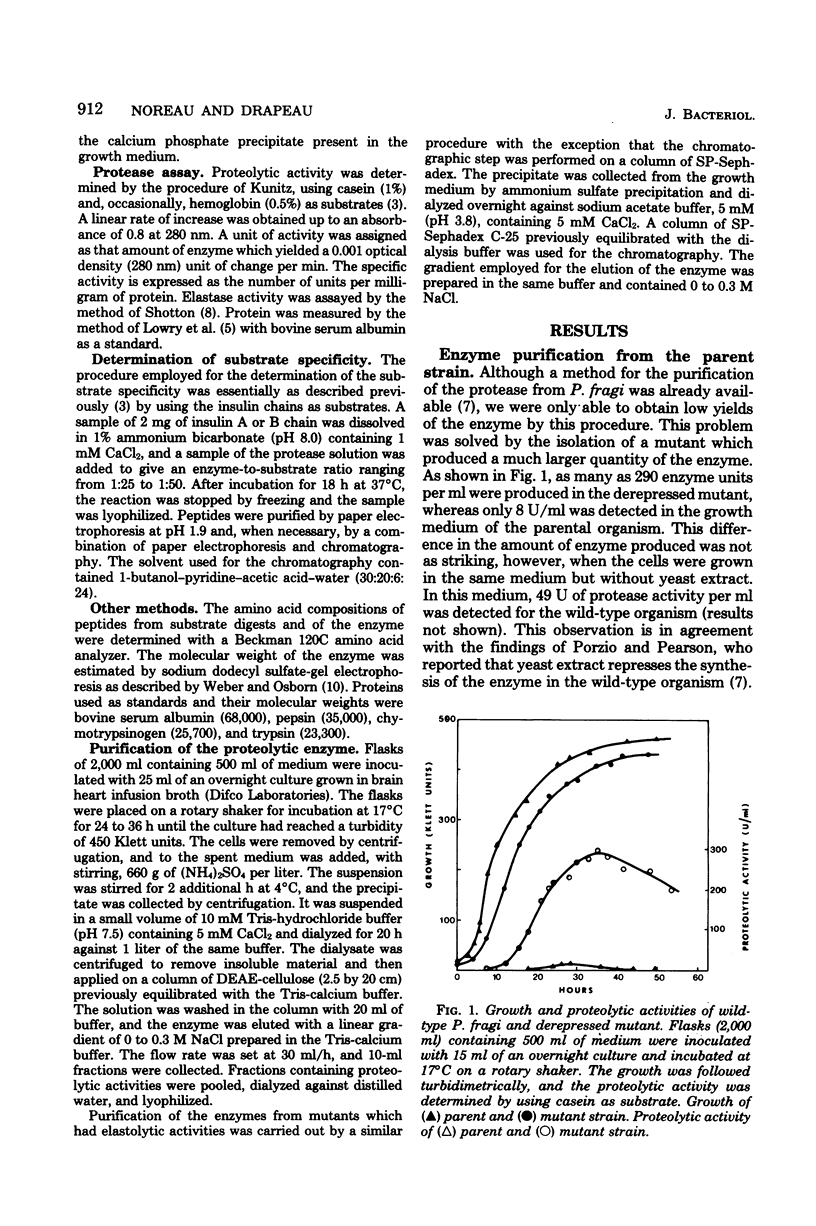
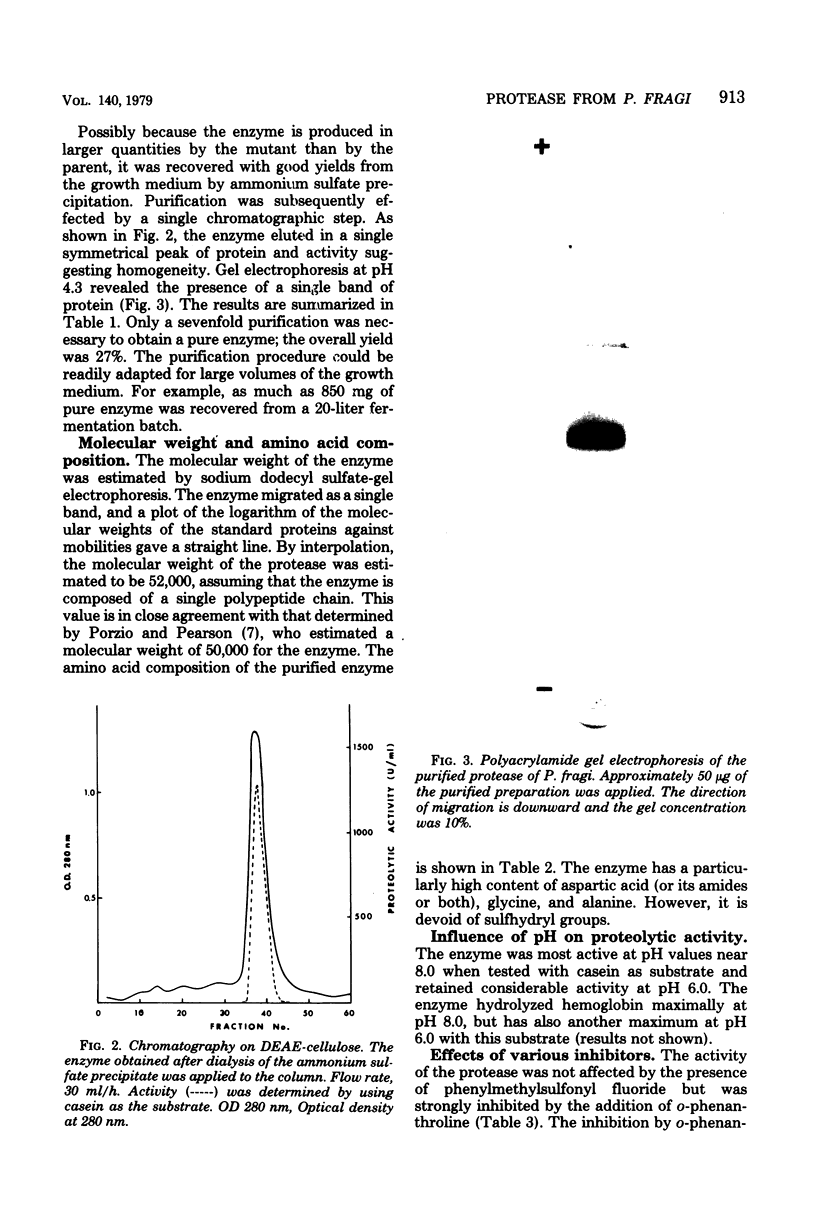

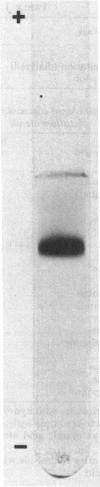
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drapeau G. R., Boily Y., Houmard J. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6720–6726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R. Role of metalloprotease in activation of the precursor of staphylococcal protease. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.607-613.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzio M. A., Pearson A. M. Isolation of an extracellular neutral proteinase from Pseudomonas fragi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;384(1):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Watson H. C. Three-dimensional structure of tosyl-elastase. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):811–816. doi: 10.1038/225811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]