Abstract
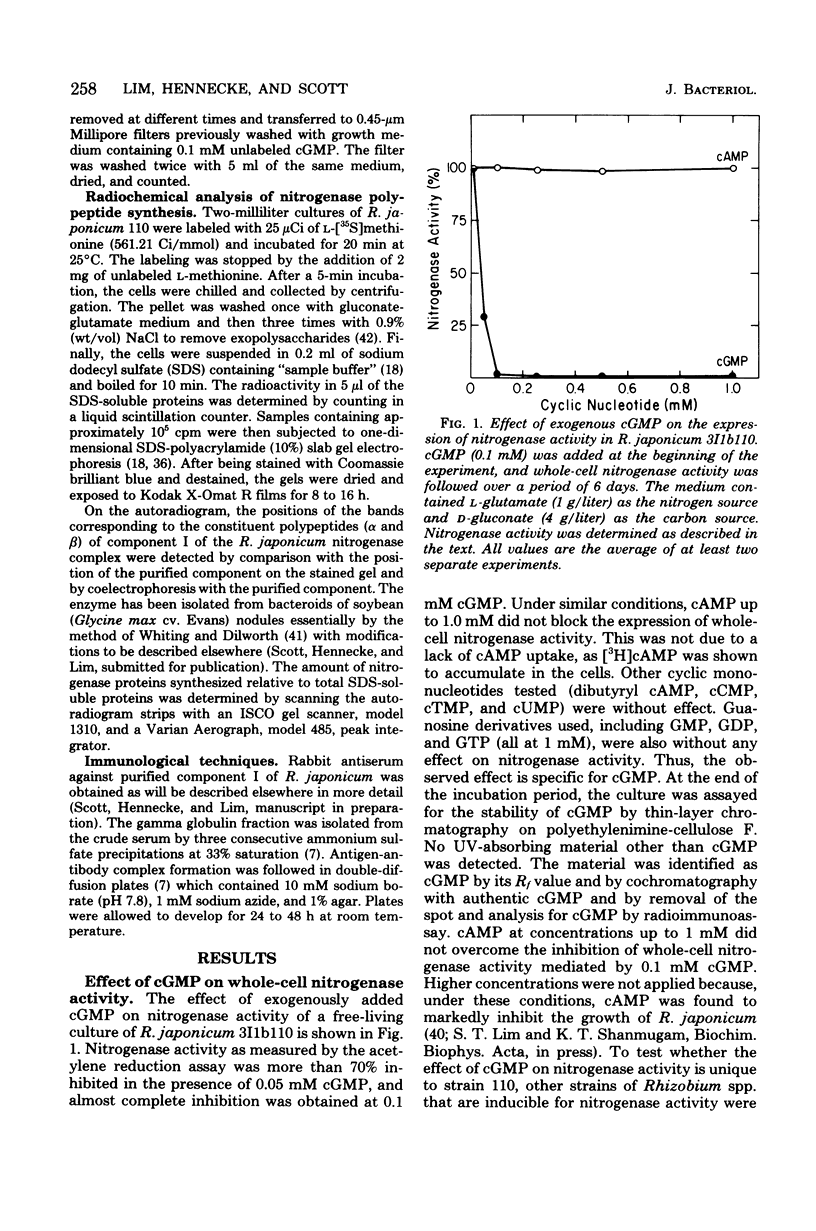
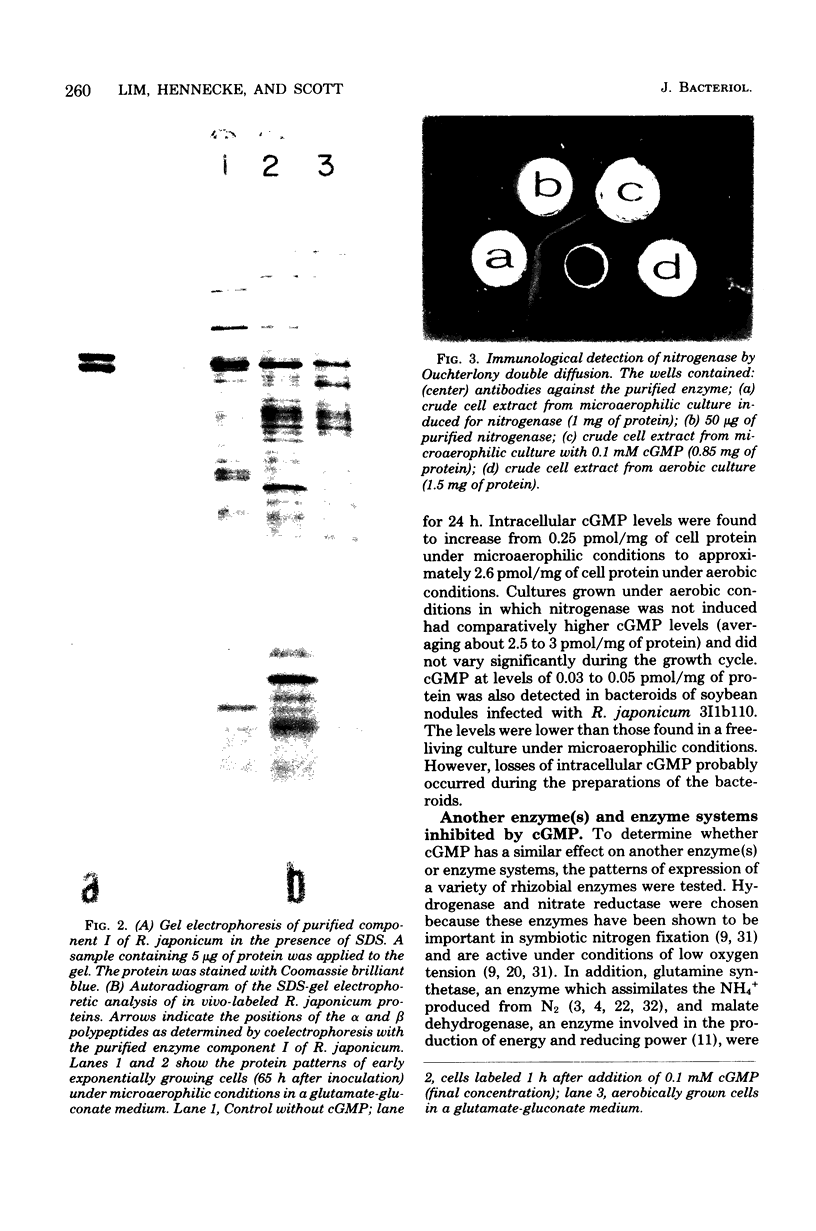
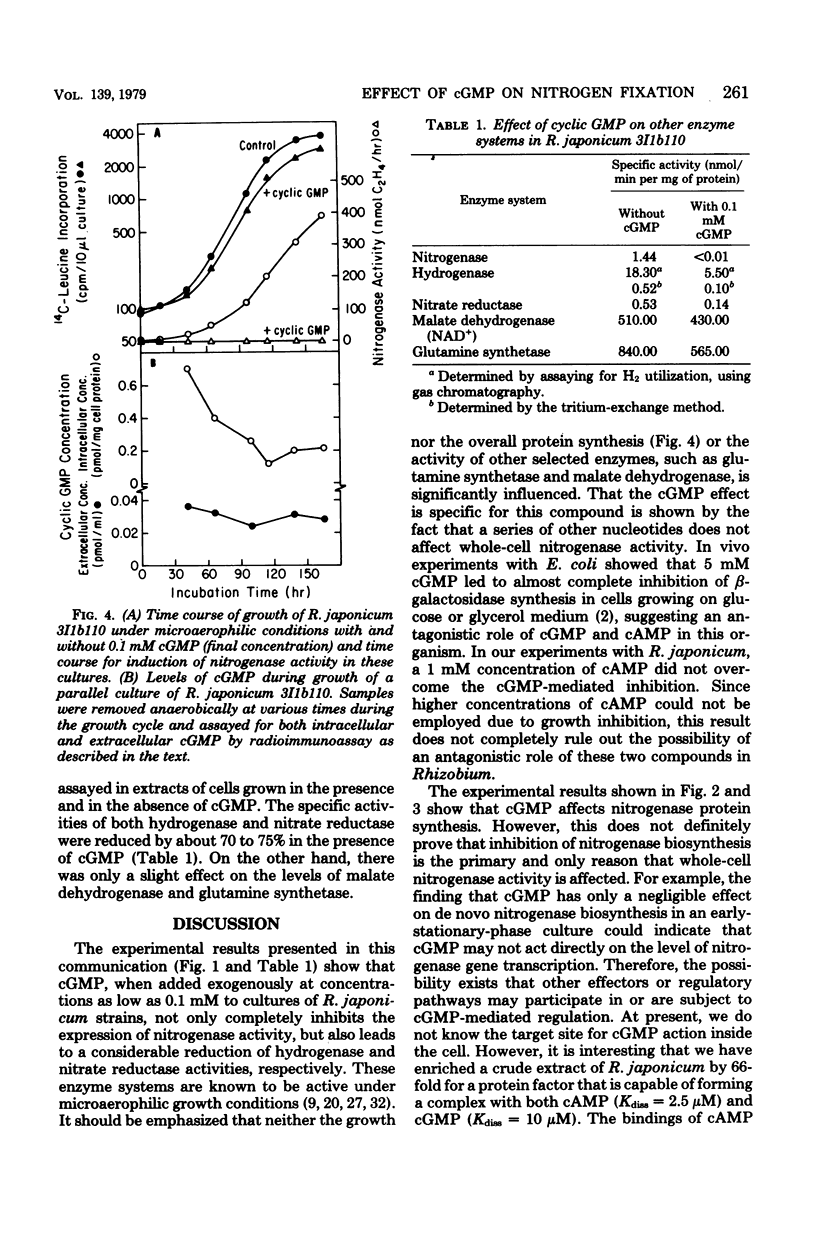
The addition of exogenous cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cGMP) at a concentration of 0.1 mM to a free-living culture of Rhizobium japonicum 3I1b110 was found to completely inhibit the expression of nitrogenase activity and markedly inhibit the expression of hydrogenase and nitrate reductase activities. The effect was specific for cGMP. Experiments on the in vivo incorporation of radioactive methionine and subsequent analysis of the labeled proteins on polyacrylamide gels showed that the biosynthesis of nitrogenase polypeptides was inhibited. It appears that the time of addition of cGMP is important since the effect was only seen during the early stages of nif gene expression. The intracellular level of cGMP was found to respond to physiological changes in the cell, and there was a fall in cGMP concentrations when nitrogenase was induced. Microaerophilic-aerobic shift experiments showed that intracellular levels increased from 0.25 pmol/mg of cell protein under microaerophilic conditions to 2.6 pmol/mg of cell protein under aerobic conditions, suggesting that the cellular pool size of cGMP may be under redox control.
Full text
PDF




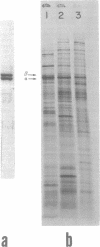
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. B., Pastan I. The cyclic AMP receptor of Escherichia coli: immunological studies in extracts of Escherichia coli and other organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 5;320(3):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artman M., Werthamer S. Effect of cyclic guanosine 3,5-monophosphate on the synthesis of enzymes sensitive to caatabolite repression in intact cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):980–983. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.980-983.