Abstract
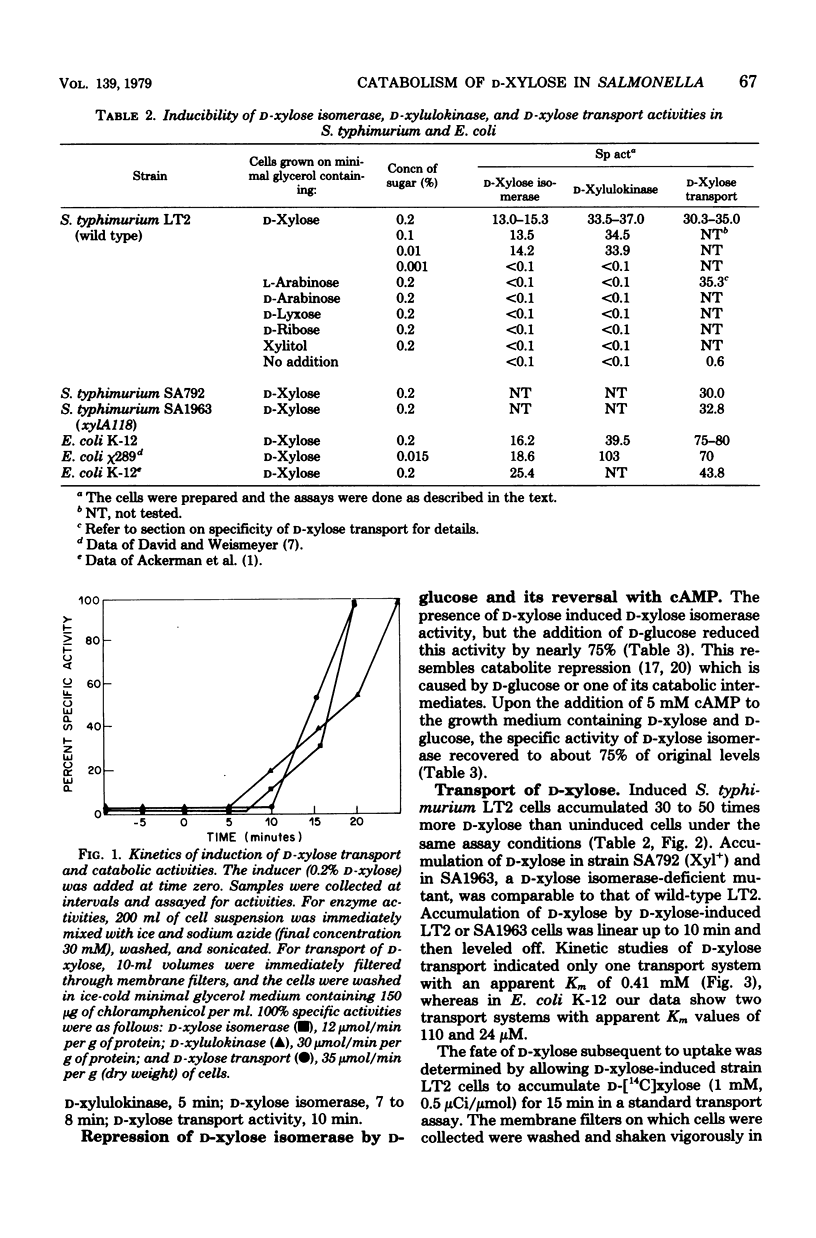
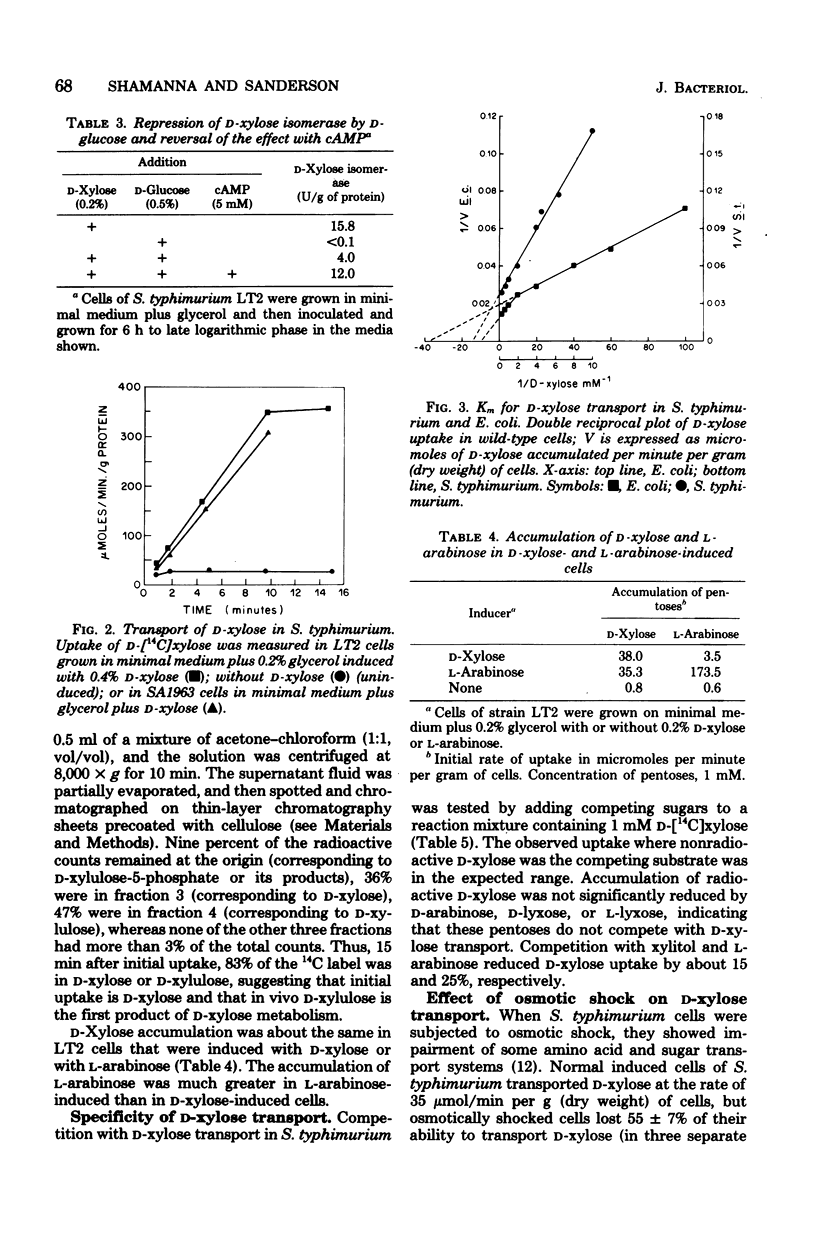
Salmonella typhimurium LT2 grows on D-xylose as sole carbon source with a generation time of 105 to 110 min. The following activities are induced at the indicated time after the addition of the inducer, D-xylose: D-xylulokinase (5 min), D-xylose isomerase (7 to 8 min), and D-xylose transport (10 min). All other pentoses and pentitols tested failed to induce isomerase or kinase. Synthesis of D-xylose isomerase was subject to catabolite repression, which was reversed by the addition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Most of the radioactive counts from D-[14C]xylose were initially accumulated in the cell in the form of D-xylose or D-xylulose. D-Xylose uptake in a mutant which was deficient in D-xylose isomerase was equal to that of the wild type. The apparent Km for D-xylose uptake was 0.41 mM. Some L-arabinose was accumulated in D-xylose-induced cells, and some D-xylose was accumulated in L-arabinose-induced cells. D-Xylitol and L-arabinose competed against C-xylose uptake, but D-arabinose, D-lyxose, and L-lyxose did not. Osmotic shock reduced the uptake of D-xylose by about 50%; by equilibrium dialysis, a D-xylose-binding protein was detected in the supernatant fluid after spheroplasts were formed from D-xylose-induced cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman R. S., Cozzarelli N. R., Epstein W. Accumulation of toxic concentrations of methylglyoxal by wild-type Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):357–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.357-362.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R., Koshland D. E., Jr A ribose binding protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1348–1353. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90860-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. The reduction and restoration of galactose transport in osmotically shocked cells of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. I. Purification and specificity of the galactose- and leucine-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3116–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. E., Hogg R. W. A second transport system for L-arabinose in Escherichia coli B-r controlled by the araC gene. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):606–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.606-613.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of free pentose and pentose in nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J., Wiesmeyer H. Regulation of ribose metabolism in Escherichia coli. I. The ribose catabolic pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 14;208(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong C. E., Morris R. G., Kandrach M., Rosen B. P. A multichamber equilibrium dialysis apparatus. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):514–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D., Calvo J. M., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.215-219.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg R. W., Englesberg E. L-arabinose binding protein from Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):423–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.423-432.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny C. P., Englesberg E. The L-arabinose permease system in Escherichia coli B/r. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. An L-arabinose binding protein and arabinose permeation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Nov 28;46(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamanna D. K., Sanderson K. E. Genetics and regulation of D-xylose utilization in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.71-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Physiological basis of transient repression of catabolic enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):411–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.411-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R. C., Furlong C. E. Purification and properties of a ribose-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6926–6929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. L., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of D-xylose and D-arabitol catabolism by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1404–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1404-1411.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. A. Carbohydrate metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:521–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Strange P. G., Heavey R., Koshland D. E. Properties of the galactose binding protein of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):381–386. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



