Abstract
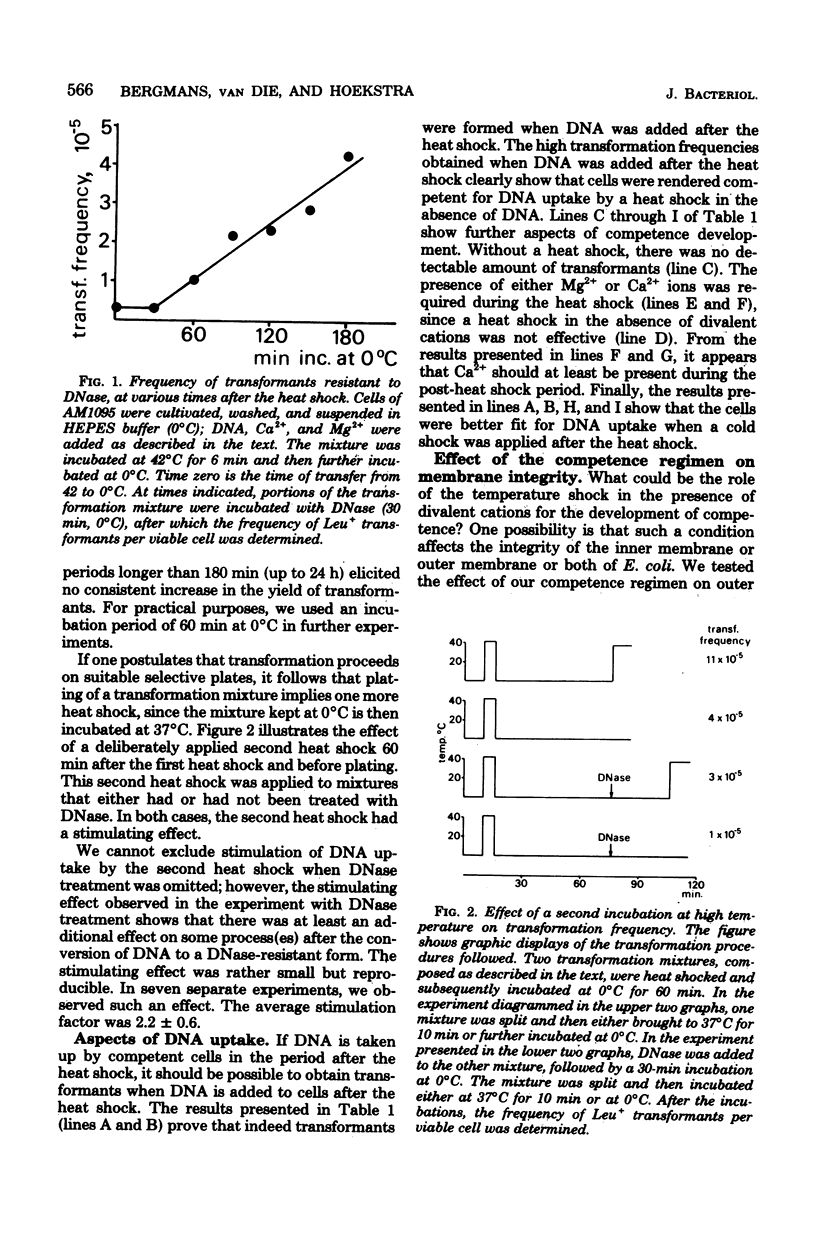
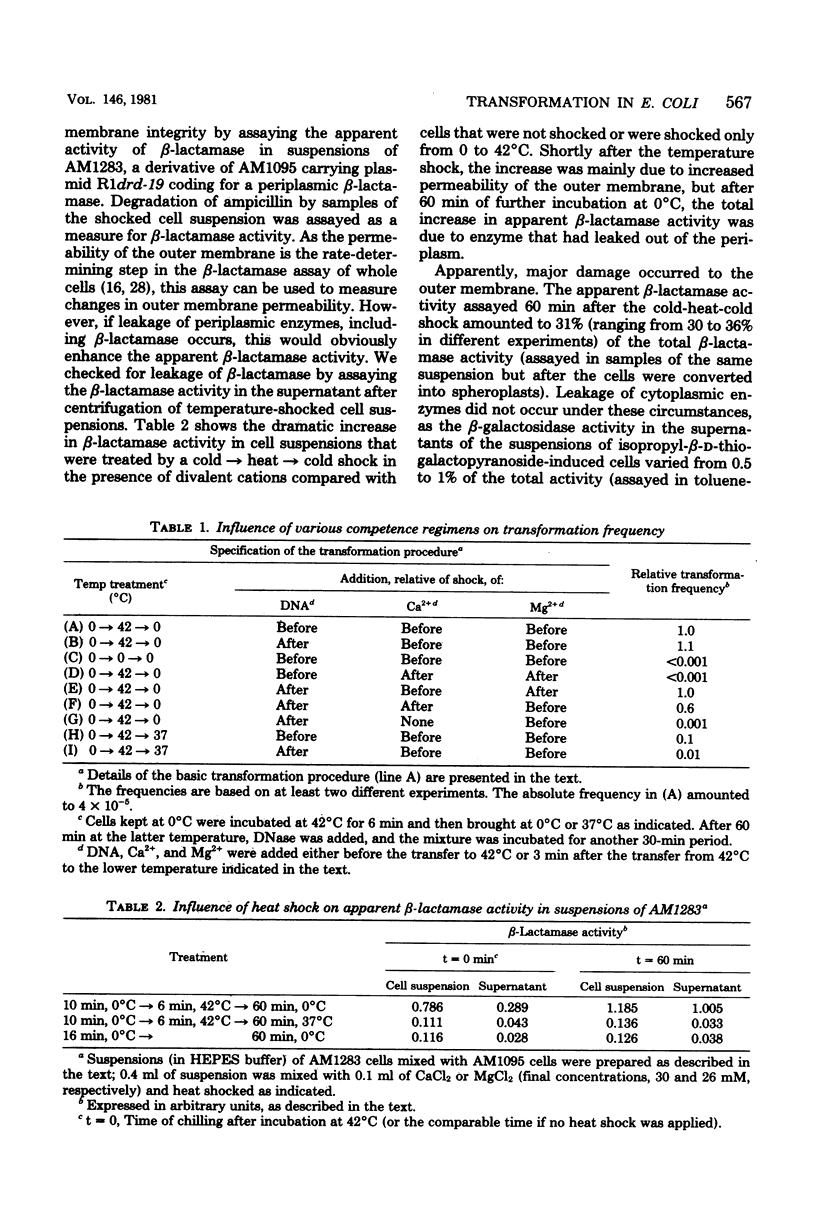
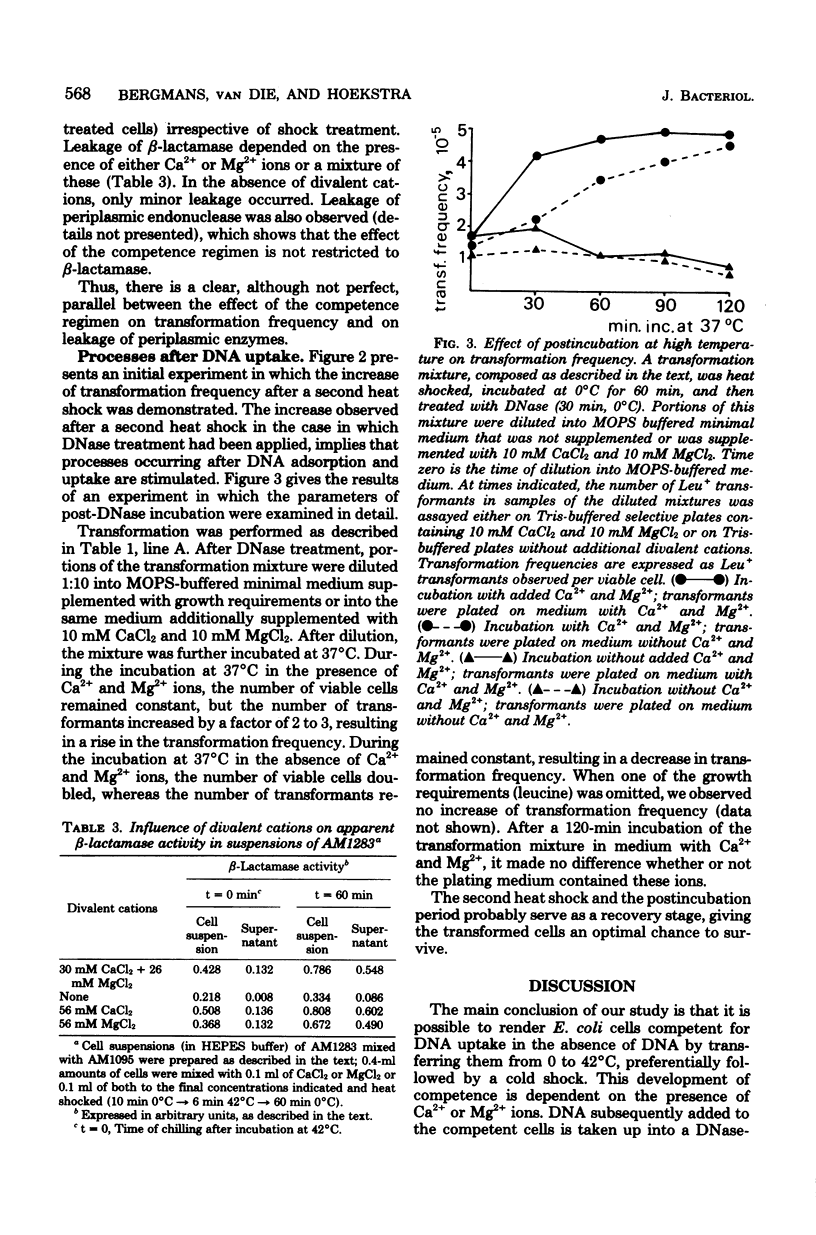
Transformation experiments with Escherichia coli recipient cells and linear chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are reported. E. coli can be rendered competent for DNA uptake by a temperature shock (0 degrees C leads to 42 degrees C leads to 0 degrees C) of the recipient cells in the presence of a high concentration of either Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions. Uptake of DNA into a deoxyribonuclease-resistant form, for which the presence of Ca2+ is essential, was possible during the temperature shock but appeared to occur most readily after the heat shock during incubation at 0 degrees C. When DNA was added to cells that had been heat shocked in the presence of divalent cations only, DNA uptake also occurred. This suggests that competence induction and uptake may be regarded as separate stages. Under conditions used to induce competence, we observed an extensive release of periplasmic enzymes, probably reflecting membrane damage induced during development of competence. After the conversion of donor DNA into a deoxyribonuclease-resistant form, transformants could be selected. It appeared that incubation, before plating, of the transformation mixture in a medium containing high Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations and supplemented with all growth requirements increased the transformation frequency. This incubation probably causes recovery of physiologically labile cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard J. P., Howe T. G., Richmond M. H. Purification of sex pili from Escherichia coli carrying a derepressed F-like R factor. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):814–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.814-820.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzinger R. Transfection of Enterobacteriaceae and its applications. