Abstract
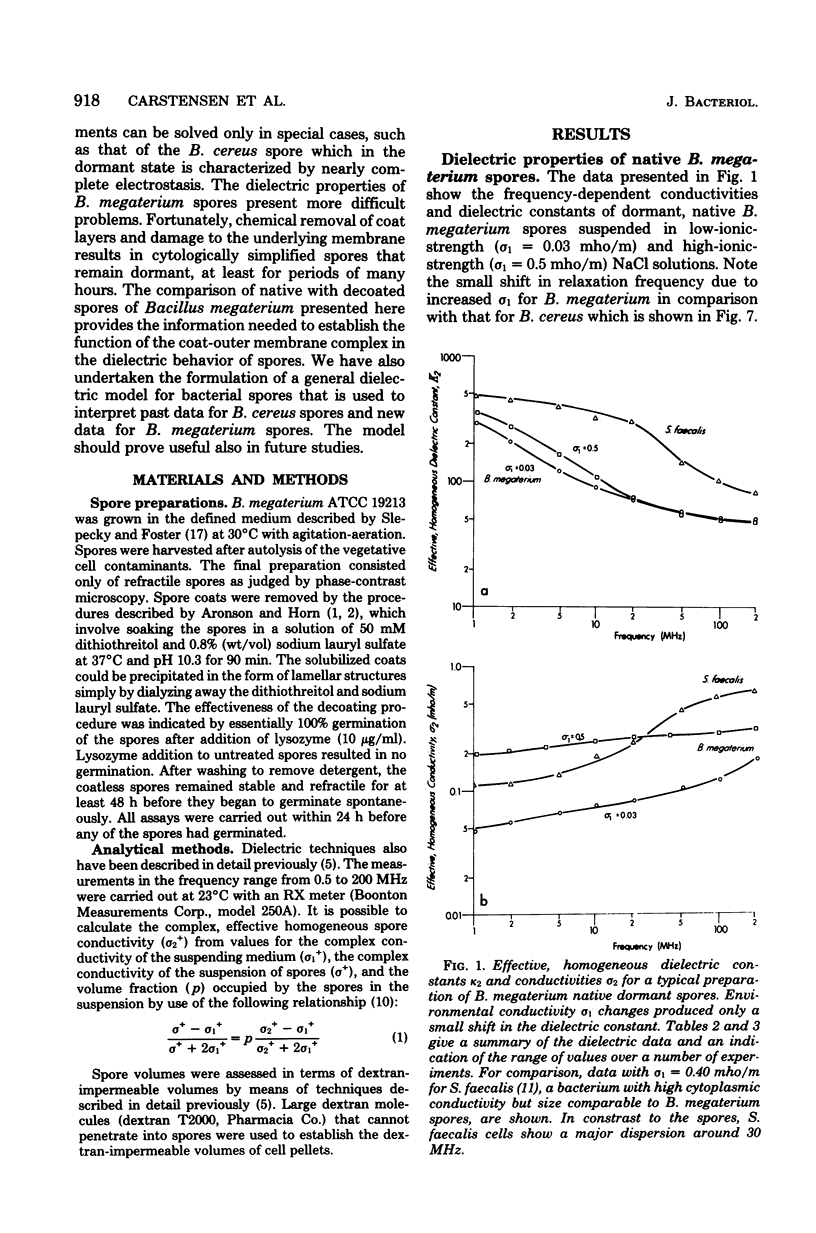
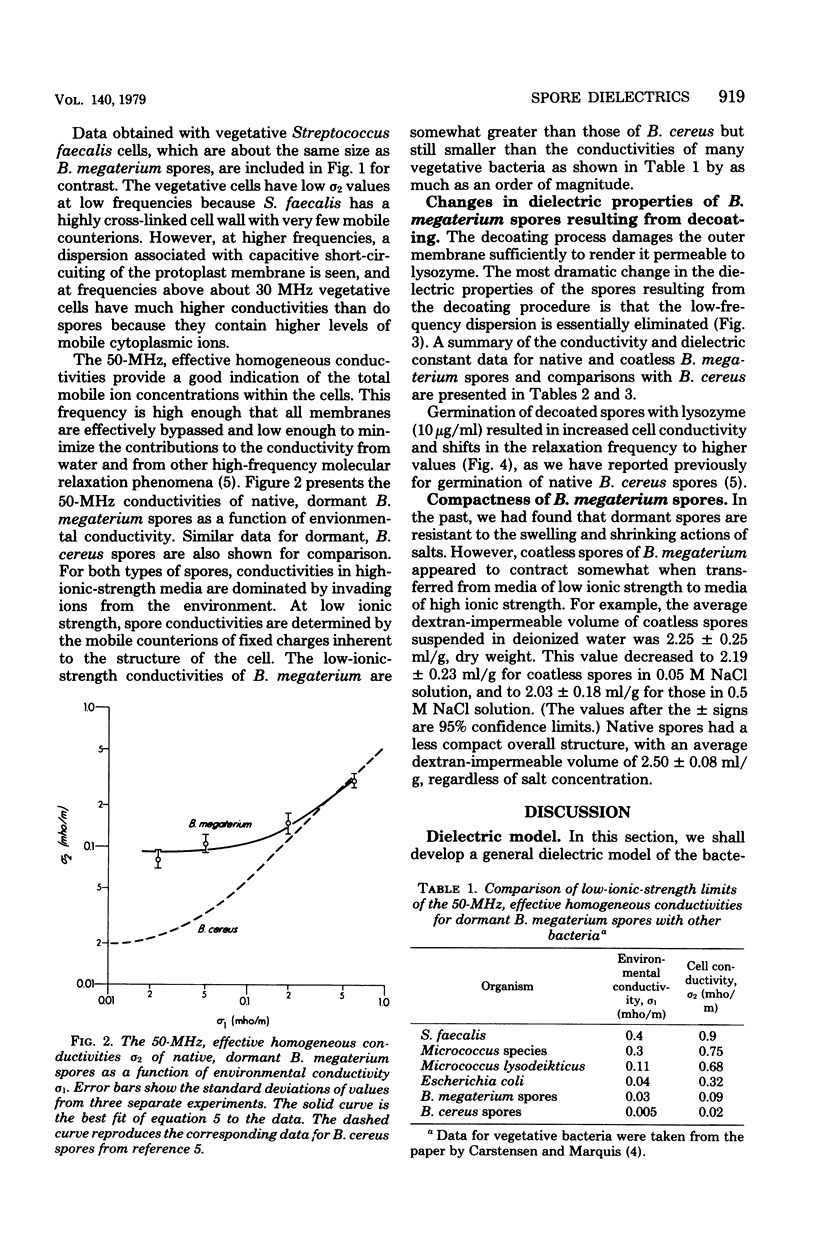
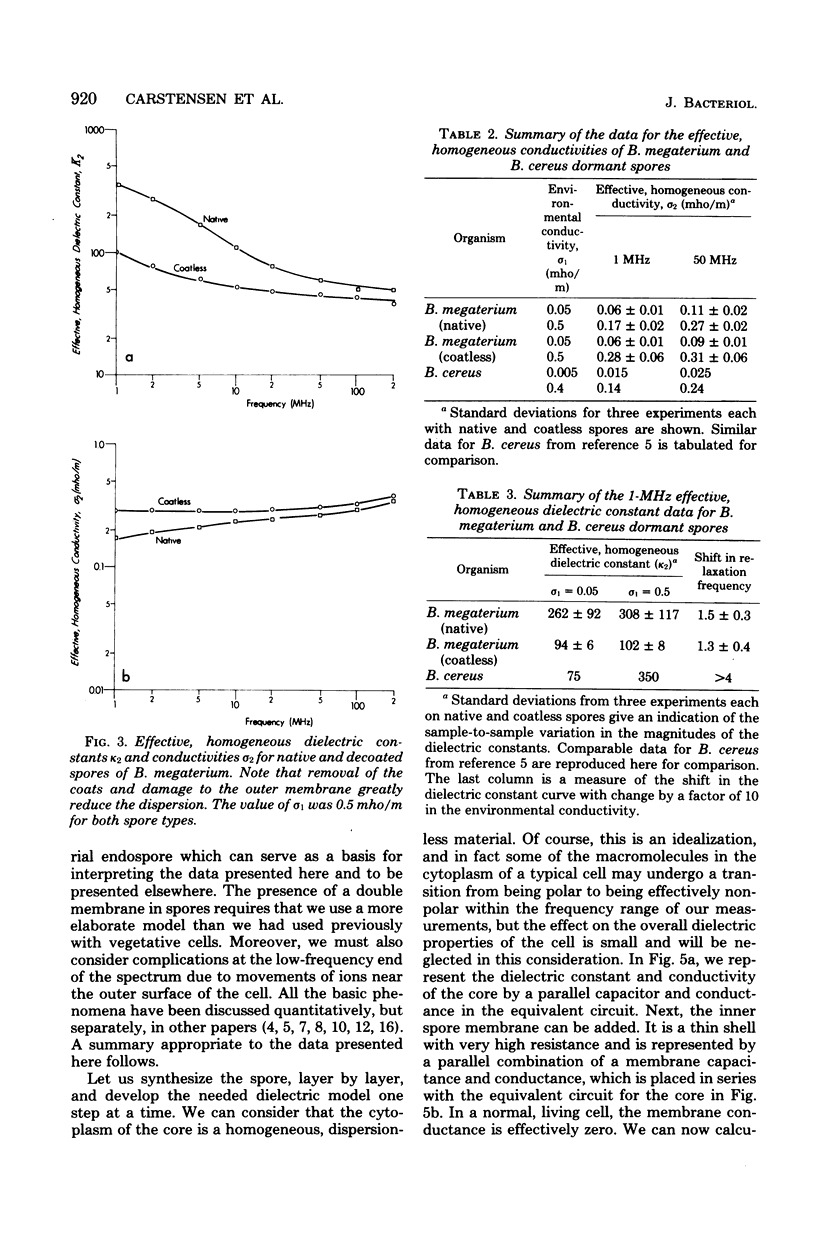
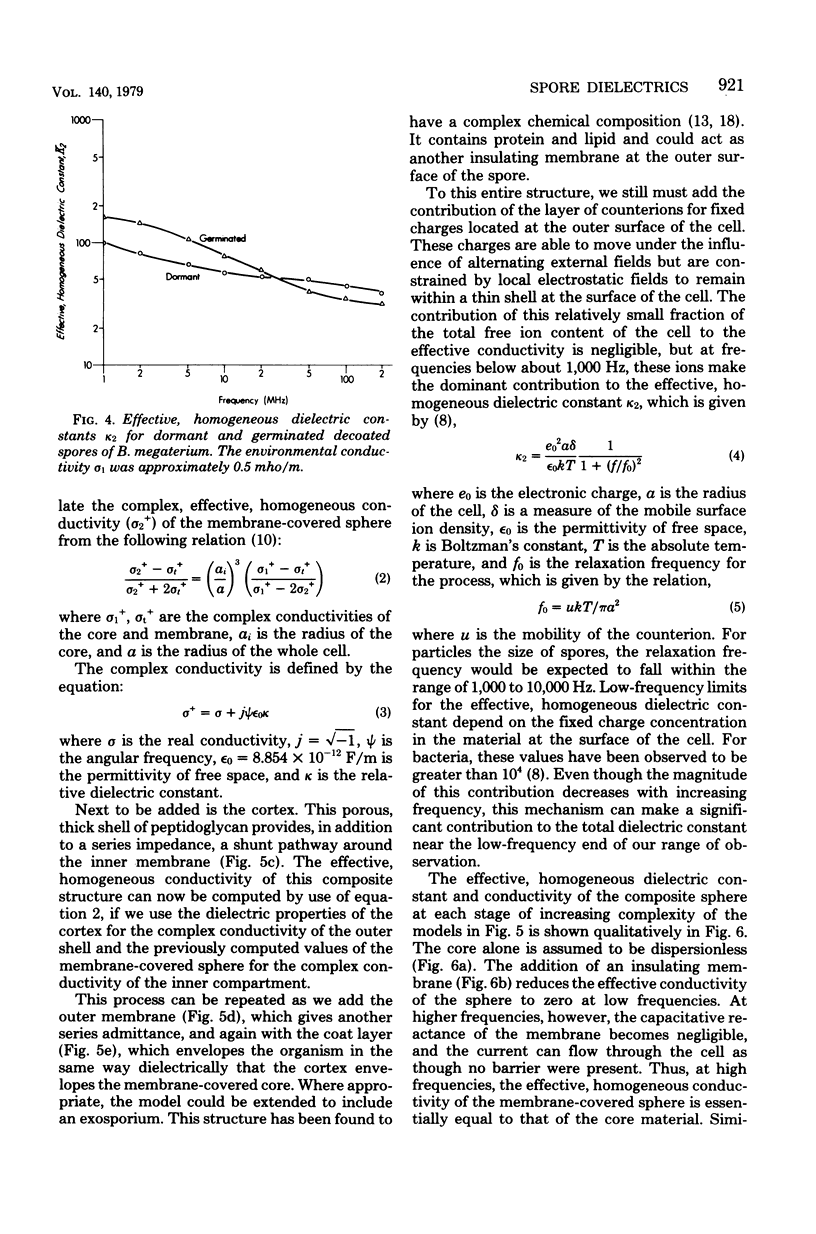
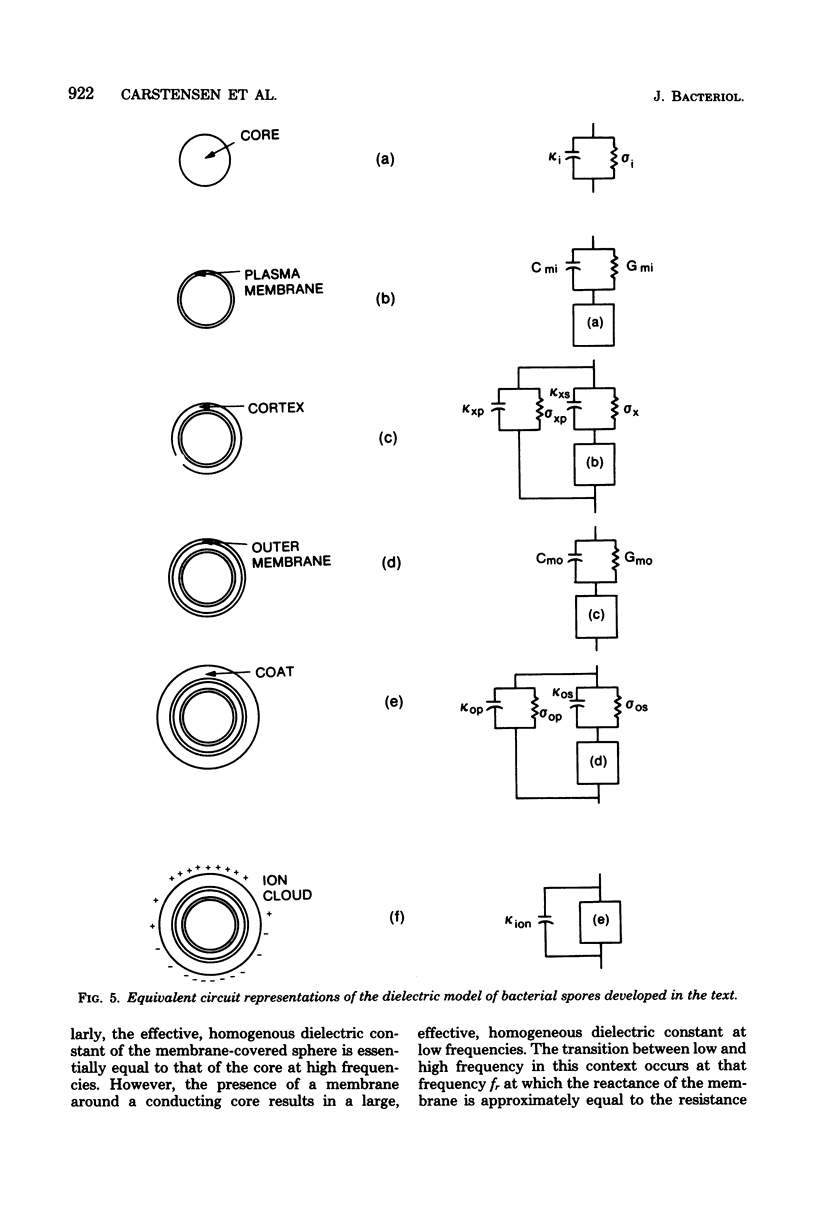
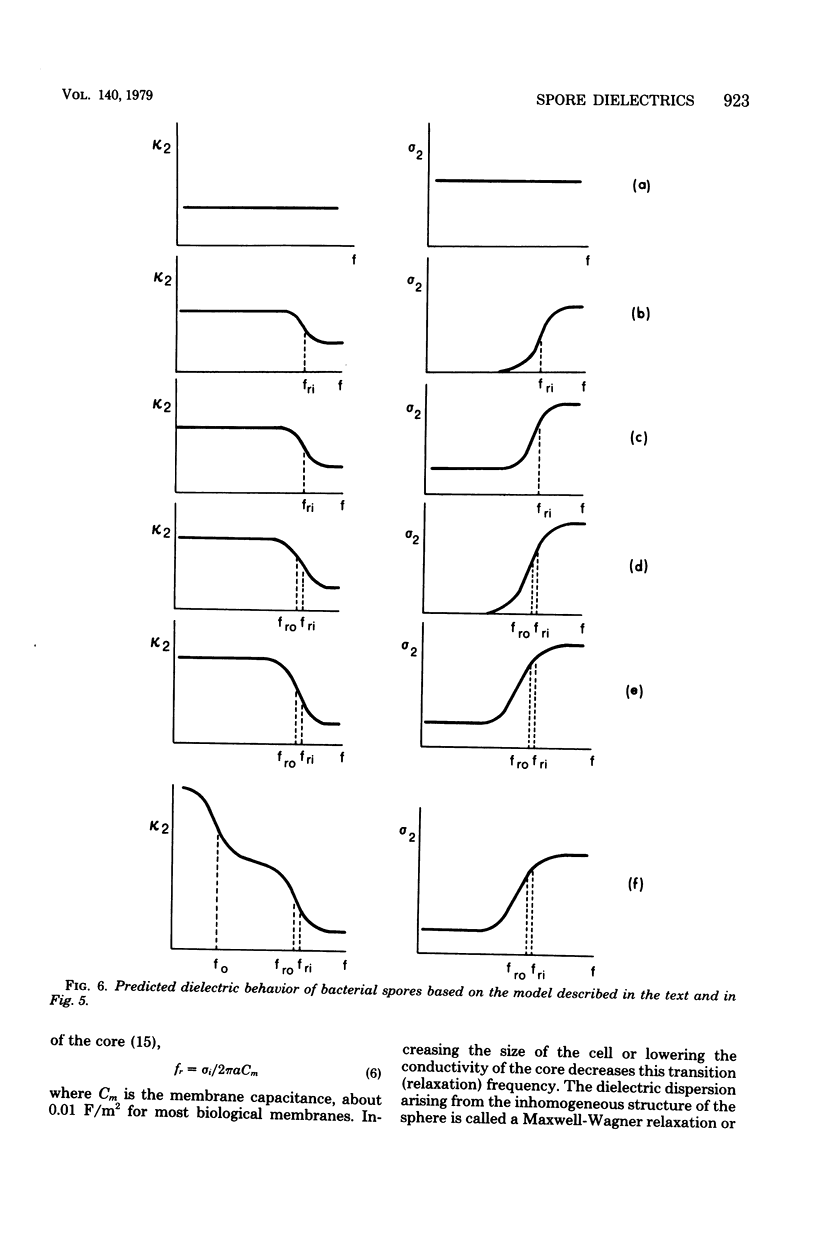
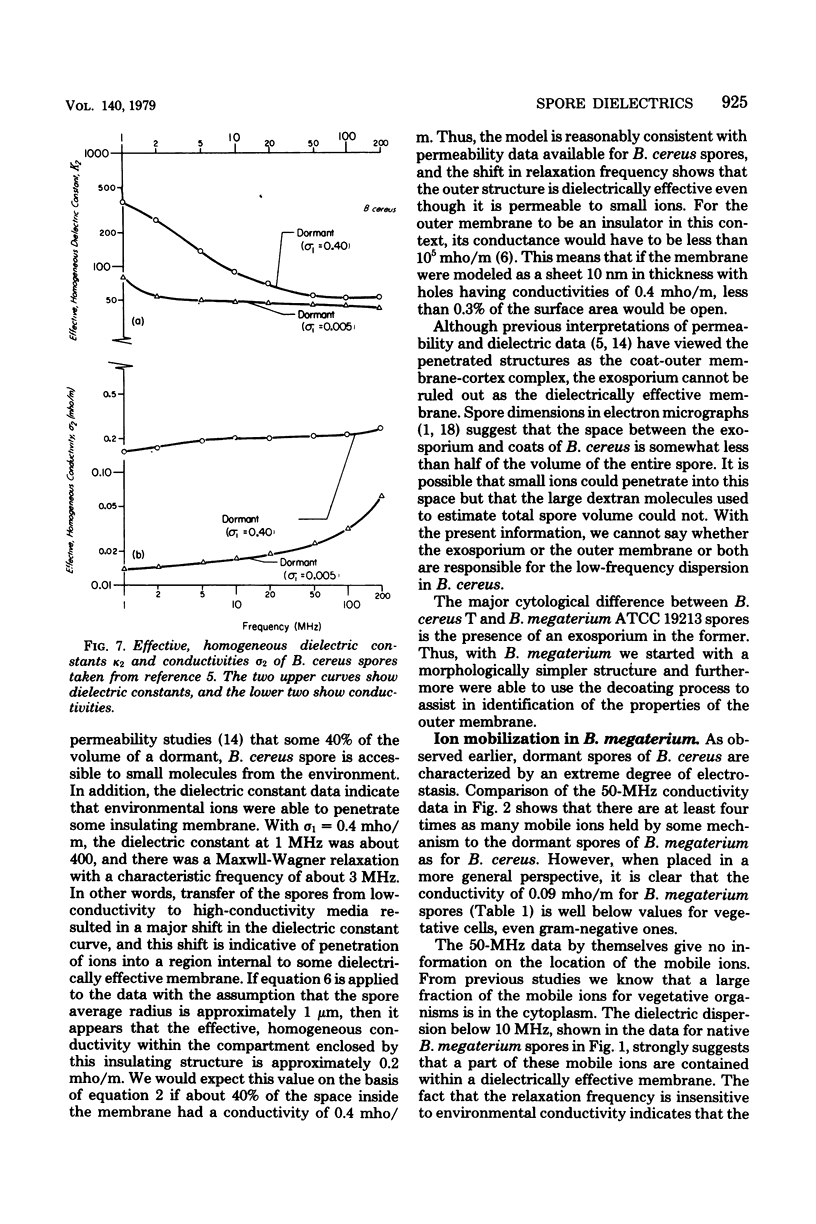
A general model for use in interpreting dielectric data obtained with bacterial endospores is developed and applied to past results for Bacillus cereus spores and new results for Bacillus megaterium spores. The latter were also subjected to a decoating treatment to yield dormant cells with damaged outer membranes that could be germinated with lysozyme. For both spore types, core ions appeared to be completely immobilized, and decoating of B. megaterium spores did not affect this extreme state of electrostasis in the core. The cortex