Abstract
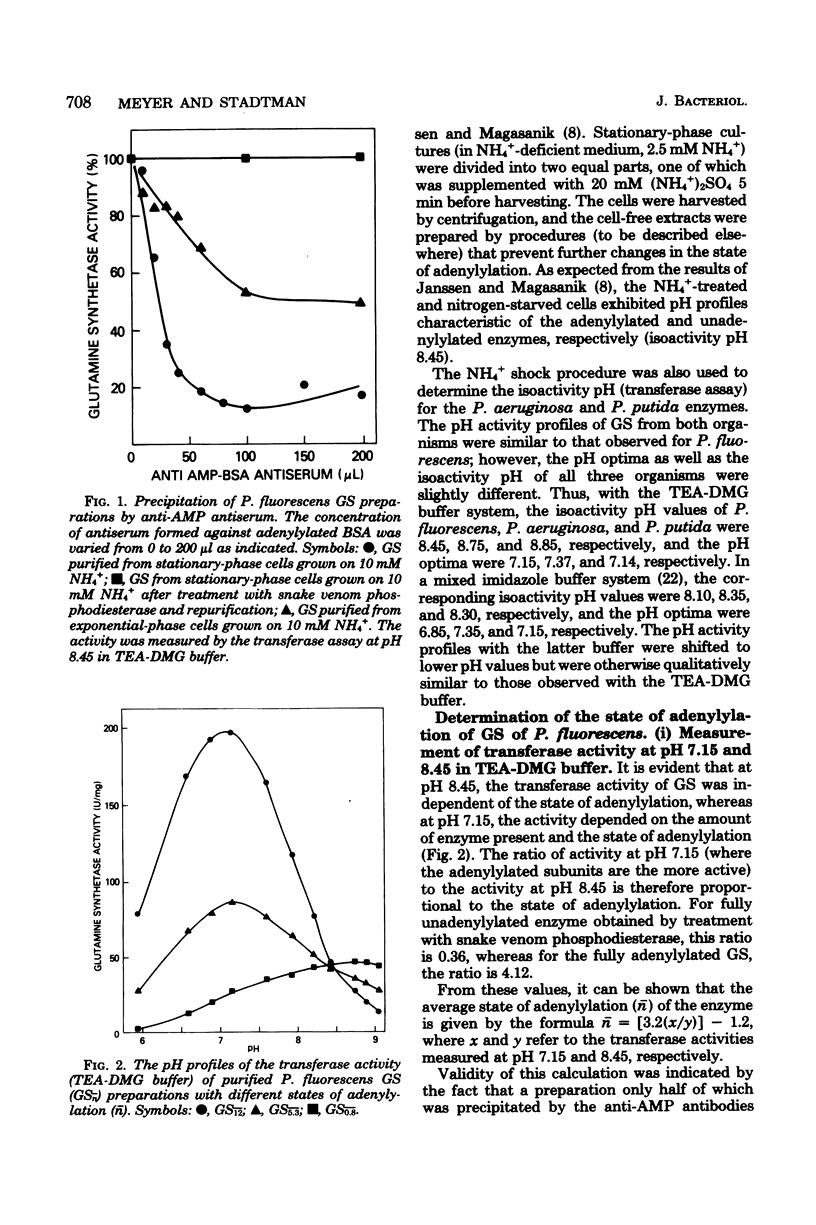
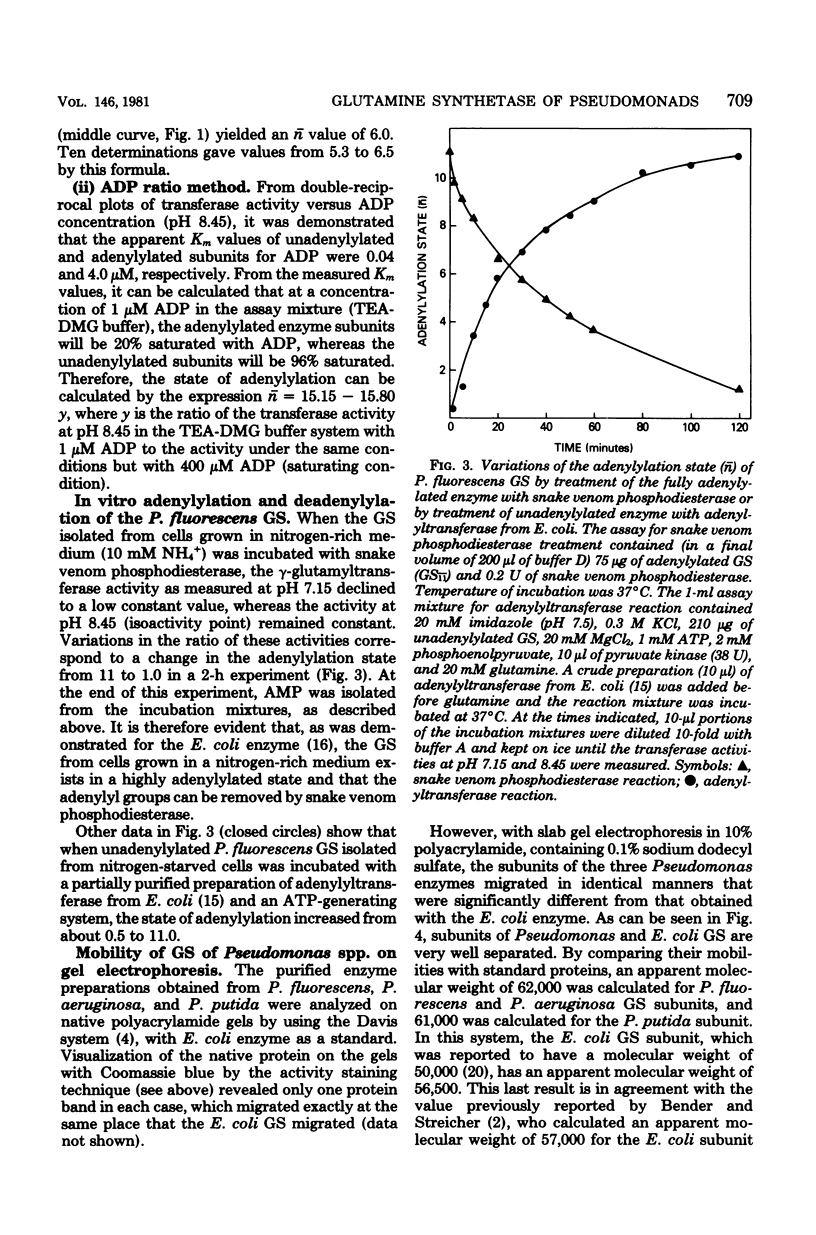
The glutamine synthetases from several Pseudomonas species were purified to homogeneity, and their properties were compared with those reported for the enzymes from Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. The glutamine synthetase from Pseudomonas fluorescens was unique because it was nearly precipitated quantitatively as a homogeneous protein during dialysis of partially purified preparations against buffer containing 10 mM imidazole (pH 7.0) and 10 mM MnCl2. The glutamine synthetases from Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were purified by affinity chromatography on Affi-blue gel. Dodecamerous forms of the E. coli and P. fluorescens glutamine synthetases had identical mobilities during polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Their dissociated subunits, however, migrated differently and were readily separated by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels containing 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. This difference in subunit mobilities is not related to the state of adenylylation. Regulation of the Pseudomonas glutamine synthetase activity is mediated by an adenylylation-deadenylylation cyclic cascade system. A sensitive procedure was developed for measuring the average number of adenylylated subunits per enzyme molecule for the glutamine synthetase from P. fluorescens. This method takes advantage of the large differences in transferase activity of the adenylylated and unadenylylated subunits at pH 6.0 and of the fact that the activities of both kinds of subunits are the same at pH 8.45.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Streicher S. L. Glutamine synthetase regulation, adenylylation state, and strain specificity analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):1000–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.1000-1007.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo C., Holzer H. Enzymatic inactivation of glutamine synthetase in Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr 3;4(2):190–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hanau R. Relation between the adenylylation state of glutamine synthetase and the expression of other genes involved in nitrogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1282–1289. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1282-1289.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J., Stadtman E. R. Use of AMP specific antibodies to differentiate between adenylylated and unadenylylated E. coli glutamine synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 14;82(3):865–870. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90863-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen K. A., Magasanik B. Glutamine synthetase of Klebsiella aerogenes: genetic and physiological properties of mutants in the adenylylation system. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.993-1000.