Abstract
Significant selective enrichments of mutants defective in catabolic pathways can be achieved by exposure of pseudomonad cells to halogenated analogs of growth substrates. Between 3 and 95% of viable clones rescued from such enrichments have been defective in specific catabolic pathways. This has been demonstrated for eight different catabolic pathways for aromatic compounds in pseudomonads, in which the genes are located on plasmids or on the chromosome. The plasmid-encoded pathways studied include those for the catabolism of p-cymene (CYM), m- and p-xylenes (TOL), naphthalene (NAH), salicylate (SAL), and 4-methylphthalate (MOP), and the chromosome-encoded pathways include those for p-hydroxybenzoate, monohydric phenols, and p-anisate utilization. The recalcitrance of halogenated compounds may, in part, be explained by these observations, which introduce an as yet not widely recognized factor in assessment of biodegradability of halogenated compounds and their effects on the transformation of the natural substrates.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D. The two-way selection of mutants and revertants in respect of acetate utilization and resistance to fluoro-acetate in Aspergillus nidulans. Genet Res. 1965 Nov;6(3):317–329. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitt S., McCullough W., Roberts C. F. Analysis of acetate non-utilizing (acu) mutants in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Feb;92(2):263–282. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEHRMAN E. J., STANIER R. Y. Observations on the oxidation of halogenated nicotinic acids. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):947–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLELY A. G., DAGLEY S. A possible lethal synthesis of monofluormalate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Sep;35:256–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carhart G., Hegeman G. Improved method of selection for mutants of Pseudomonas putida. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1046–1047. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1046-1047.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Friello D. A., Bopp L. H. Transposition of plasmid DNA segments specifying hydrocarbon degradation and their expression in various microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3109–3112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrank J. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: ring cleavage of 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate and subsequent reactions. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1365–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1365-1374.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrank J. J., Ribbons D. W. p-cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: initial reactions. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1356–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1356-1364.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn N. W., Gunsalus I. C. Transmissible plasmid coding early enzymes of naphthalene oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):974–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.974-979.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., ANDERSON R. L., WEINBERG R., LEE N., HOFFEE P., HUTTENHAUER G., BOYER H. L-Arabinose-sensitive, L-ribulose 5-phosphate 4-epimerase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:137–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.137-146.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. 6-Hydroxynicotinic acid as an intermediate in the oxidation of nicotinic acid by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochem J. 1955 Jun;60(2):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj0600303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Pateman J. A. The genetic analysis of regulation of amidase synthesis in Aspergillus nidulans. II. Mutants resistant to fluoroacetamide. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02430517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Smith J. Genetic control of glucose uptake by Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 15;20(3):270–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy M. H. Frameshift mutations in the lactose operon of E. coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:189–201. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche H. P. Bromopyruvate inactivation of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconic aldolase. I. Kinetic evidence for active site specificity. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2273–2280. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Isolation of a mutant TOL plasmid with increased activity and transmissibility from Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.39-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Ornston M. K., Chou G. Isolation of spontaneous mutant strains of Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90666-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J. J. Microbial cooxidations involving hydrocarbons. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):59–72. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.59-72.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOELLMANN G., SHAW E. Direct evidence for the presence of histidine in the active center of chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:252–255. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Sadler J. R. The nature of lactose operator constitive mutations. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 28;59(2):273–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAIN R. L., WIGHTMAN F. The growth regulating activity of certain omega-substituted alkyl carboxylic acids in relation to their beta-oxidation within the plant. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Sep 27;142(909):525–536. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Bayly R. C., Di Berardino D. Pseudomonas putida mutants defective in the metabolism of the products of meta fission of catechol and its methyl analogues. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):31–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.31-37.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
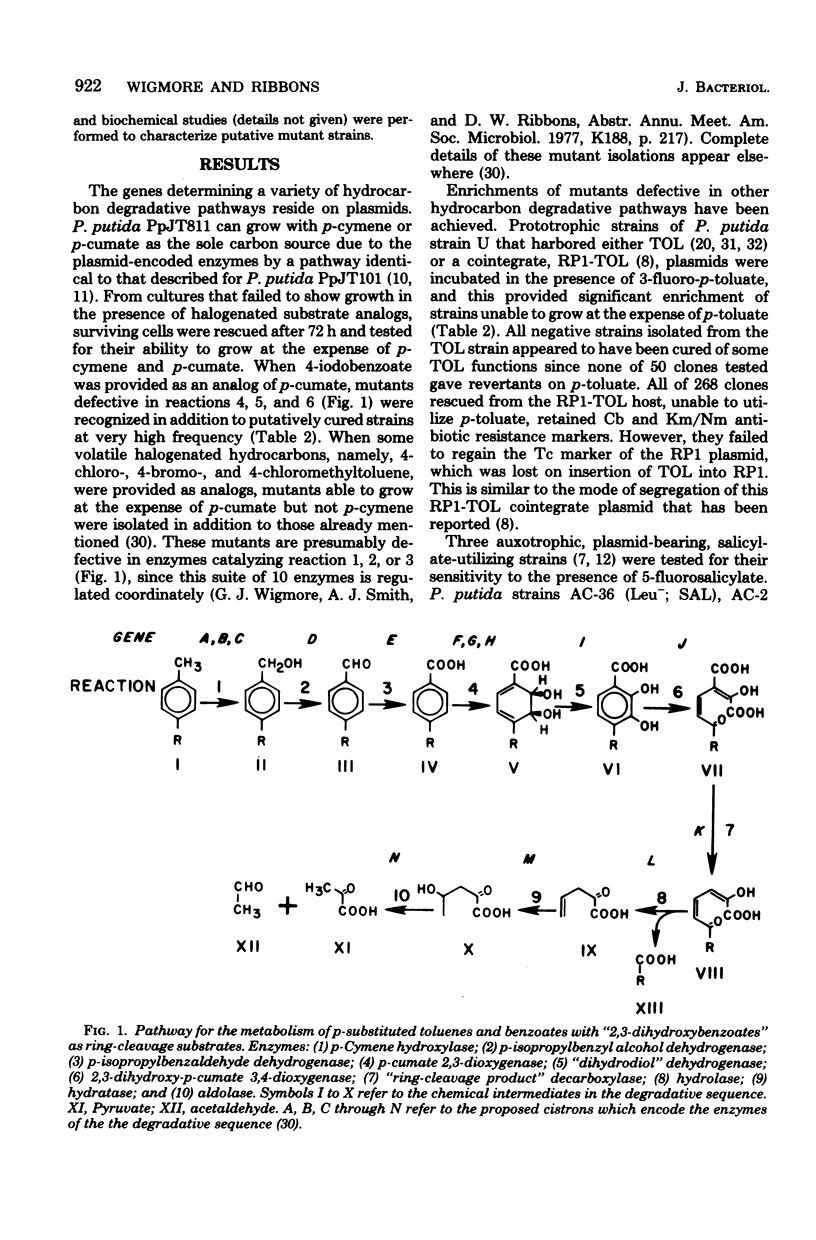
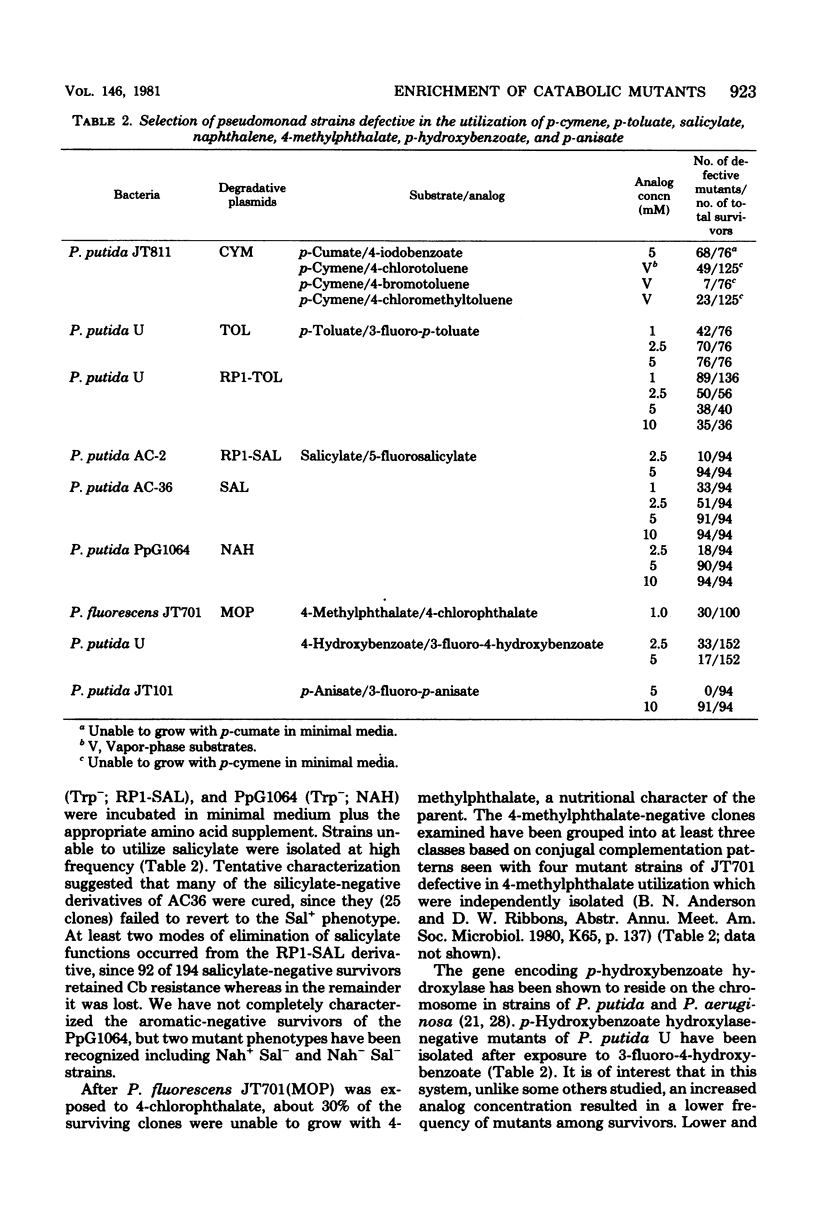
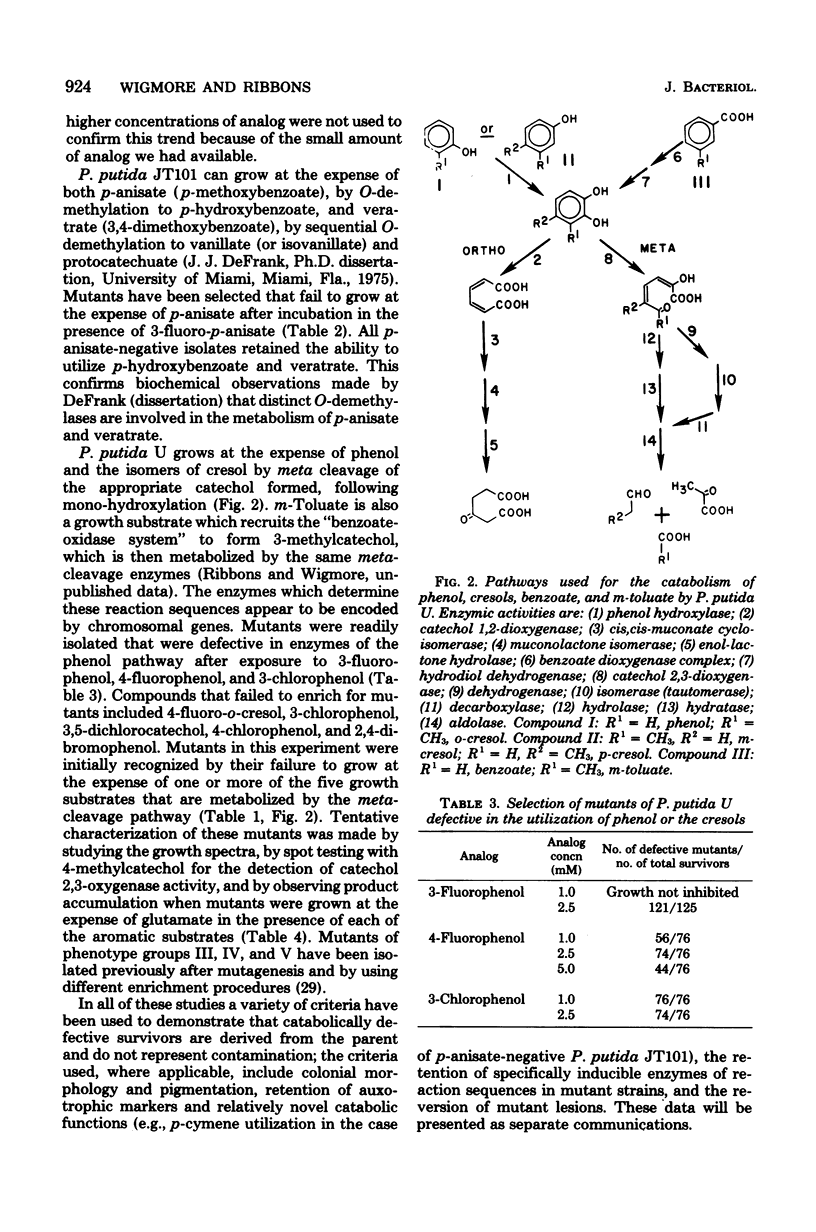
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: selective enrichment of defective mutants by using halogenated substrate analogs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):816–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.816-824.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. L., Dunn N. W. Transmissible plasmid coding for the degradation of benzoate and m-toluate in Pseudomonas arvilla mt-2. Genet Res. 1974 Apr;23(2):227–232. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