of B. megaterium appeared to contain a high level of mobile ions, in the cortex of B. cereus. The outer membrane-coat complex of B. megaterium acted dielectrically as an insulating layer around the cortex, so that native dormant spores showed a Maxwell-Wagner dispersion over the frequency range from about 1 to 20 MHz. The decoating treatment resulted in a shift in the dispersion to frequencies below the range of observation. Increases in cell conductivity in response to increases in environmental ionic strength indicated that the coats. of B. megaterium could be penetrated by environmental ions and that they had an inherent fixed charge concentration of about 10 to 20 milliequivalents per liter. In contrast, the dispersion for B. cereus spores was very sensitive to changes in environmental ion concentration, and it appeared that some 40% of the spore volume could be penetrated by environmental ions and that these ions traversed a dielectrically effective layer, either the exosporium or the outer membrane. It appears that dormancy is associated with extreme electrostasis of core ions but not necessarily of ions in enveloping structures and that the coat-outer membrane complex is dielectrically effective but not required for maintenance of extreme electrostasis in the core.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. Structure and morphogenesis of the bacterial spore coat. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):360–402. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.360-402.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Cox H. A., Mercer W. B., Natale L. A. Passive Electrical Properties of Microorganisms: I. Conductivity of Escherichia coli and Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biophys J. 1965 May;5(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(65)86717-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Marquis R. E., Gerhardt P. Dielectric study of the physical state of electrolytes and water within Bacillus cereus spores. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.106-113.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Smearing R. W. Dielectric properties of osmium-fixed erythrocytes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1967 Oct;14(4):216–222. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1967.4502508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Bacterial conductivity in the determination of surface charge by microelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):506–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. V. Low-frequency dielectric dispersion of bacteria. Biophys J. 1973 Jan;13(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85966-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E., Carstensen E. L. Electric conductivity and internal osmolality of intact bacterial cells. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1198–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1198-1206.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E., Mayzel K., Carstensen E. L. Cation exchange in cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):975–982. doi: 10.1139/m76-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz L. L., Beaman T. C., Gerhardt P. Chemical composition of exosporium from spores of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.196-201.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAN H. P. Electrical properties of tissue and cell suspensions. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1957;5:147–209. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3111-2.50008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEPECKY R., FOSTER J. W. Alterations in metal content of spores of Bacillus megaterium and the effect on some spore properties. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.117-123.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer R., Cabrera Beaman T., Gerhardt P. Macromolecular sieving by the dormant spore of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):868–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.868-873.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



