Abstract
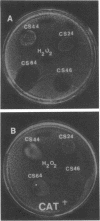
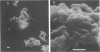
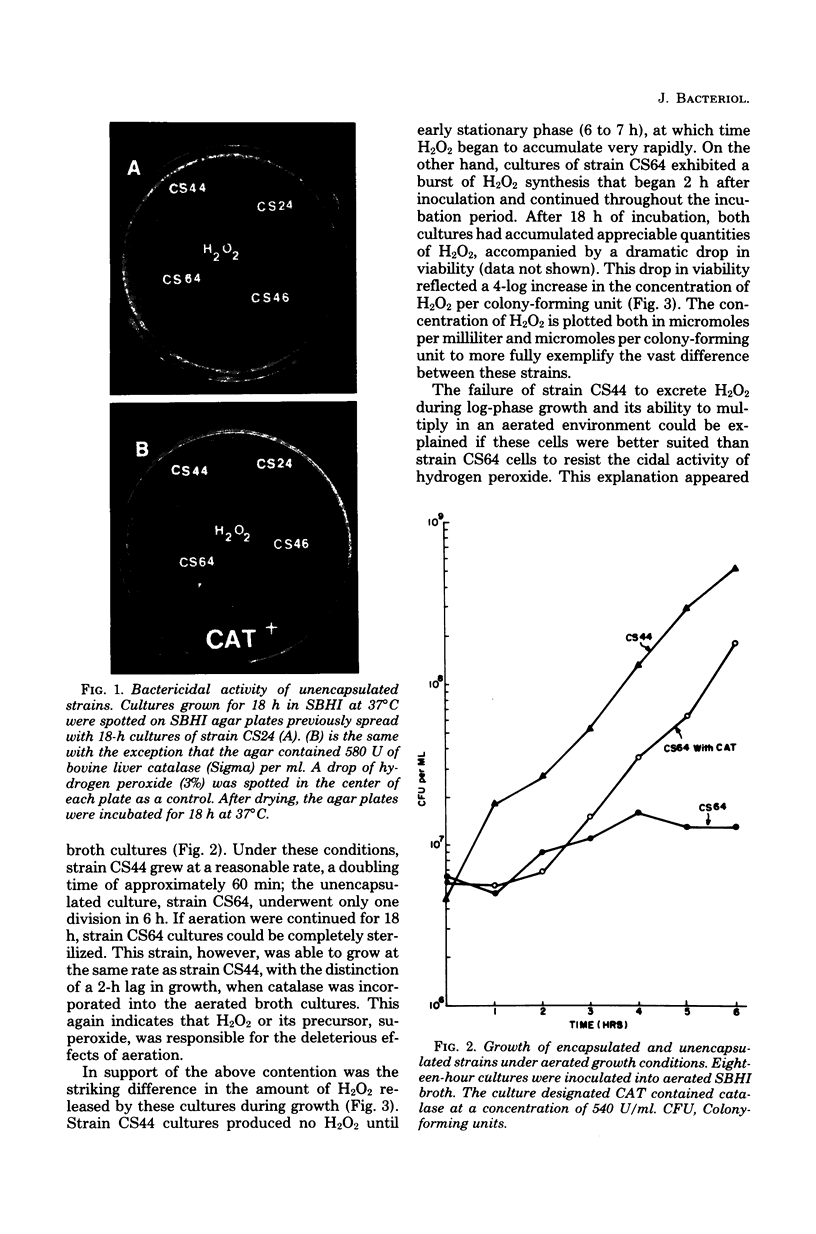
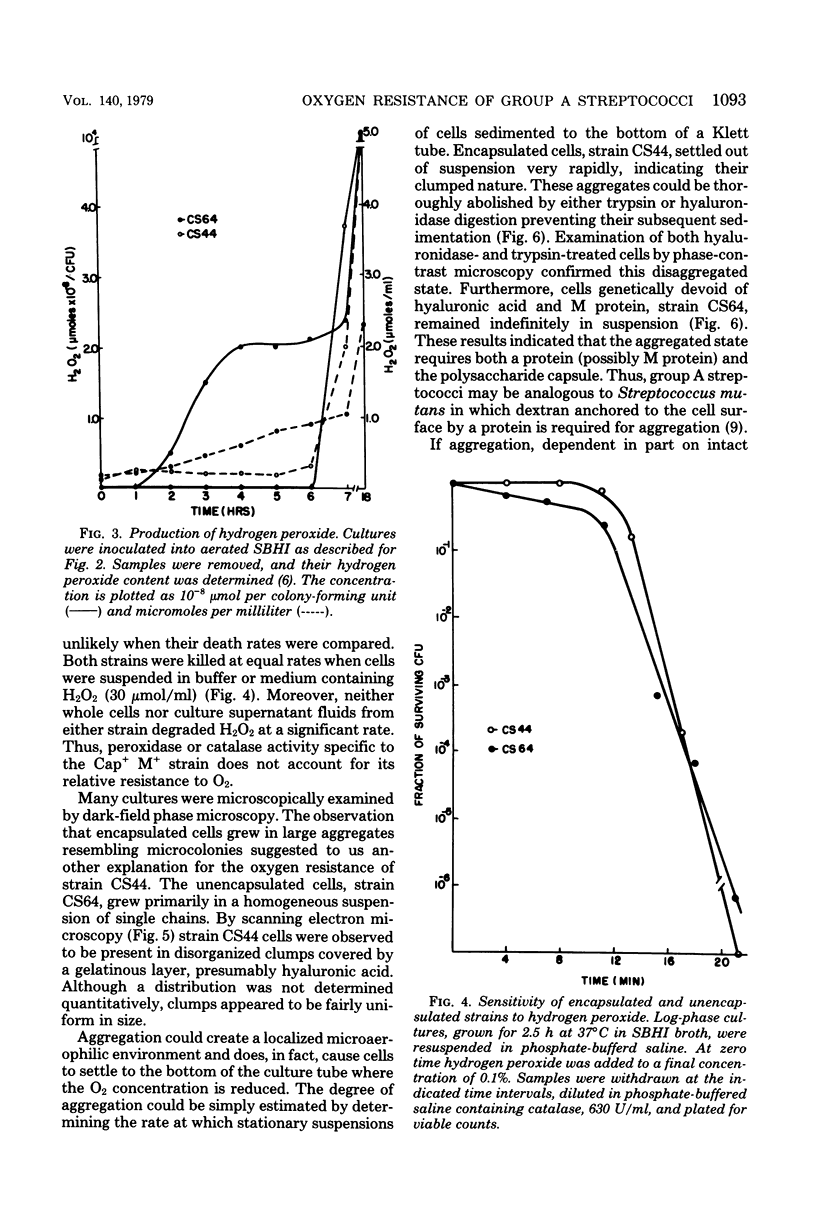
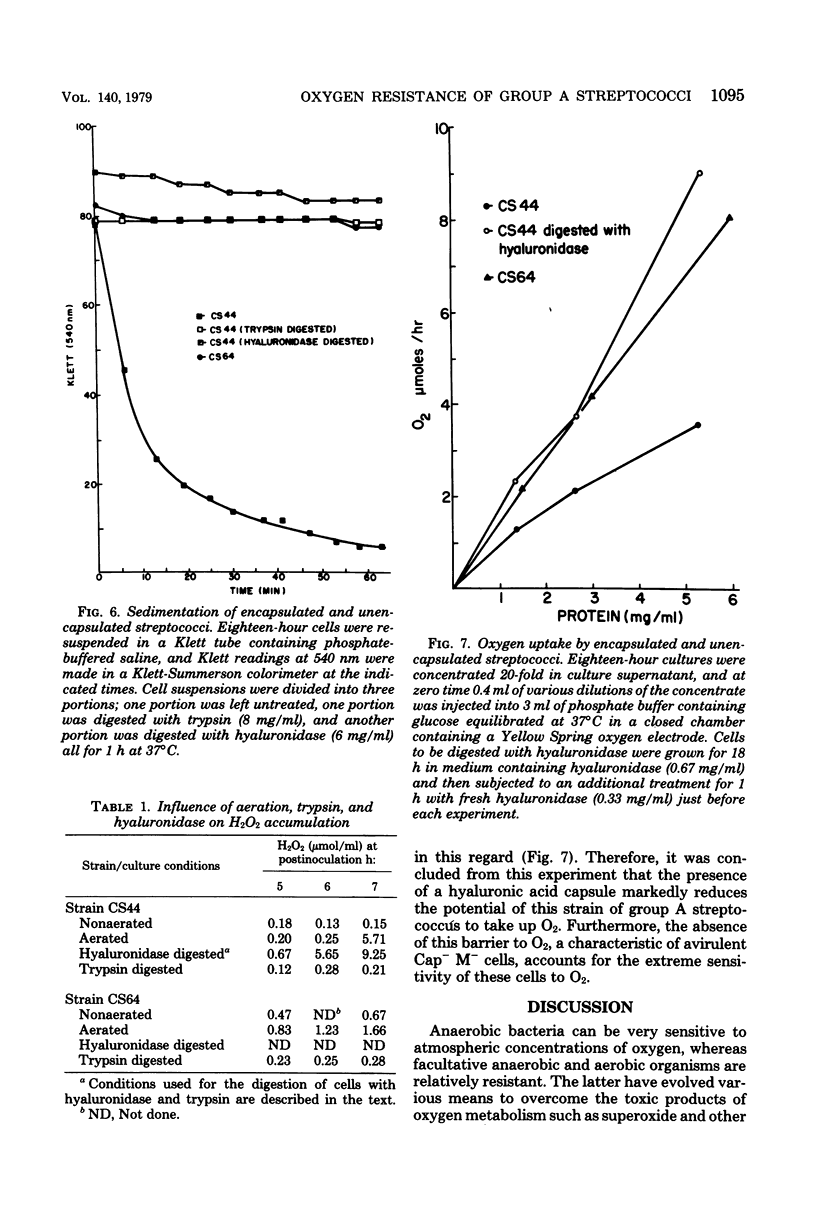
Unencapsulated variants of encapsulated, M-protein-positive group A streptococci are oxygen sensitive and secrete inhibitory concentrations of hydrogen peroxide when grown in aerated broth cultures. The organisms were equally sensitive to hydrogen peroxide, and neither exhibited catalase or peroxidase activity, suggesting that differences in oxygen sensitivity reflect dissimilarity in oxygen uptake. The encapsulated parental culture was found to grow in aggregates that take up oxygen more slowly than unencapsulated, oxygen-sensitive derivatives. Moreover, the latter grow in an unaggregated, homogenous suspension. The enzyme hyaluronidase was able to disrupt aggregates of the encapsulated strain increase the rate that these cells take up oxygen, and cause the accumulation of toxic concentrations of hydrogen peroxide earlier in their growth cycle. The evidence presented shows that the aggregation of streptococcal cells by their hyaluronic acid capsule provides this organism with a novel means to avoid self-destruction by oxygen metabolites--cells are shielded from oxygen. The reduced surface-to-volume ratio and limited diffusion of oxygen into the interior of aggregates are proposed as the protective mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthaswamy H. N., Eisenstark A. Repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced single-strand breaks