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L. Activity of nitrogenase and glutamine synthetase in relation to availability of oxygen in continuous cultures of a strain of cowpea Rhizobium sp. supplied with excess ammonium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L., Gibson A. H., Dudman W. F. Nitrogenase activity and respiration of cultures of Rhizobium spp. with special reference to concentrations of dissolved oxygen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cailla H. L., Vannier C. J., Delaage M. A. Guanosine 3', 5'-cyclicmonophosphate assay at 10(-15)-mole level. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(83)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel R. M., Gray J. Nitrate reductase from anaerobically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):247–251. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Chen B., Anderson W., Nissley P., Gottesman M., Pastan I., Perlman R. Lac DNA, RNA polymerase and cyclic AMP receptor protein, cyclic AMP, lac repressor and inducer are the essential elements for controlled lac transcription. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):139–142. doi: 10.1038/newbio231139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Lupo M. Glutamate transport in wild-type and mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1288–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1288-1295.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. W., Beringer J. E. Genetic hydridization of root-nodule bacteria (Rhizobium). Basic Life Sci. 1977;9:81–90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0880-5_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. L. Acetylene reduction by pure cultures of Rhizobia. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1265–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1265-1268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T. Determination of Hydrogenase in Free-living Cultures of Rhizobium japonicum and Energy Efficiency of Soybean Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):609–611. