Abstract
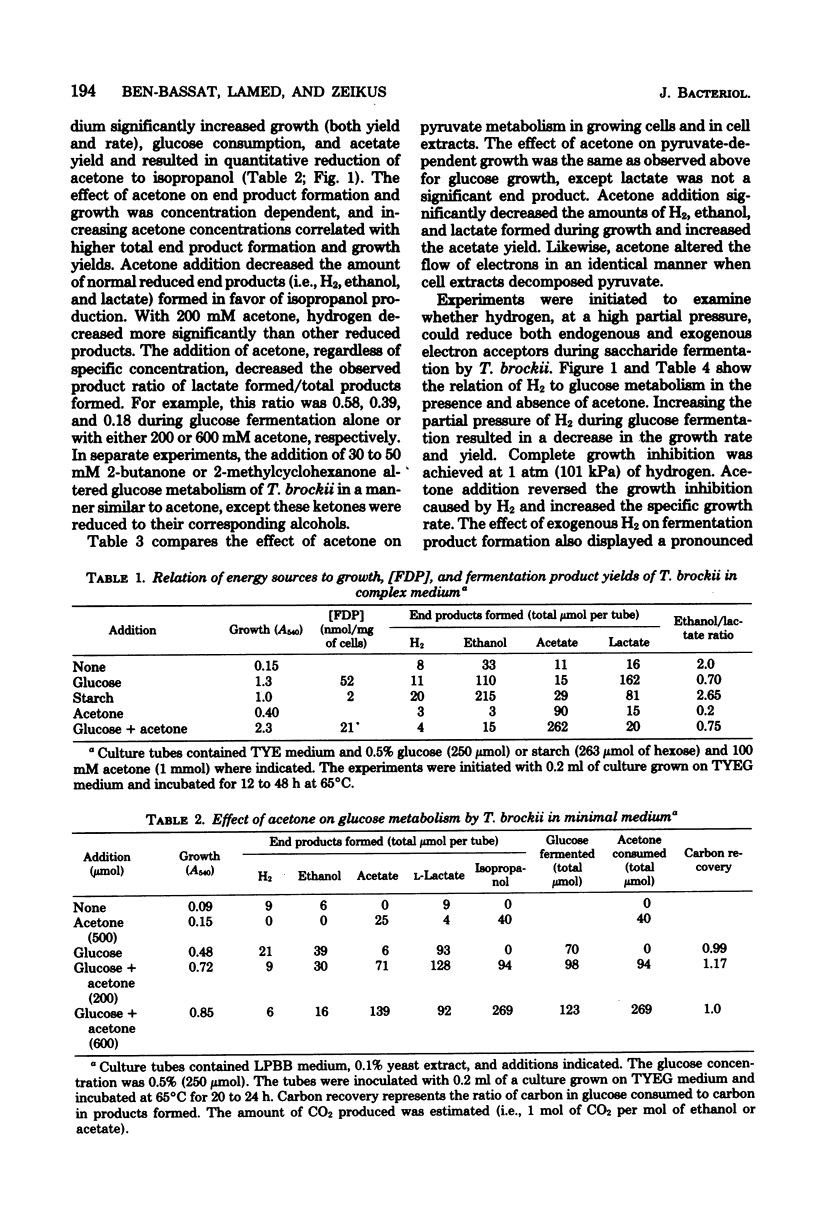
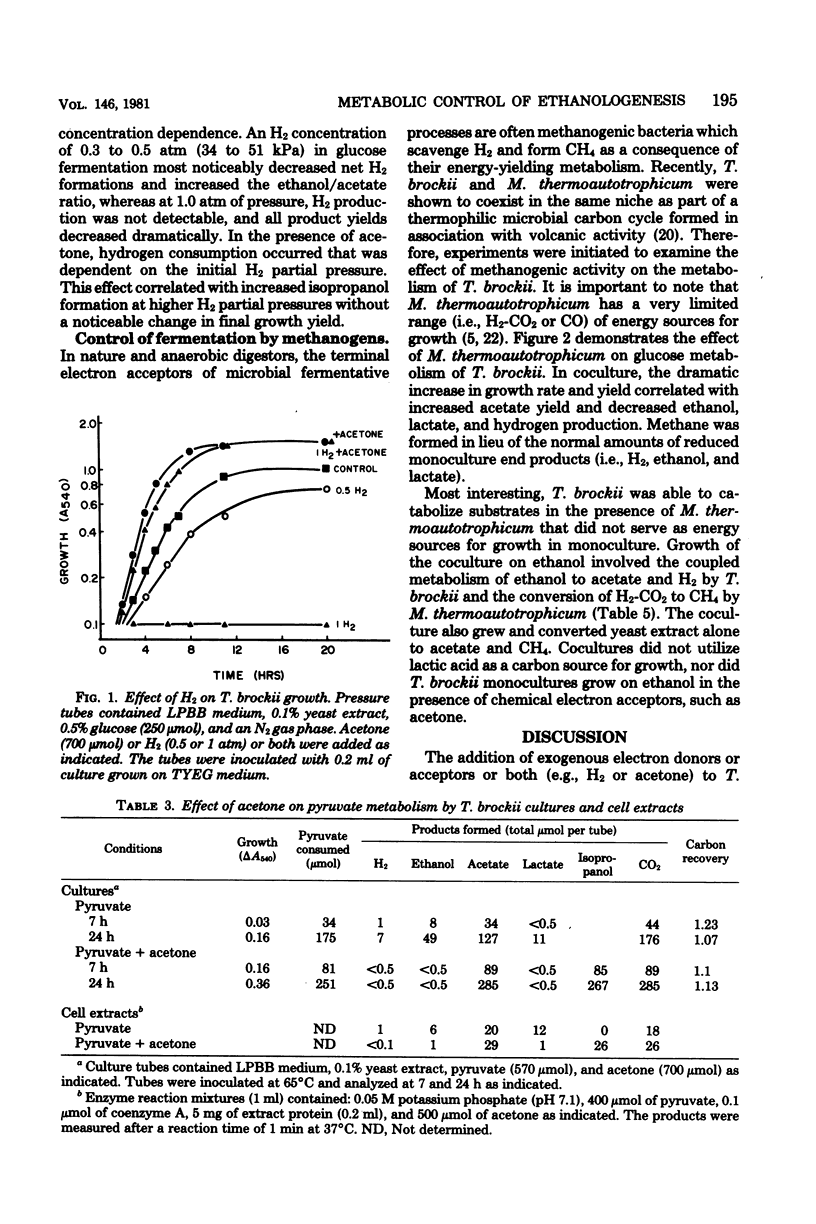
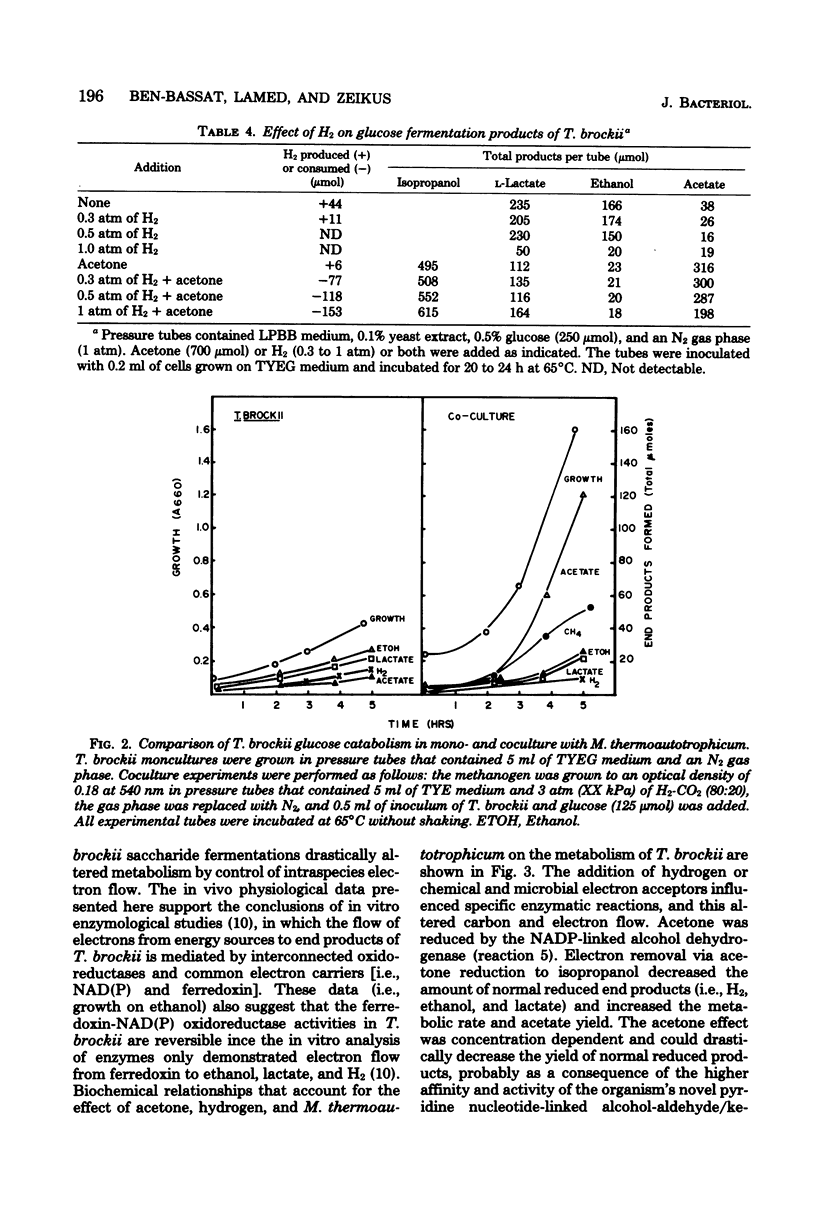
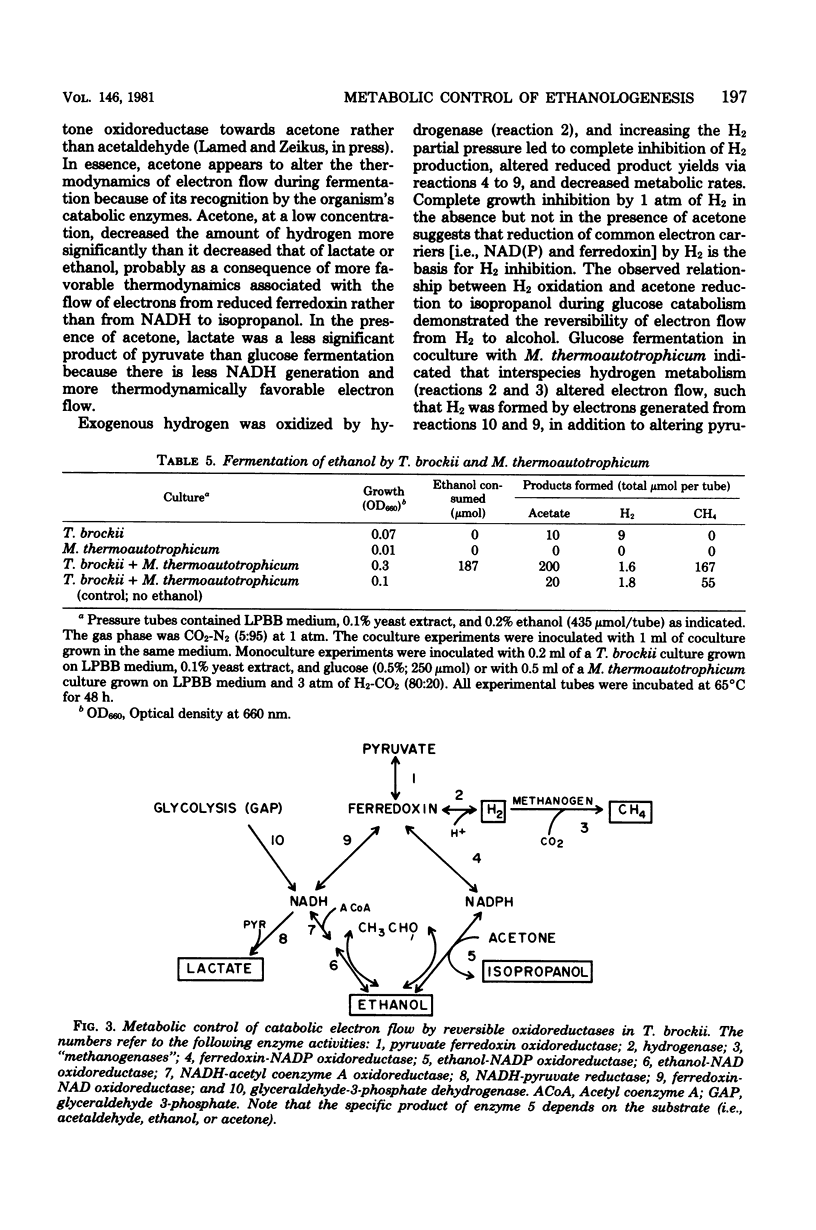
Specific changes in the chemical and microbial composition of Thermoanaerobium brockii fermentations were compared and related to alterations of process rates, end product yields, and growth parameters. Fermentation of starch as compared with glucose was associated with significant decreases in growth rate and intracellular fructose-1,6-bisphosphate concentration and with a dramatic increase in the ethanol/lactate product ratio. Glucose or pyruvate fermentation in the presence of acetone was correlated with increased substrate consumption, growth (both rate and yield), acetate yield, and quantitative reduction of acetone to isopropanol in lieu of normal reduced fermentation products (i.e., H2, ethanol, lactate). Acetone altered pyruvate phosphoroclastic activity of cell extracts in that H2, lactate, and ethanol levels decreased, whereas the