Abstract
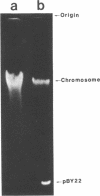
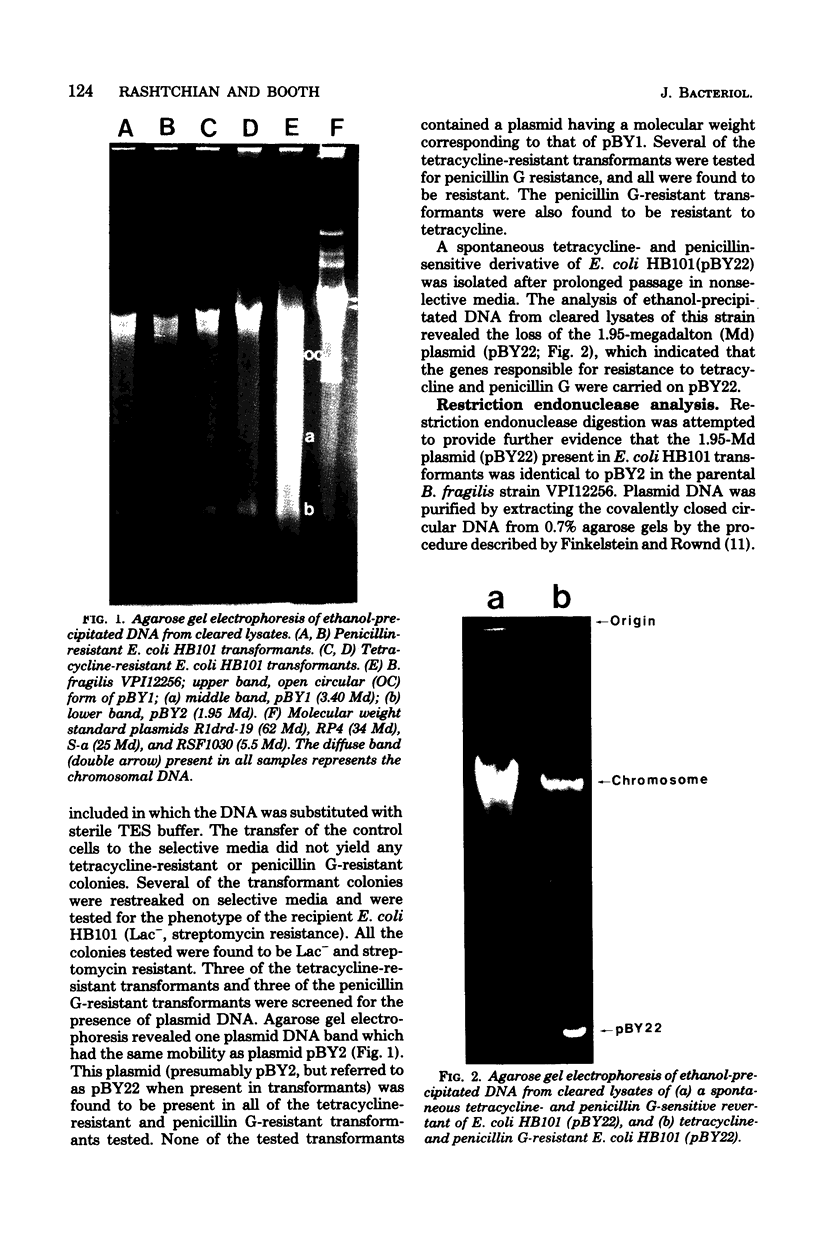
A Bacteroides fragilis strain resistant to penicillin G, tetracycline, and clindamycin was screened for the presence of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Agarose gel electrophoresis of ethanol-precipitated DNA from cleared lysates of this strain revealed two plasmid DNA bands. The molecular weights of the plasmids were estimated by their relative mobility in agarose gel and compared with standard plasmids with known molecular weights. The molecular weights were 3.40 +/- 0.20 x 10(6) and 1.95 +/- 0.05 x 10(6) for plasmids pBY1 and pBY2, respectively. Plasmid DNA purified by cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradient centrifugation was used to transform a restriction- and modification-negative strain of Escherichia coli. Penicillin G- and tetracycline-resistant transformants were screened for the presence of plasmid DNA. A plasmid band corresponding to a molecular weight of 1.95 x 10(6) was present in all transformants tested. Curing experiments demonstrated that the plasmid, referred to as pBY22 when present in transformants, was responsible for penicillin G and tetracycline resistance. Plasmid pBY22 was mobilized and transferred to other E. coli strains by plasmid R1drd-19. Stability of pBY22 was examined in different E. coli strains and was shown to be stably maintained in both restriction-negative and restriction-positive strains. Unexpectedly, pBY2 and pBY22 were resistant to digestion by 12 different restriction endonucleases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman V. P., Groot Obbink D. J. Screening for transferable antibiotic resistance in the clinical laboratory. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Mar;5(2):167–172. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid molecular weights and homologies of plasmids conferring linked resistance to streptomycin and sulfonamides. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):618–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.618-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth S. J., Van Tassell R. L., Johnson J. L., Wilkins T. D. Bacteriophages of Bacteroides. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):325–336. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes R. C. Molecular structure of bacterial plasmids. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Sep;36(3):361–405. doi: 10.1128/br.36.3.361-405.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Rownd T. H. A rapid method for extracting DNA from agarose gels. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Davis C. E. Isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from two strains of Bacteroides. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):503–510. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.503-510.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Jr, Davis C. E. Identification of a conjugative R plasmid in Bacteroides ochraceus capable of transfer to Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):181–182. doi: 10.1038/274181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Sublett R., Hedges R. W., Jacob A., Falkow S. Origin of the TEM-beta-lactamase gene found on plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.250-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini C., Behme R. J. Transfer of multiple antibiotic resistance from Bacteroides fragilis to Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):597–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Sutter V. L., Pickett M. J., Blachman U., Greenwood J. R., Grinenko V., Citron D. Detection, identification, and comparison of Capnocytophaga, Bacteroides ochraceus, and DF-1. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):557–562. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.557-562.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk B. F., Kasper D. L. Bacteroides fragilis subspecies in clinical isolates. Ann Intern Med. 1977 May;86(5):569–571. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-5-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privitera G., Dublanchet A., Sebald M. Transfer of multiple antibiotic resistance between subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):97–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashtchian A., Nouravarsani R., Miller G. R., Gerlach E. H. Increased production of beta-lactamase under anaerobic conditions in some strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):772–775. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Falkow S. Conjugal transfer of R plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):630–631. doi: 10.1038/266630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Gene. 1980 Mar;8(4):329–343. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R. Anaerobes and transferable drug resistance. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):113–114. doi: 10.1038/274113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Sparling P. F. Transformation-derived Neisseria gonorrhoeae plasmids with altered structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.510-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler P. W., Keller R., Traub N. Isolation and characterization of several cryptic plasmids from clinical isolates of Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):544–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to six antibiotics determined by standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):188–193. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinnell W. H., Macrina F. L. Extrachromosomal elements in a variety of strains representing the Bacteroides fragilis group of organisms. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):955–964. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.955-964.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tassell R. L., Wilkins T. D. Isolation of auxotrophs of Bacteroides fragilis. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1619–1621. doi: 10.1139/m78-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Jones K. R., Macrina F. L. Transferable lincosamide-macrolide resistance in Bacteroides. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. L., Hollis D., Holdeman L. V. Synonymy of strains of Center for Disease Control group DF-1 with species of Capnocytophaga. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):550–556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.550-556.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E., Mayer L. Genetic determinants of microbial resistance to antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]