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig R. A., Signer E. R. Glutamine synthetase and control of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):245–248. doi: 10.1038/267245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti using RP4. Basic Life Sci. 1977;9:91–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0880-5_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisseley S. P., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. In vitro transcription of the gal operon requires cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gara F., Shanmugam K. T. Regulation of nitrogen fixation by Rhizobia. Export of fixed N2 as NH+4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. S., Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels and activities of adenylate cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in Pseudomonas and Bacteroides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):87–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.87-96.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjepkema J., Evans H. J. Nitrogen fixation by free-living Rhizobium in a defined liquid medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):625–628. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilo R. M., Dobson J. G., Jr Separation of purine 3',5'-cyclic nucleotides and nucleosides by thin-layer chromatography on PEI cellulose. J Chromatogr. 1976 Jan 21;116(2):465–467. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Signer E. R. Catabolite-repression-like phenomenon in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1197–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1197-1200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch R. G., Elkan G. H. The role of ammonia, L-glutamate, and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the regulation of ammonia assimilation in Rhizobium japonicum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 18;538(2):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Dilworth M. J. Legume root nodule nitrogenase. Purification, properties, and studies on its genetic control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):337–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert J. S., Albersheim P. Host-symbiont interactions. I. The lectins of legumes interact with the o-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides of their symbiont Rhizobia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]