acetate concentration increased. Glucose fermentation in the presence of exogenous hydrogen was associated with inhibition of endogenous H2 production and either increased ethanol/acetate product ratios and decreased growth at less than 0.5 atm (51 kPa) of H2 or total growth inhibition at 1.0 atm (102 kPA). The effects of exogenous hydrogen on glucose fermentation were totally reversed by the addition of acetone. Glucose fermentation in coculture with Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum correlated with increased growth (both rate and yield), acetate yield, and the formation of methane in lieu of monoculture reduced products. In coculture, but not monoculture, T. brockii grew on ethanol as the energy source, and acetate and methane were the end products as a direct consequence of hydrogen consumption by the methanogen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. T. Inhibitory effects of H2 on growth of Clostridium cellobioparum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):342–348. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.342-348.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Fuchs G., Thauer R. K., Zeikus J. G. Carbon monoxide oxidation by methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.118-126.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannotti E. L., Kafkewitz D., Wolin M. J., Bryant M. P. Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1231–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1231-1240.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Thauer R. K., Leimenstoll G., Decker K. Function of reduced pyridine nucleotide-ferredoxin oxidoreductases in saccharolytic Clostridia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Zeikus J. G. Ethanol production by thermophilic bacteria: relationship between fermentation product yields of and catabolic enzyme activities in Clostridium thermocellum and Thermoanaerobium brockii. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):569–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.569-578.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitdemange H., Cherrier C., Raval R., Gay R. Regulation of the NADH and NADPH-ferredoxin oxidoreductases in clostridia of the butyric group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 24;421(2):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheifinger C. C., Linehan B., Wolin M. J. H2 production by Selenomonas ruminantium in the absence and presence of methanogenic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):480–483. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.480-483.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and change of fermentation products in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.55-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Ben-Bassat A., Hegge P. W. Microbiology of methanogenesis in thermal, volcanic environments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):432–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.432-440.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