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Adenylylation/deadenylylation control of the glutamine synthetase of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Kleiner D. The glutamine synthetase from Azotobacter vinelandii: purification, characterization, regulation and localization. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig R. A., Signer E. R. Glutamine synthetase and control of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):245–248. doi: 10.1038/267245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecke D., Wulff K., Liess K., Holzer H. Characterization of a glutamine synthetase inactivating enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):452–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Shelton E., Stadtman E. R. Zinc-induced paracrystalline aggregation of glutamine synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):155–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Park R., Wittenberger M. New enzymic assays for glutamine synthetase adenylytransferase and its regulatory protein PIIA. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 15;88(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Kingdon H. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. VII. Adenylyl glutamine synthetase: a new form of the enzyme with altered regulatory and kinetic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):642–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siedel J., Shelton E. Purification and properties of Azotobacter vinelandii glutamine synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):214–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey G., Van Baalen C., Tabita F. R. Nitrogen and ammonia assimilation in the cyanobacteria: regulation of glutamine synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 May;194(2):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Hohman R. J., Davis J. N., Wittenberger M., Chock P. B., Rhee S. G. Subunit interaction of adenylylated glutamine synthetase. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1980;32:144–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81503-4_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Smyrniotis P. Z., Davis J. N., Wittenberger M. E. Enzymic procedures for determining the average state of adenylylation of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Tyler B. Purification of glutamine synthetase from a variety of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):69–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.69-78.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Laskowski M., Sr Venom exonuclease (phosphodiesterase) immobilized on concanavalin-A-sepharose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90954-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Ciardi J. E., Stadtman E. R. Comparative biochemical and immunological studies of bacterial glutamine synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):858–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.858-868.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Shapiro B., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





