Fig. 2. aPKC regulates subcellular localization of PAR1 in Xenopus ectoderm.
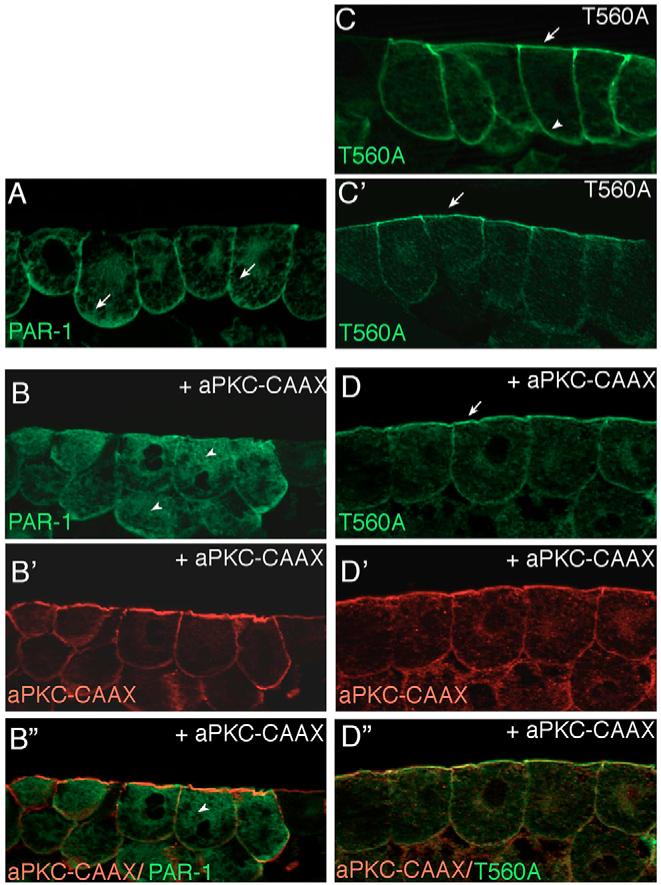
(A,B) aPKC inhibits cortical localization of PAR1. (A) PAR1 is predominantly localized to the basolateral cortex of superficial ectoderm cells (arrows). (B) Overexpression of aPKC-CAAX mislocalizes PAR1 to the cytoplasm (arrowheads). (C,D) The apical localization of T560A, the non-phosphorylatable PAR1 mutant (C’) is not affected by aPKC-CAAX (D). At higher doses of injected RNA, T560A was distributed all around the cell cortex, both apically and basolaterally (C). The distribution of coinjected membrane-associated aPKC-CAAX is shown in B’ and D’, the increased apical staining is due to high amounts of endogenous aPKC detected by anti-aPKC antibody. B” and D”, merged images. Embryo injections were as described in Fig. 1. Frozen sections of stage 10.5-11 embryonic ectoderm were stained with anti-Myc (green) to detect PAR1 (B,D) and anti-aPKC antibodies (B’ and D’, red). At least 15 embryos per group were examined and representative sections of three independent experiments are shown.
