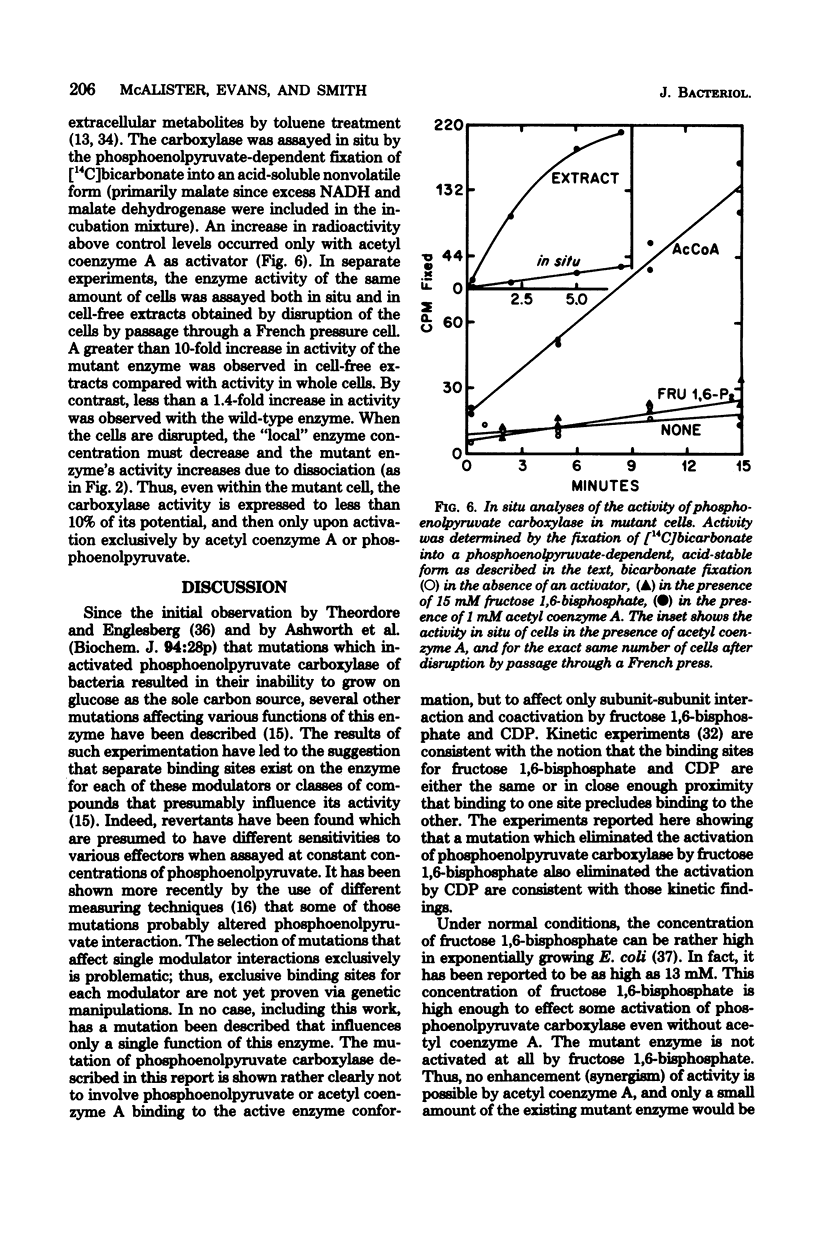
Abstract
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of Escherichia coli is activated by three different mechanisms: contiguous by acetyl coenzyme A, precursor by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, and compensatory feedback by cytidine 5'-diphosphate (CDP). Even though each activator can interact independently with the enzyme, synergistic effects are observed with some combinations, namely, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate or CDP (coregulators), with acetyl coenzyme A. A mutant was isolated that has a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase which is refractory to activation by fructose, 1,6-bisphosphate and CDP. The mutant enzyme was shown to be active primarily as the dimer and to lack cooperativity in substrate binding. The binding of acetyl coenzyme A and substrate, however, was essentially the same as that of the wild-type enzyme. The mutant cells grew extremely slowly on glucose alone as the sole carbon source. The only defect in the mutant appeared to be the inability of this enzyme to be activated by the coregulators. These data are consistent with the thesis that coregulation by fructose 1,6-bisphosphate or CDP is an essential requirement for the activation in vivo of this enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN S. S., ARBOGAST R. Chemical studies in host-virus interactions; a comparison of some properties of three mutant pairs of bacterial viruses, T2r and T2r, T4r and T4r, T6r and T6r. J Exp Med. 1950 Jun 1;91(6):619–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.6.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cánovas J. L., Kornberg H. L. Properties and regulation of phosphopyruvate carboxylase activity in Escherichia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Aug 16;165(999):189–205. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KAUFMAN H. Selecting bacterial mutants by the penicillin method. Science. 1960 Feb 26;131(3400):604–605. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3400.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. W., Smith T. E. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: effect of allosteric inhibitors on the kinetic parameters and sedimentation behavior. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui K., Nishikido T., Ishihara K., Katsuki H. Studies on the allosteric effectors and some properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1970 Aug;68(2):215–226. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa M., Izui K., Katsuki H. Studies on the allosteric properties of mutationally altered phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases of Escherichia coli. Discrimination of allosteric sites. J Biochem. 1977 May;81(5):1473–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Berg C. M. Differential recovery of auxotrophs after penicillin enrichment in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.297-300.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D. Allosteric controls of amphilbolic pathways in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Mar;34(1):20–39. doi: 10.1128/br.34.1.20-39.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D., Maeba P., Cook R. A. Interaction of macroions and dioxane with the allosteric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5177–5182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D., Maeba P. Regulation of the activity of phosphoenolypyruvate carboxylase by fructose diphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jan 24;22(2):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
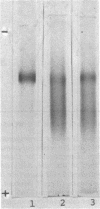
- Scrutton M. C., Fatebene F. An assay system for localisation of pyruvate and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity on polyacrylamide gels and its application to detection of these enzymes in tissue and cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. Kinetic studies of acetyl coenzyme A activated phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: reverse effects with a fatty acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):626–636. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. Nucleotide regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):568–574. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R., Willis M. S. Concerted regulation in vitro of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8402–8407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smando R., Waygood E. B., Sanwal B. D. Cooperative interactions in the binding of allosteric effectors to phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):182–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E., Balasubramanian K. A., Beezley A. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Studies on the mechanism of synergistic activation by nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1635–1642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Physical and chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4234–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: characterization and sedimentation behavior. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):611–622. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: competitive regulation by acetyl-coenzyme A and aspartate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):512–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: studies on the mechanism of multiple allosteric interactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):538–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. E., Perry M. Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: kinetics and mechanism of inactivation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THEODORE T. S., ENGLESBERG E. MUTANT OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM DEFICIENT IN THE CARBON DIOXIDE-FIXING ENZYME PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVIC CARBOXYLASE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:946–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.946-955.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]