Abstract
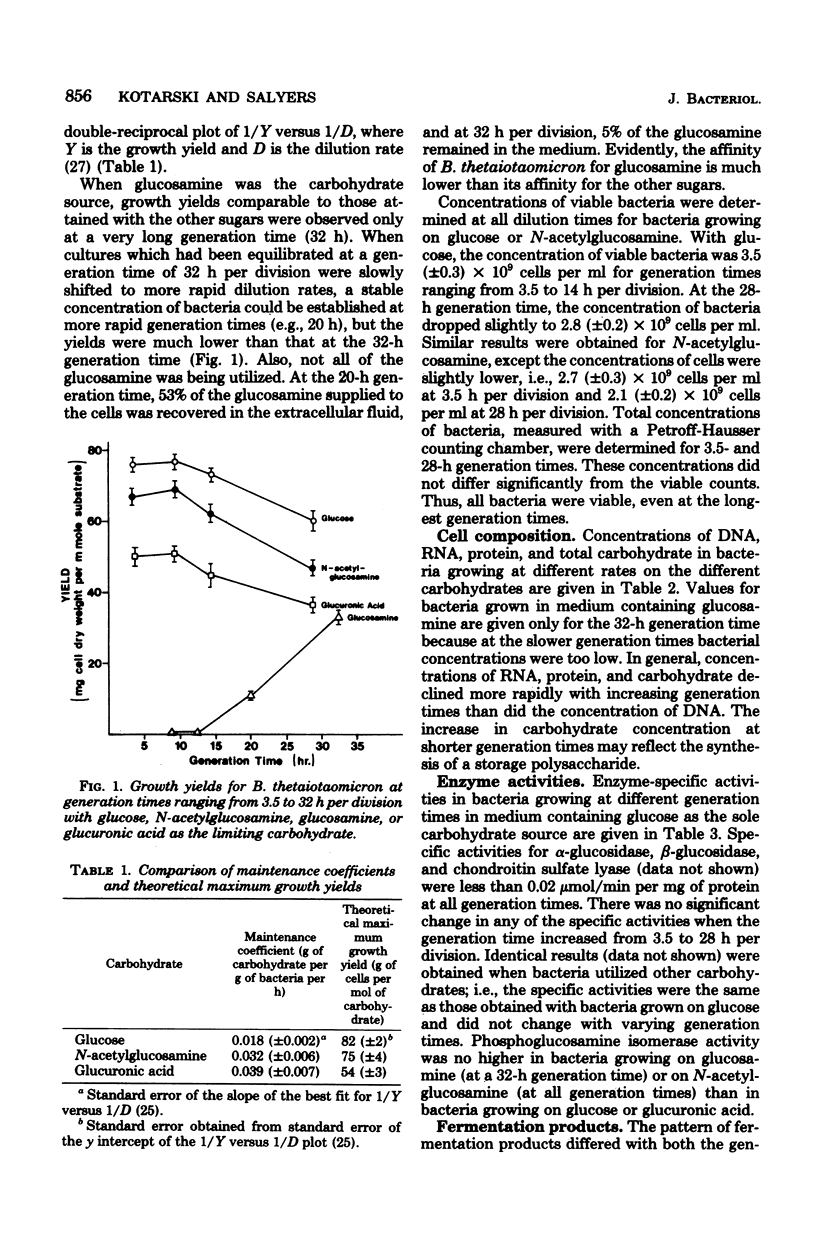
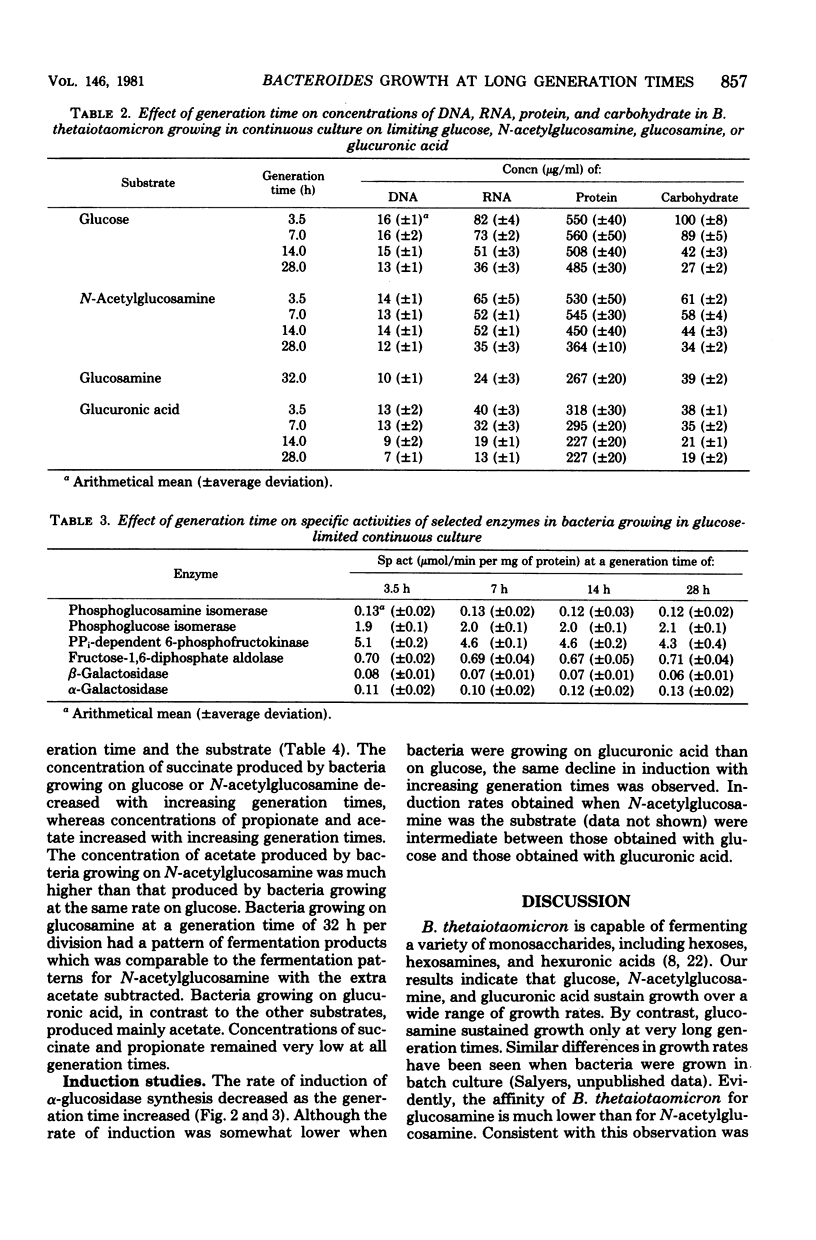
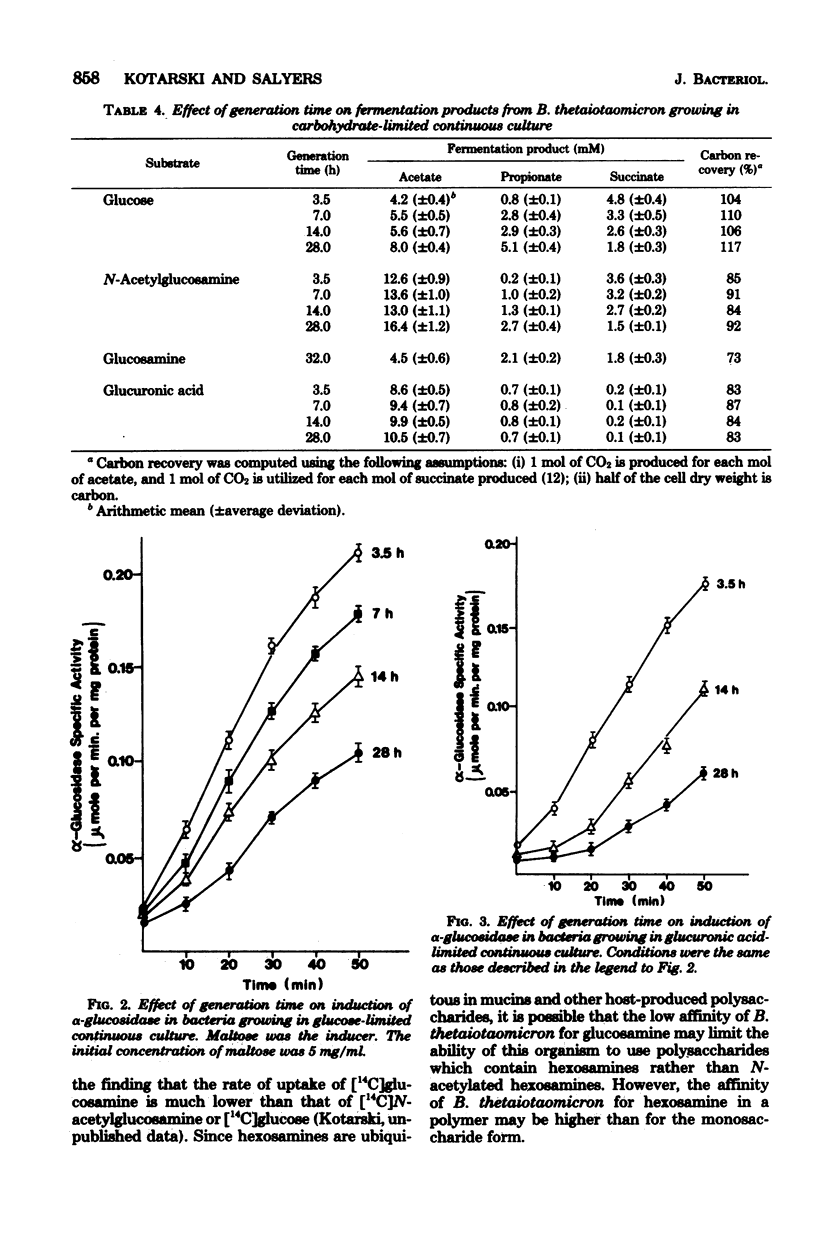
We investigated the ability of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, an obligate anaerobe from human colonic microflora, to grow in a carbohydrate-limited continuous culture at generation times ranging from 3.5 to 28 h per division. Four carbohydrates were tested: glucose, N-acetylglucosamine, glucuronic acid, and glucosamine. At a generation time of 3.5 h per division, the growth yields for bacteria growing on glucose, N-acetylglucosamine, and glucuronic acid were 76, 68, and 50 g of cells (dry weight) per mol of substrate, respectively. Growth yields at 28 h per division were 61, 52, and 37 g/mol of substrate, respectively. When glucosamine was the carbohydrate source, a stable population of bacteria was attainable only at generation times longer than 12 h per division. Growth yields at 15 and 32 h per division were 11 and 33 g/mol of substrate, respectively. There was no significant variation with increasing generation times in the specific activities of selected glycolytic enzymes, of disaccharidases such as α- and β-glucosidases and α- and β-galactosidases, or of the polysaccharidase chondroitin sulfate lyase. By contrast, the pattern of fermentation products varied with both the generation time and the carbon source. At a generation time of 3.5 h per division, the main products from the fermentation of glucose were acetate and succinate, with a trace of propionate. At 28 h per division, propionate concentrations were higher and succinate concentrations were lower than at 3.5 h per division. The products from the fermentation of glucosamine were the same as those from glucose fermentation. However, when N-acetylglucosamine was fermented, the concentration of acetate was much higher at all generation times than when glucose was the carbon source. When glucuronic acid was the carbon source, acetate was the main fermentation product, and only traces of propionate and succinate were detected. Another characteristic that varied with the growth rate was the ability of B. thetaiotaomicron to produce the inducible enzyme α-glucosidase when exposed to maltose. The ability of the organism to produce this enzyme declined with increasing generation times.