Abstract
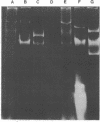
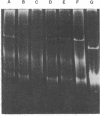
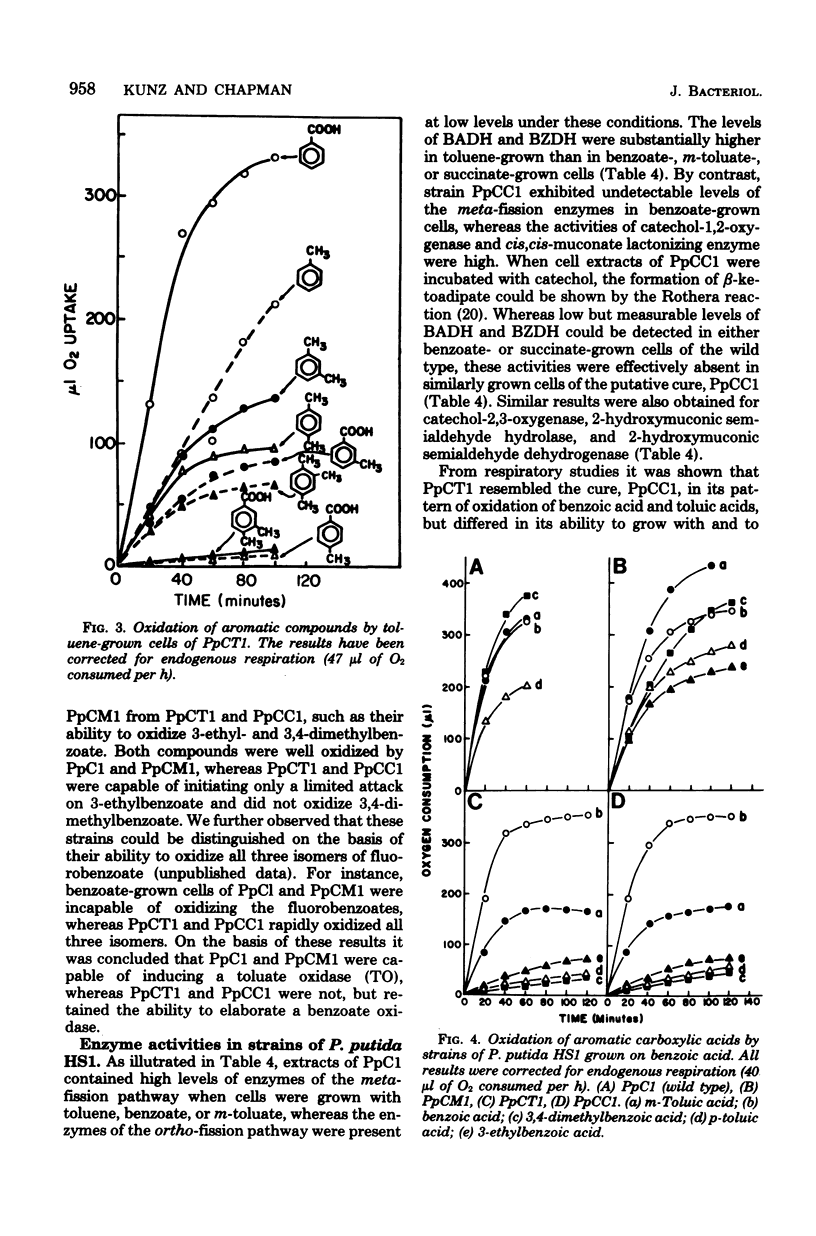
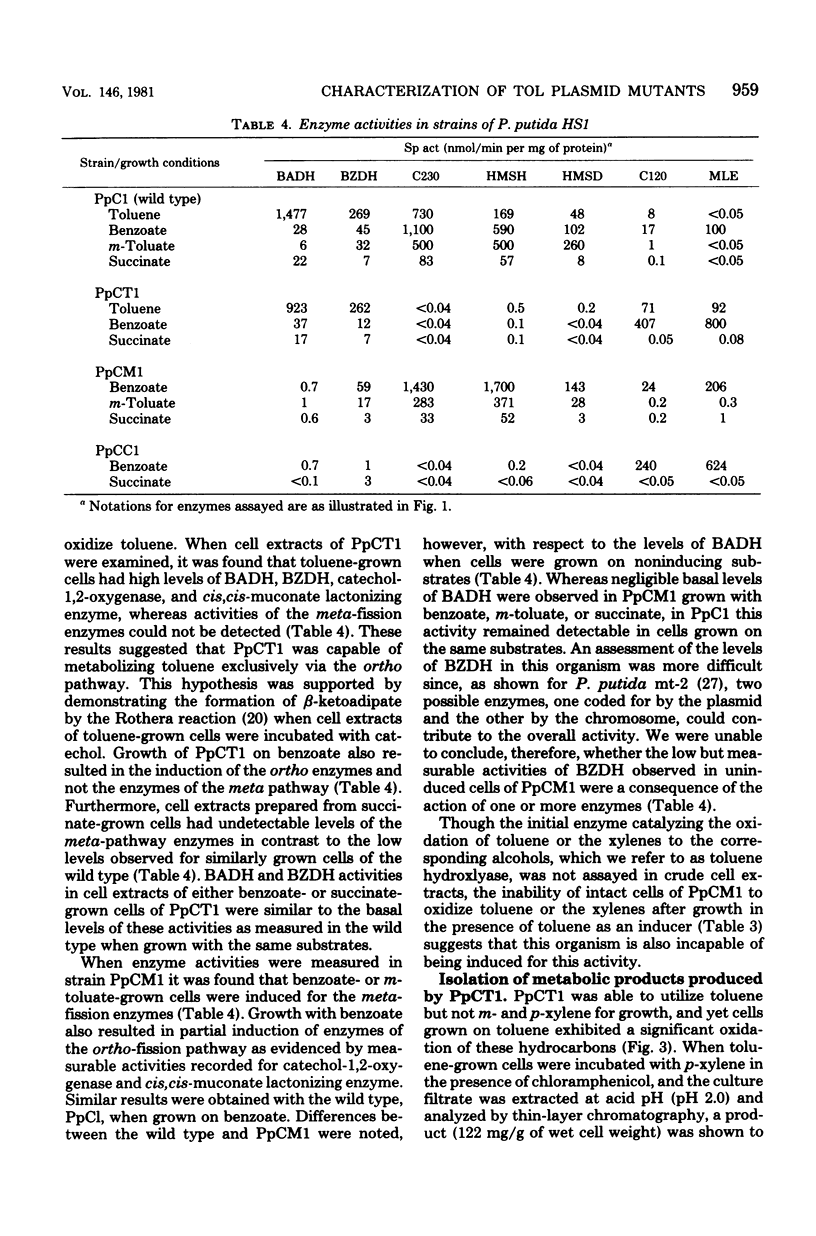
A strain of Pseudomonas (P. putida HS1) was found to resemble P. putida (arvilla) mt-2 in its ability to degrade toluene, m- and p-xylene, 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene), and 3-ethyltoluene via oxidation of a methyl substituent and reactions of the meta-fission pathway. The ability to degrade these substrates by P. putida HS1 (PpC1) was shown to be encoded by a TOL (pDK1) plasmid as evidenced by: (i) spontaneous loss of the TOL-related phenotype after growth with benzoate, (ii) transfer of the TOL character from the wild type into cured recipients by conjugation, and (iii) isolation of a plasmid of identical molecular weight (120 X 10(6)) from both the wild type and an exconjugant obtained by mating wild type with a putative cured recipient. In addition to the isolation of apparent cured strains having lost the entire TOL-related phenotype, two additional mutant classes were observed after growth on benzoate. One class, represented by PpCT1, was unable to utilize the alkyl-substituted aromatic compounds but retained the ability to grow with toluene and benzyl alcohol. Analysis of PpCT1 revealed that it was unable to synthesize the TOL-encoded toluate oxidase and enzymes