Abstract
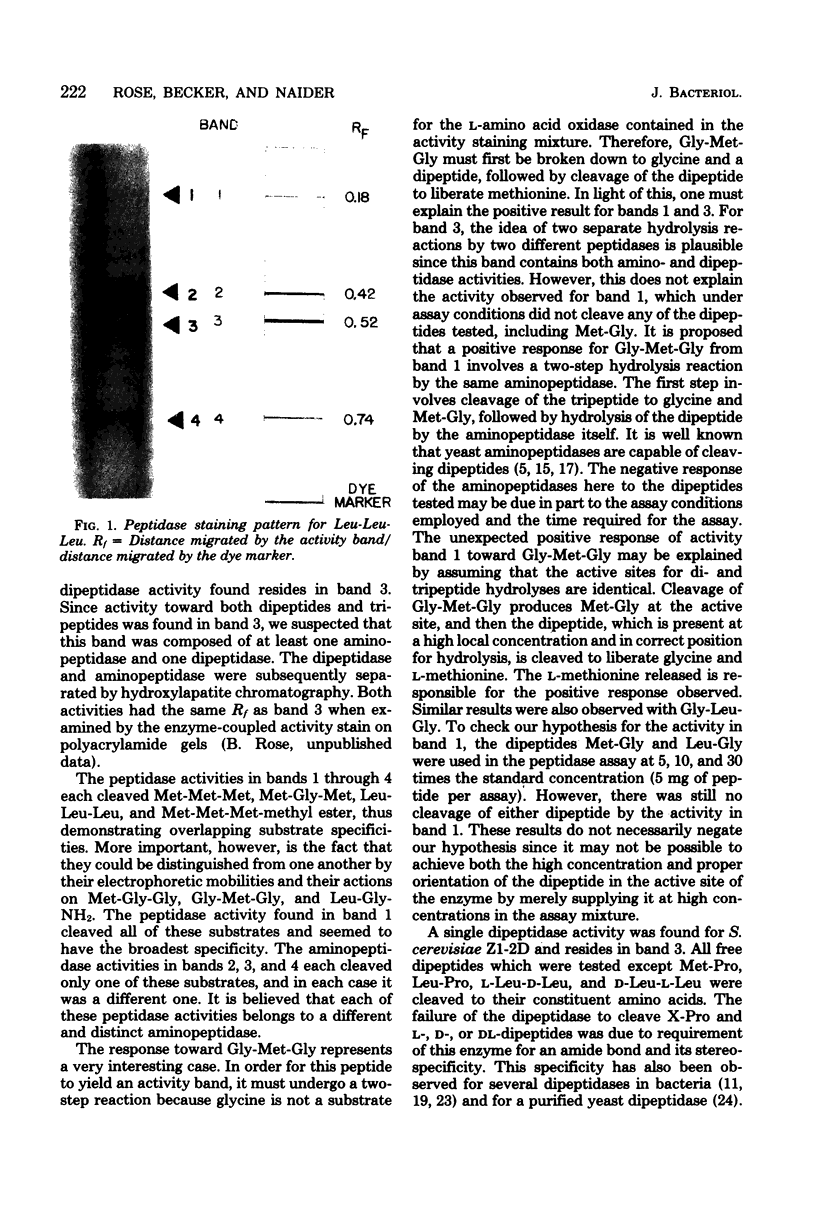
At least four distinct aminopeptidase activities and a single dipeptidase activity were found in cell extracts of a leucine-lysine auxotroph of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The assay for peptidase activity involved polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by an enzyme-coupled activity staining procedure. The aminopeptidases had largely overlapping specificities but could be distinguished from one another by their electrophoretic mobilities and activities toward different peptide substrates. Substrates tested included both free and blocked di- and tripeptides and amino acid derivatives.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chappelet-Tordo D., Lazdunski C., Murgier M., Lazdunski A. Aminopeptidase N from Escherichia coli: ionizable active-center groups and substrate specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):293–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmazeaud M. J., Devoyod J. J. Mise en évidence et caractérisation partielle de différentes peptidases chez Saccharomyces lactis. Ann Biol Anim Biochim Biophys. 1974;14(2):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R., Bai Y., Hata T. Kinetic studies of carboxypeptidase Y. I. Kinetic parameters for the hydrolysis of synthetic substrates. J Biochem. 1975 Jan 1;77(1?):69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R. Carboxypeptidase Y. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:568–587. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R., Moore S., Stein W. H. Carboxypeptidase from yeast. Large scale preparation and the application to COOH-terminal analysis of peptides and proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Brown J. L. Partial purification and characterization of two peptidases from Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 29;370(2):530–540. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Harris H. Human red cell peptidases. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):351–355. doi: 10.1038/215351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz G., Röhm K. H. Yeast aminopeptidase I. Chemical composition and catalytic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):933–949. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Schwartz G. Peptidase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.603-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naider F., Becker J. M., Katzir-Katchalski E. Utilization of methionine-containing peptides and their derivatives by a methionine-requiring auxotroph of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):9–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson E. K. A dipeptidase from Escherichia coli B. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:377–386. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. Transport and hydrolysis of peptides by microorganisms. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(50):305–334. doi: 10.1002/9780470720318.ch17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabier D., Desmazeaud M. J. Inventaire des différentes activités peptidasiques intracellulaires de Streptococcus thermophilus. Purification et propriétés d'une dipeptide-hydrolase et d'une aminopeptidase. Biochimie. 1973;55(4):389–404. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhm K. H. Properties of a highly purified dipeptidase (EC 3.4.13.?) from brewer's yeast. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jun;355(6):675–686. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senkpiel K., Uhlemann A., Barth A. alpha-Aminoacylpeptidhydrolasen (EC 3.4.11) und Dipeptidhydrolasen (EC 3.4.13) in Mikroorganismen und Samenpflanzen. Pharmazie. 1976;31(2):73–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoaf C. R., Berko R. M., Heizer W. D. Isolation and characterization of four peptide hydrolases from the brush border of rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):694–719. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds S. Garvan Award address of the American Chemical Society: peptidase activity and peptide metabolism in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 6;9(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/bi00803a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. J., Gilvarg C. Peptide transport and metabolism in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:397–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and properties of an aminopeptidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4760–4769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]