Abstract
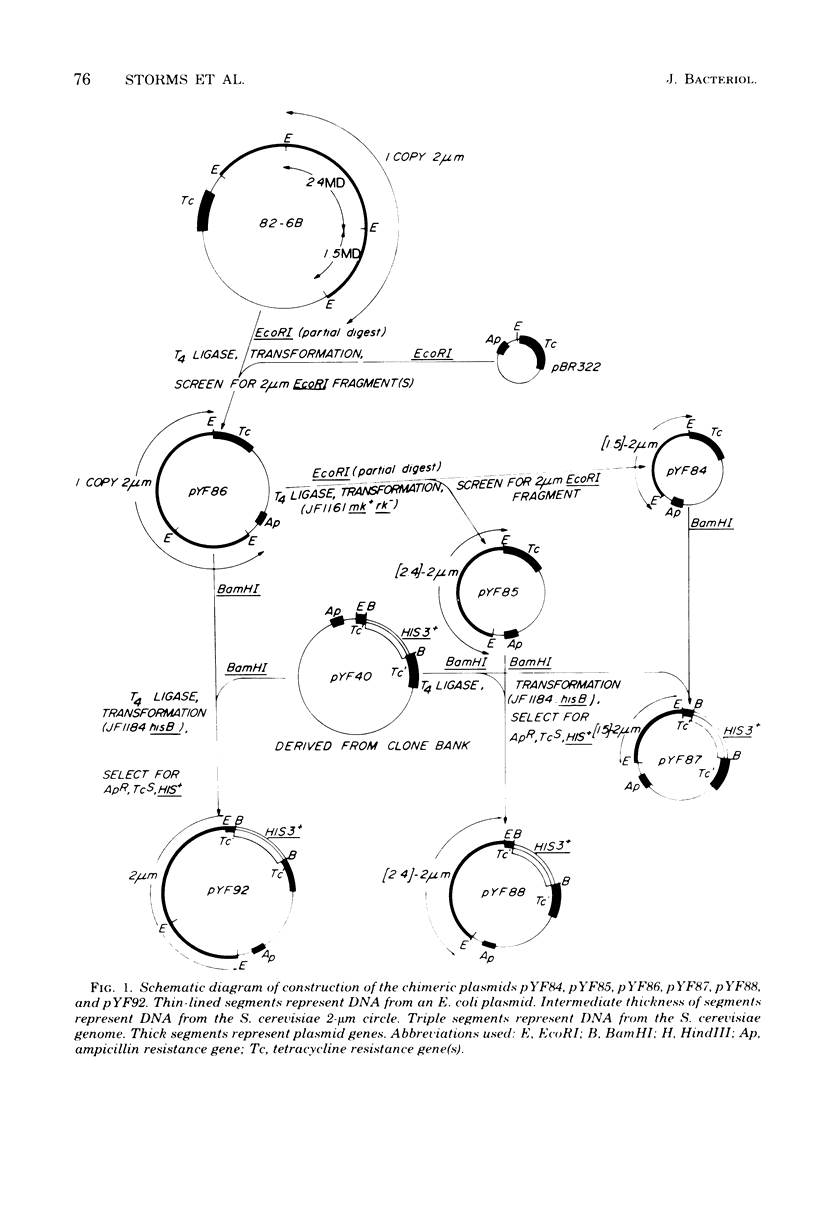
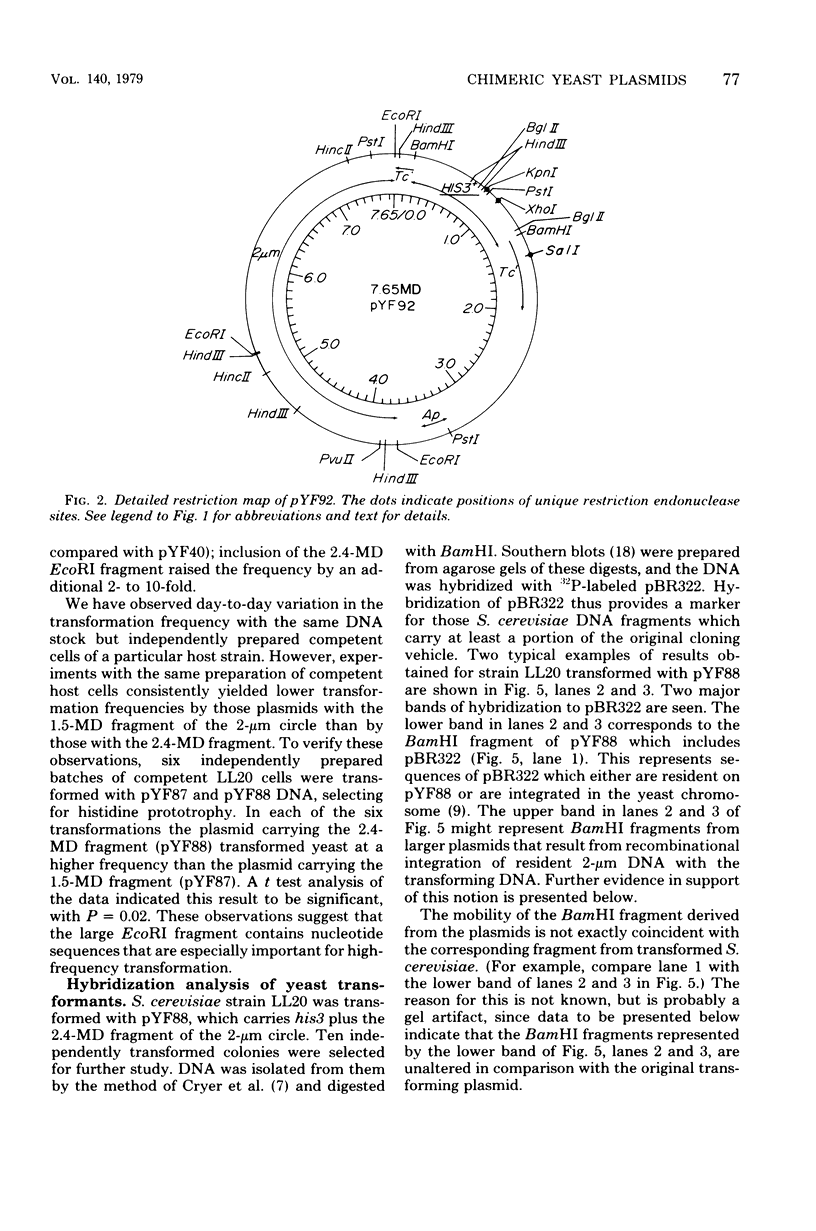
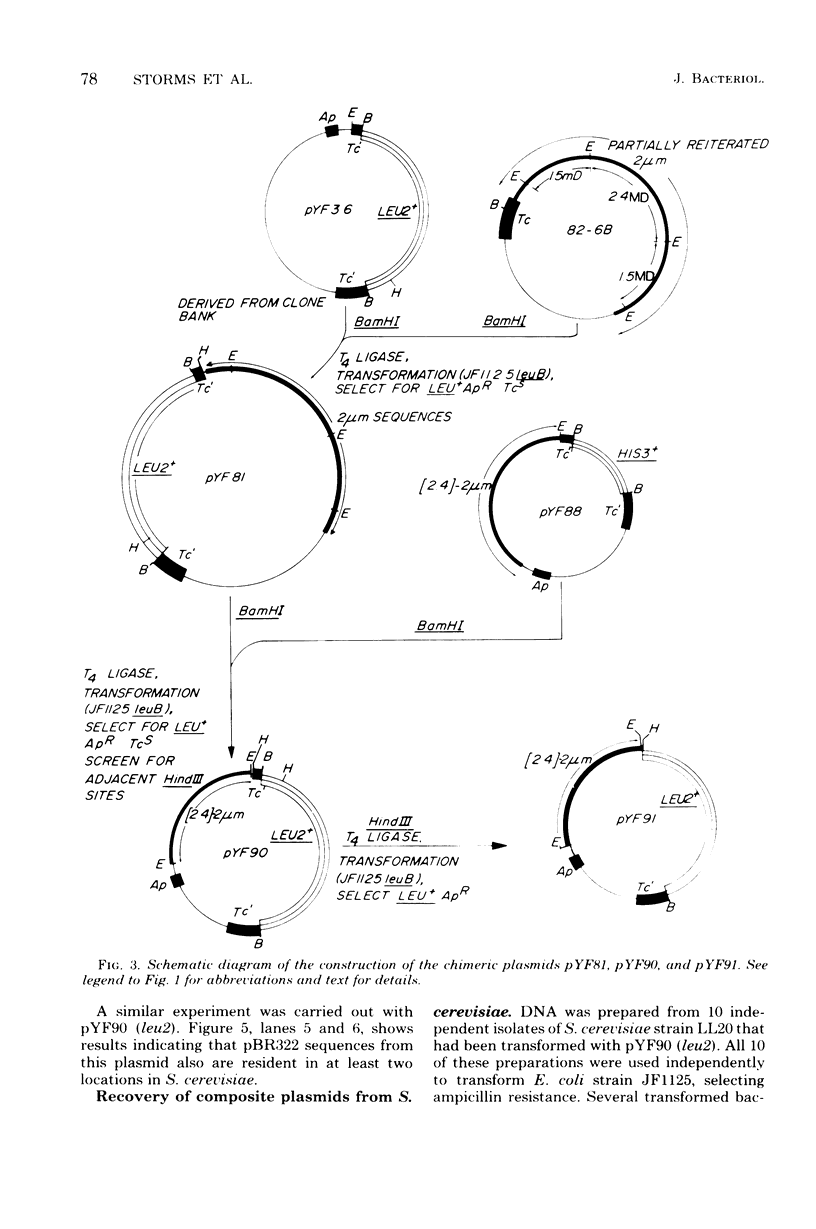
Two sets of plasmids, each carrying a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene and a portion or all of the yeast 2-micron circle linked to the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322, have been constructed. One of these sets contains a BamHI fragment of S. cerevisiae deoxyribonucleic acid that includes the yeast his3 gene, whereas the other set contains a BamHI fragment of S. cerevisiae that includes the yeast leu2 gene. All plasmids transform S. cerevisiae and E. coli with a high frequency, possess unique restriction endonuclease sites, and are retrievable from both host organisms. Plasmids carrying the 2.4-megadalton EcoRI fragment of the 2-micron circle transform yeast with 2- to 10-fold greater frequency than those carrying the 1.5-megadalton EcoRI fragment of the 2-micron circle. Restriction endonuclease analysis of plasmics retrieved from S. cerevisiae transformed with plasmics carrying the 2.4-megadalton EcoRI fragment showed that in 13 of 96 cases the original plasmic has acquired an additional copy of the 2-mcron circle. These altered plasmids appear to have arisen by means of an interplasmid recombination event while in S. cerevisiae. A clone bank of S. cerevisiae genes based upon one of these composite plasmids has been constructed. By using this bank and selecting directly in S. cerevisiae, the ura3, tyr1, and met2 genes have been cloned.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. H. Growth Requirements of Virus-Resistant Mutants of Escherichia Coli Strain "B". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1946 May;32(5):120–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.32.5.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzkin B., Carbon J. Functional expression of cloned yeast DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):487–491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Functional genetic expression of eukaryotic DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1471–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]