of the meta pathway but retained the ability to elaborate activities for toluene hydroxylase, benzyl alcohol, and benzaldehyde dehydrogenase, thereby mediating initial oxidation of toluene to benzoate, which was then further metabolized via enzymes of the chromosomally encoded ortho-fission pathway. A second class of mutants had lost the ability to utilize the hydrocarbons but could still grow with m-toluate but not p-toluate, 3,4-dimethylbenzoate, or 3-ethylbenzoate, intermediates in the oxidation of the corresponding hydrocarbons. Our such mutant, PpCM1, could no longer synthesize enzymes required for initial oxidation of the hydrocarbons, but was able to produce the toluate oxidase and enzymes of the meta pathway, thereby facilitating degradation of m-toluate. Neither PpCT1, PpCM1, nor a putative cured strain, PpCC1, reverted at detectable frequencies (less than 10(-9). Analysis of each strain for plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid revealed the presence of a single plasmid in each strain with the following molecular weights: PpCM1, 100 X 10(6) (pDKM1); PpCT1, 80 X 10(6) (pDKT1); PpCC1 20 X 10(6) (pDKC1). The results suggest that the TOL (pDK1) plasmid has undergone deletions giving rise to smaller replicons which either encode for only a fraction of the wild-type catabolic functions (pDKM1, pDKT1) or have lost all catabolic activities (pDKC1).
