Abstract
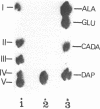
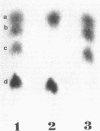
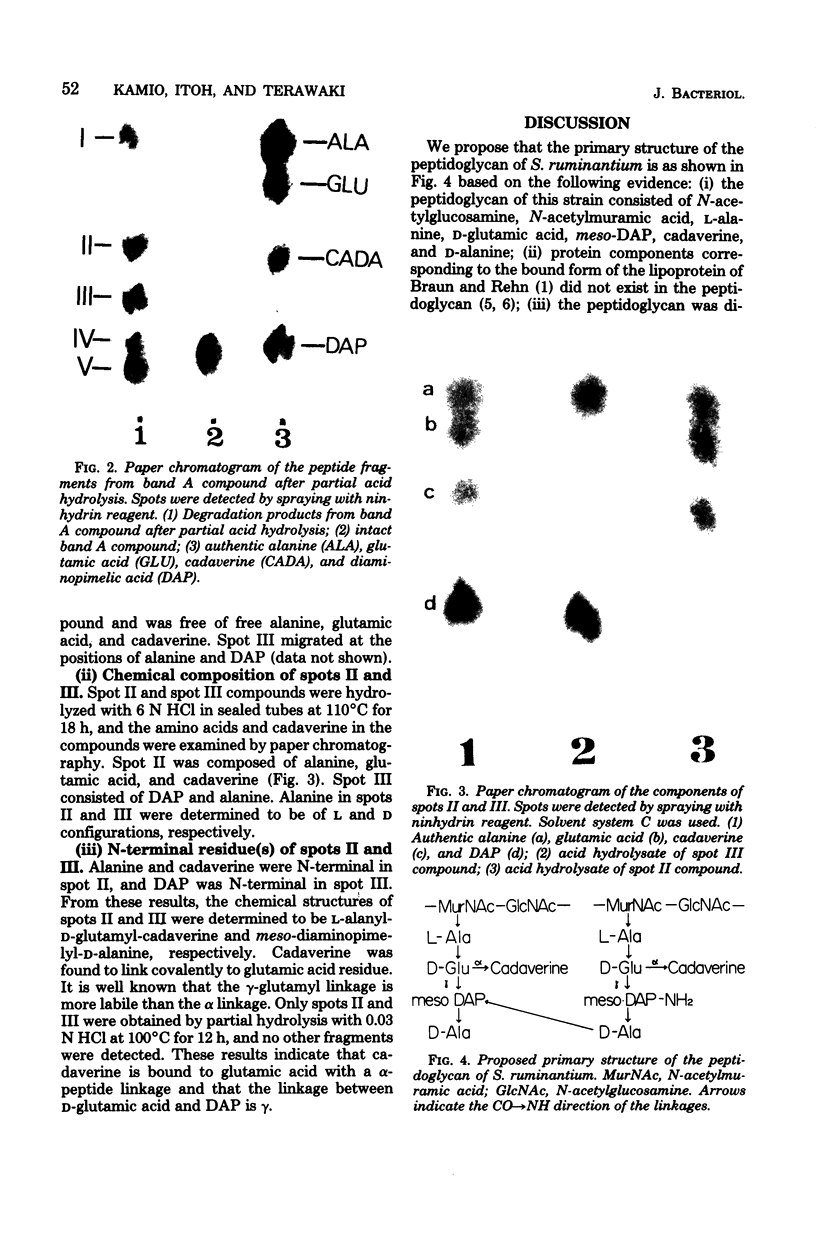
The peptidoglycan of Selenomonas ruminantium, a strictly anaerobic bacterium, contains cadaverine (Y. Kamio, Y. Itoh, Y. Terawaki, and T. Kusano, J. Bacteriol. 145:122-128, 1981). This report describes the chemical structure of the peptidoglycan of this bacterium. The [14C]cadaverine-labeled peptidoglycan was degraded with the lytic enzymes prepared from Streptomyces albus G into three small fragments including a major fragment (band A compound). Bank A compound was composed of L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, meso-diaminopimelic acid, D-alanine, and cadaverine in the molar ratio 0.98:1.0:1.0:0.98:0.97. Diaminopimelic acid, L-alanine, and cadaverine were N-terminal residues in band A compound. When the [14C]cadaverine-labeled band A compound was subjected to partial acid hydrolysis, two peptide fragments were obtained. One of them consisted of diaminopimelic acid and D-alanine; diaminopimelic acid was the N-terminal amino acid, and the other fragment was composed of L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, and cadaverine, of which L-alanine and cadaverine were N-terminal. These results lead us to conclude that the primary peptide structure of band A compound is L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelyl-D-alanine and that cadaverine links covalently to the D-glutamic acid residue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. 8. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reaction in strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3180–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Itoh Y., Terawaki Y., Kusano T. Cadaverine is covalently linked to peptidoglycan in Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):122–128. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.122-128.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Takahashi H. Outer membrane proteins and cell surface structure of Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.899-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Takahashi H. Function of growth factors for rumen microorganisms. I. Nutritional characteristics of Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.456-463.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIMOSIGH J., PELZER H., MAASS D., WEIDEL W. Chemical characterization of mucopeptides released from the E. coli B cell wall by enzymic action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 1;46:68–80. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90647-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]