in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.187-191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton L., Malinowski D. P., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase and oxygen metabolism in Streptococcus faecalis and comparisons with other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.229-236.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Johnson Z. Possible dual function of M protein: resistance to bacteriophage A25 and resistance to phagocytosis by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):280–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.280-292.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Johnson Z., Wannamaker L. Genetic instability of M protein and serum opacity factor of group A streptocci: evidence suggesting extrachromosomal control. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):109–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.109-118.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emiliani E., Riera B. Enzymatic oxalate decarboxylation in Aspergillus niger. II. Hydrogen peroxide formation and other characteristics of the oxalate decarboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 8;167(2):414–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E. B., Gerson J., Taber H., Rhaese H. J., Freese E. Inactivating DNA alterations induced by peroxides and peroxide-producing agents. Mutat Res. 1967 Sep-Oct;4(5):517–531. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F. Streptococcus mutans dextransucrase: mode of interaction with high-molecular-weight dextran and role in cellular aggregation. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):365–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.365-372.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmström B., Ricica J. Production of hyaluronic Acid by a streptococcal strain in batch culture. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1409-1413.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A., JACOB F., RITZ E., GAGE M. Induction de la production de bactériophages et d'une colicine par les peroxydes, les ethylèneimines et les halogénoalcoylamines. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1952 Jun 4;234(23):2308–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malke H., Starke R., Jacob H. E., Köhler W. Bacteriocine-like activity of group-A streptococci due to the production of peroxide. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):367–374. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Keele B. B., Jr, Fridovich I. An enzyme-based theory of obligate anaerobiosis: the physiological function of superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1024–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEELEY H. W., VANDEMARK P. J. An adaptive peroxidation by Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;61(1):27–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.1.27-35.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T. The relative importance of the capsule and the M-antigen in determining colony form of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W., Almquist S., Skjold S. Intergroup phage reactions and transduction between group C and group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1338–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]