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley S. A., Duggleby C. J., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Hardy K. G., Broda P. Two modes of loss of the Tol function from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 20;154(2):203–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00330838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Bacterial metabolism of para- and meta-xylene: oxidation of a methyl substituent. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):923–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.923-929.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. S., Hossler F. E., Stone R. W. Metabolism of p- and m-xylene by species of Pseudomonas. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Sep;14(9):1005–1009. doi: 10.1139/m68-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby C. J., Bayley S. A., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Broda P. Molecular sizes and relationships of TOL plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1274-1280.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friello D. A., Mylroie J. R., Gibson D. T., Rogers J. E., Chakrabarty A. M. XYL, a nonconjugative xylene-degradative plasmid in Pseudomonas Pxy. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1217–1224. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1217-1224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T. Initial reactions in the bacterial degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig B. 1976 Jul;162(1-2):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. B., Gunsalus I. C. Isolation of metabolic plasmid DNA from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
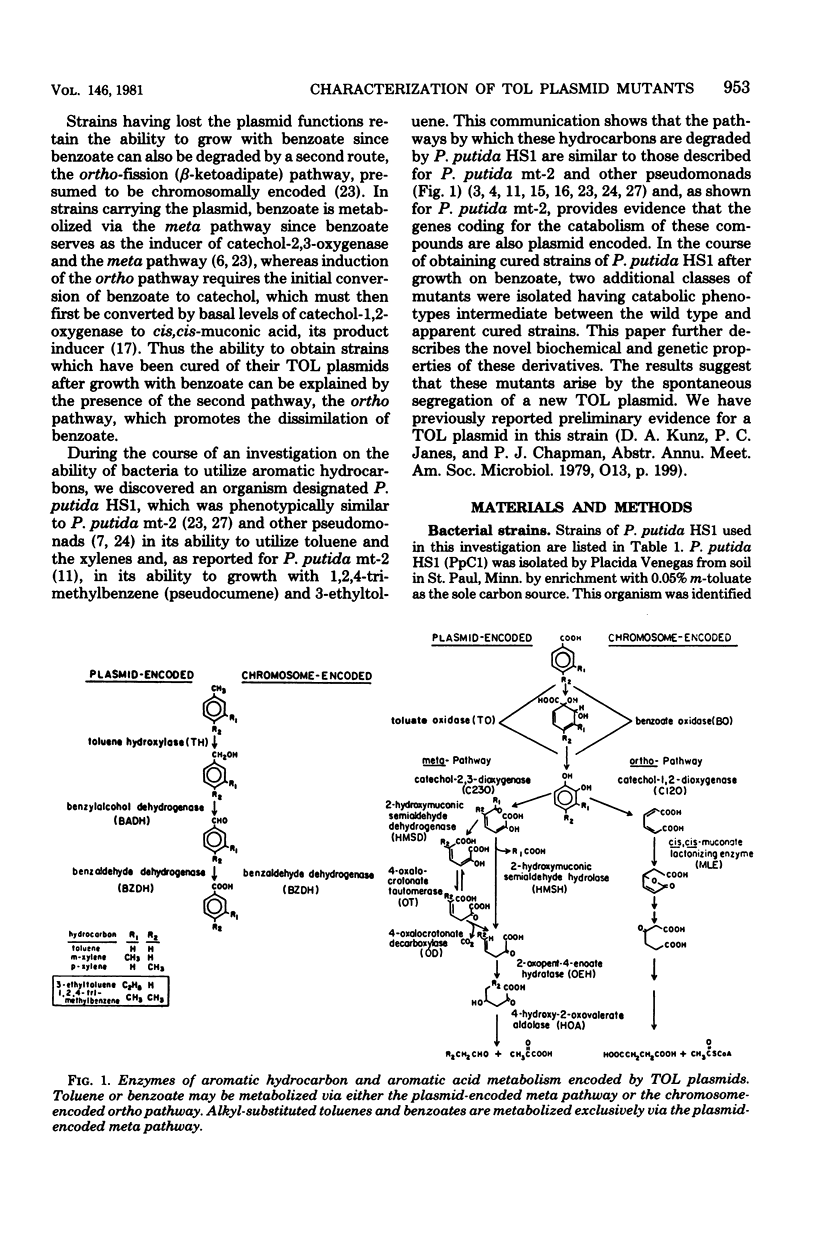
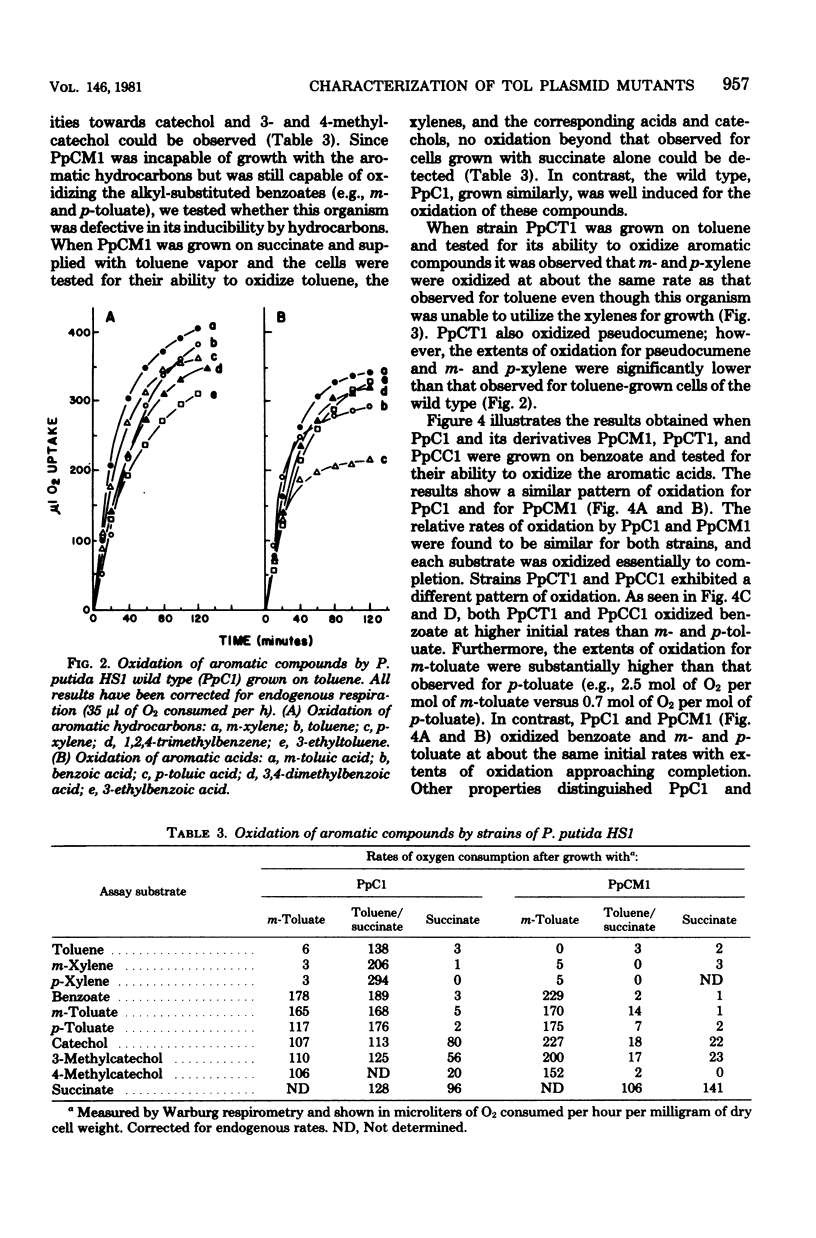
- Kunz D. A., Chapman P. J. Catabolism of pseudocumene and 3-ethyltoluene by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for new functions of the TOL (pWWO) plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):179–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.179-191.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Duggleby C. J., Sala-Trepat J. M., Williams P. A. The metabolism of benzoate and methylbenzoates via the meta-cleavage pathway by Pseudomonas arvilla mt-2. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):301–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Isolation of a mutant TOL plasmid with increased activity and transmissibility from Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.39-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Ornston M. K., Chou G. Isolation of spontaneous mutant strains of Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90666-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenate aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of benzoic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 6;542(3):412–423. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothera A. C. Note on the sodium nitro-prusside reaction for acetone. J Physiol. 1908 Dec 15;37(5-6):491–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1908.sp001285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Worsey M. J. Ubiquity of plasmids in coding for toluene and xylene metabolism in soil bacteria: evidence for the existence of new TOL plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):818–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.818-828.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. L., Dunn N. W. Transmissible plasmid coding for the degradation of benzoate and m-toluate in Pseudomonas arvilla mt-2. Genet Res. 1974 Apr;23(2):227–232. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Franklin F. C., Williams P. A. Regulation of the degradative pathway enzymes coded for by the TOL plasmid (pWWO) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.757-764.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Williams P. A. Characterization of a spontaneously occurring mutant of the TOL20 plasmid in Pseudomonas putida MT20: possible regulatory implications. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1149-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Williams P. A. Metabolism of toluene and xylenes by Pseudomonas (putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for a new function of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.7-13.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]