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Microbial growth rates in nature. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):39–58. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.39-58.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. R., Nunley J. A., 2nd, Li Y. T., Chambers R. P., Cohen W. A continuously monitored spectrophotometric assay of glycosidases with nitrophenyl glycosides. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jul;54(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Kapsimalis B. Estimates of the overall rate of growth of the intestinal microflora of hamsters, guinea pigs, and mice. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):510–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.510-512.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbal I., Kells D. I., Forstner G., Forstner J. Human intestinal goblet cell mucin. Can J Biochem. 1976 Aug;54(8):707–716. doi: 10.1139/o76-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafkewitz D., Iannotti E. L., Wolin M. J., Bryant M. P. An anaerobic chemostat that permits the collection and measurement of fermentation gases. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):612–614. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.612-614.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J. M., Ljungdahl L. G., Gottschalk G. Pathway of succinate and propionate formation in Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):84–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.84-91.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. E., South D. J., Blytt H. J., Warren L. G. Pyrophosphate:D-fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase. A new enzyme with the glycolytic function of 6-phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7737–7741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of maintenance energy expenditures and growth yields among several rumen bacteria grown on continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.537-543.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., MAALOE O., KJELDGAARD N. O. Dependency on medium and temperature of cell size and chemical composition during balanced grown of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):592–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Muirhead P. A. Quantitative method for the gas chromatographic analysis of short-chain monocarboxylic and dicarboxylic acids in fermentation media. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):374–381. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.374-381.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Kotarski S. F. Induction of chondroitin sulfate lyase activity in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):781–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.781-788.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., O'Brien M. Cellular location of enzymes involved in chondroitin sulfate breakdown by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.772-780.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller G. A., Shipley E. A., Blake J. A. Recent progress in dietary fiber (plantix) in human nutrition. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1978;10(1):31–90. doi: 10.1080/10408397809527244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. Utilization of energy for growth and maintenance in continuous and batch cultures of microorganisms. A reevaluation of the method for the determination of ATP production by measuring molar growth yields. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P. Nutritional features of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.251-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J. Control of amino sugar metabolism in Escherichia coli and isolation of mutants unable to degrade amino sugars. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):847–858. doi: 10.1042/bj1060847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