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):194–236. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.194-236.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., Oishi M. The nature of the transformation process in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jul 31;124(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00267159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. Nucleic acid transport driven by ion gradient across cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra W. P., Bergmans J. E., Zuidweg E. M. Role of recBC nuclease in Escherichia coli transformation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1031–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1031-1032.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra W. P., de Haan P. G., Bergmans J. E., Zuidweg E. M. Transformation in E. coli K12: relation of linkage to distance between markers. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Apr 23;145(1):109–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00331565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., Peters R. Distribution of lipids in cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 20;441(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Song S. A., Shaltiel L., Nurminen M. Outer membrane of Salmonella XIV. Reduced transmembrane diffusion rates in porin-deficient mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi M., Cosloy S. D. The genetic and biochemical basis of the transformability of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1568–1572. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Newton C., Nir S., Jacobson K., Poste G., Lazo R. Studies on membrane fusion. III. The role of calcium-induced phase changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):579–598. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Avdeeva A. V., Ilyashenko Enhanced uptake of donor DNA by Ca2+ treated Escherichia coli cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Jul 10;138(4):351–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00264805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Domaradsky I. V. Proton conductor vs. cold in induction of Ca(2+)-dependent competence in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;172(3):313–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00271731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Szalay A. A. Bacterial transformation using temperature-sensitive mutants deficient in peptidoglycan synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:331–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to viral nucleic acid, X. Ba2+-induced competence for transfecting DNA. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 Jul-Aug;30(4):520–522. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-7-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to viral nucleic acid. 8. Idiosyncrasy of Ca2+-dependent competence for DNA. J Biochem. 1974 Apr;75(4):895–904. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel W. Genetic transformation in E. coli: the inhibitory role of the recBC DNase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 17;51(2):306–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Verkleij A., Burnell E., Lugtenberg B. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and freeze-fracture electron microscopy studies on Escherichia coli. II. Lipopolysaccharide and lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 24;597(3):502–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Verkleij A., Leunissen-Bijvelt J., Lugtenberg B. Architecture of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. III. Protein-lipopolysaccharide complexes in intramembraneous particles. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1089-1098.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


